Introduction
AI-based face expression detection refers to the use of artificial intelligence algorithms and computer vision techniques to analyze images or videos of human faces and recognize the emotions or expressions being displayed. The technology can detect and analyze subtle changes in facial features, such as eye movement, mouth shape, and eyebrow position, to determine whether a person is happy, sad, angry, surprised, or expressing other emotions.
Discover the various fields that utilize this technology, including psychology, marketing, and human-computer interaction. Additionally, read about the logic and code behind face detection with a camera feed, including the initialization of parameters, face detection library, loop execution, and if-else conditions. Explore how the technology continuously analyzes emotions, and how the Humanoid responds with different facial expressions and movements.
Code
sprite = Sprite('Tobi')
fd = FaceDetection()
quarky = Quarky()
import time
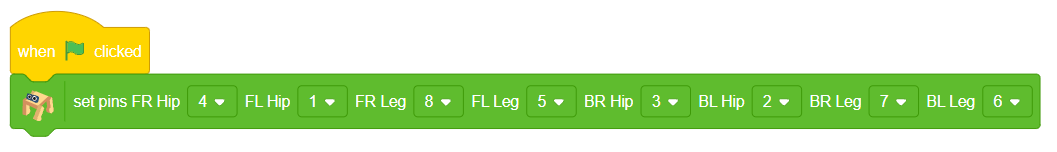
humanoid = Humanoid(7, 2, 6, 3, 8, 1)
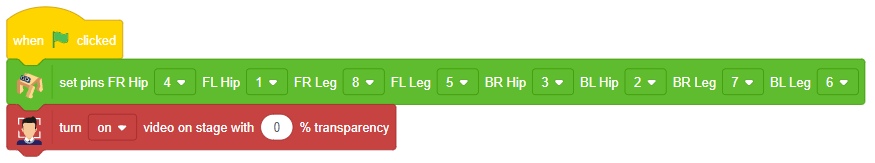
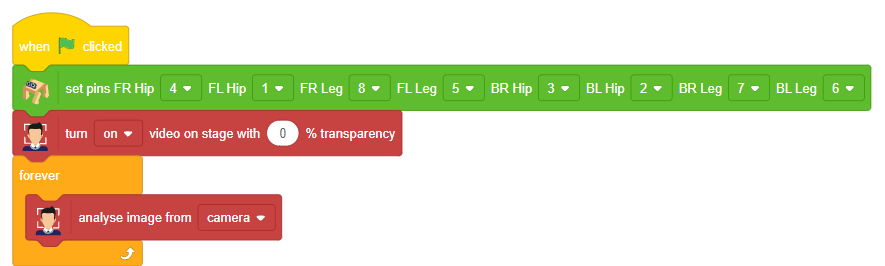
# Turn the video ON with 0% transparency
fd.video("ON", 0)
fd.enablebox()
# Run this script forever
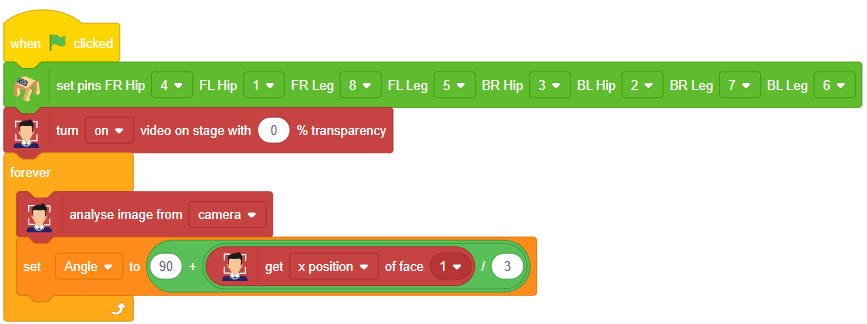
while 1:
fd.analysecamera() # Analyse image from camera
sprite.say(fd.expression()) # Say the face expressions
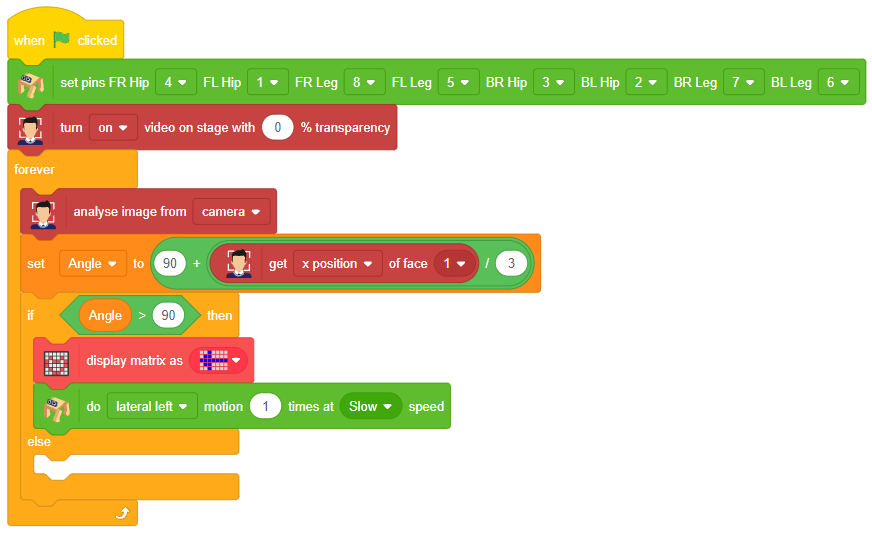
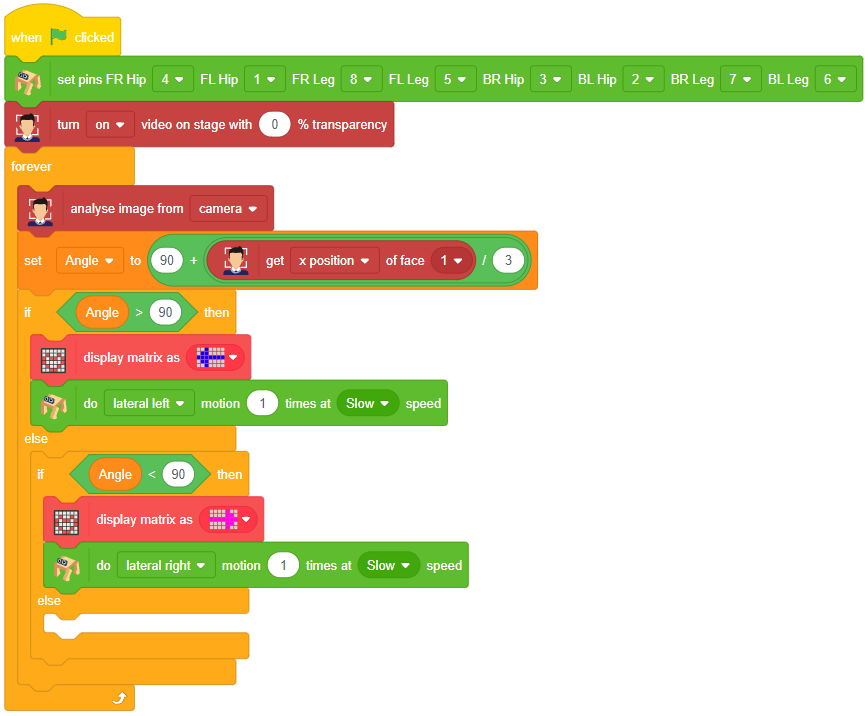
if fd.isexpression(1, "happy"): # if face expression is happy
quarky.showemotion("happy") # show happy emotion on Quarky
humanoid.action("dance2", 1000, 1)
if fd.isexpression(1, 'sad'):
quarky.showemotion("crying")
humanoid.action("updown", 1000, 1)
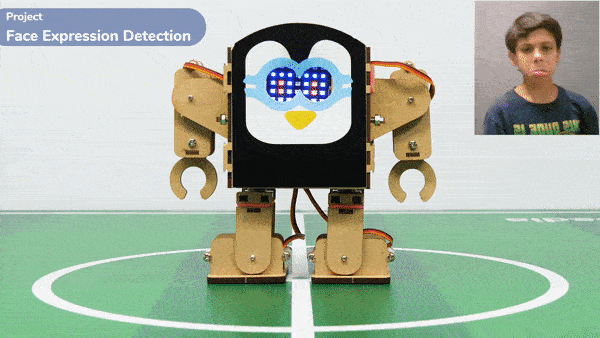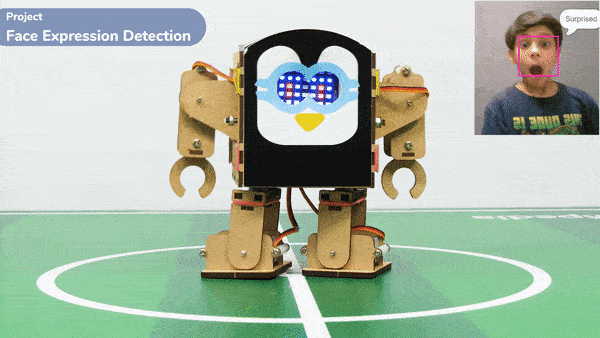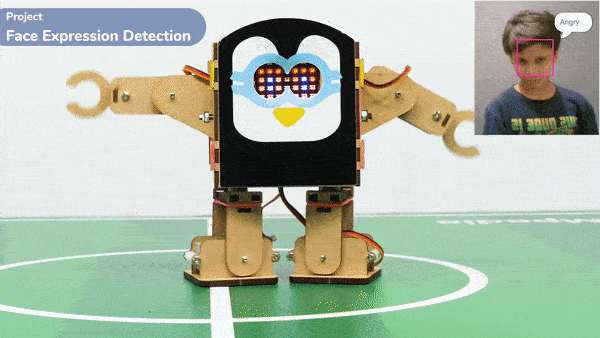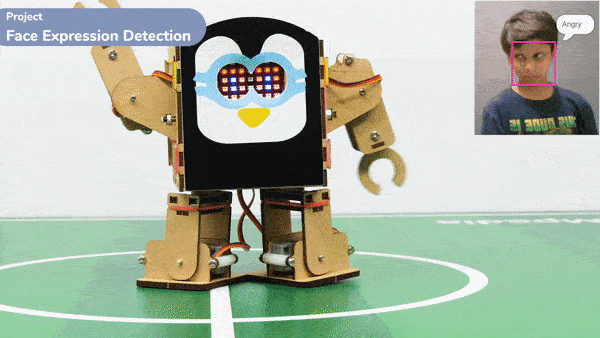
if fd.isexpression(1, 'surprise'):
quarky.showemotion('surprise')
humanoid.action("moonwalker", 1000, 1)
if fd.isexpression(1, 'angry'):
quarky.showemotion('angry')
humanoid.action("flapping2", 1000, 1)
else:
humanoid.home()
# Comment the above script, uncomment the below script and
# run this script to clear the stage and quarky display
fd.disablebox()
fd.video("off")
quarky.cleardisplay()
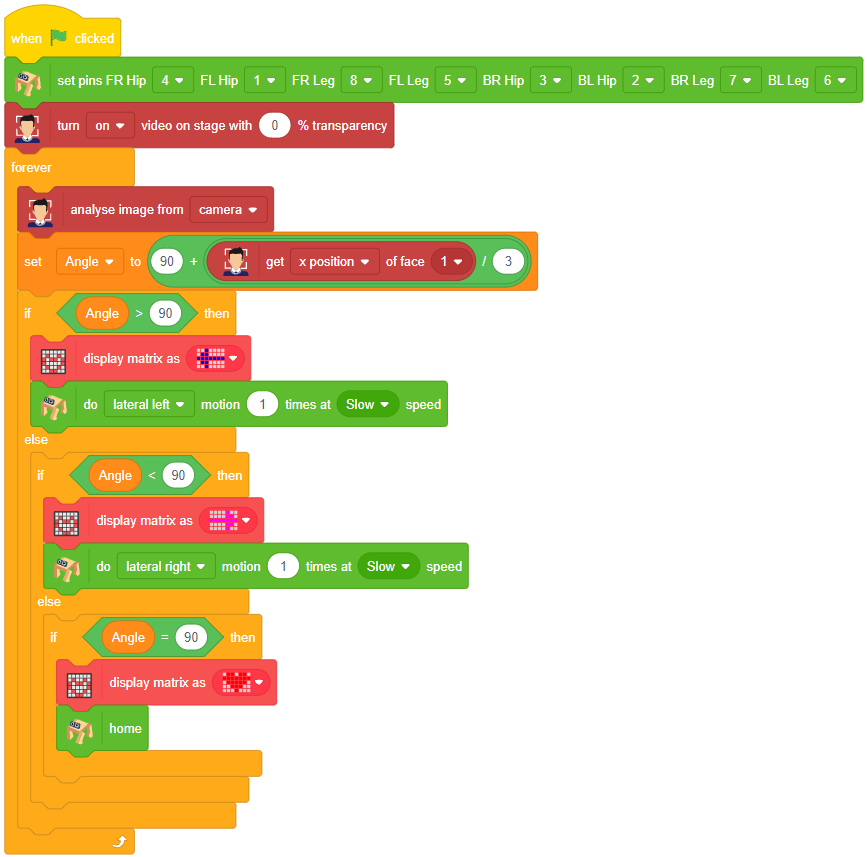
Logic
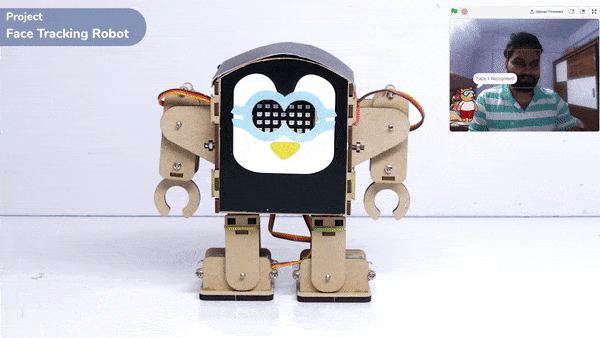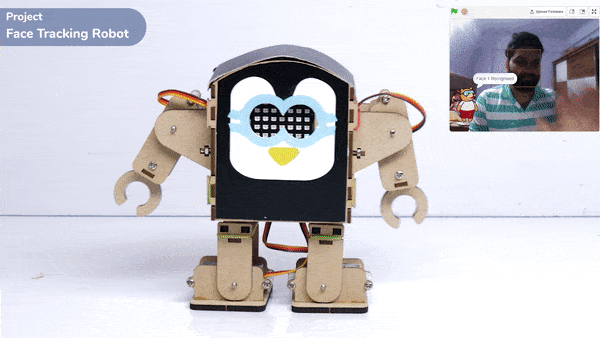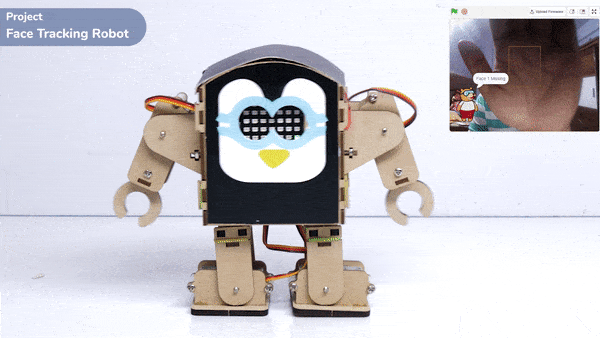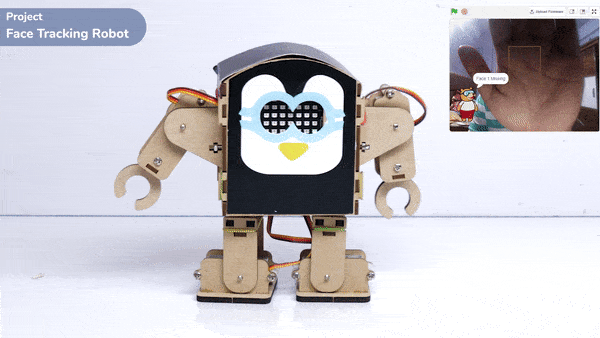
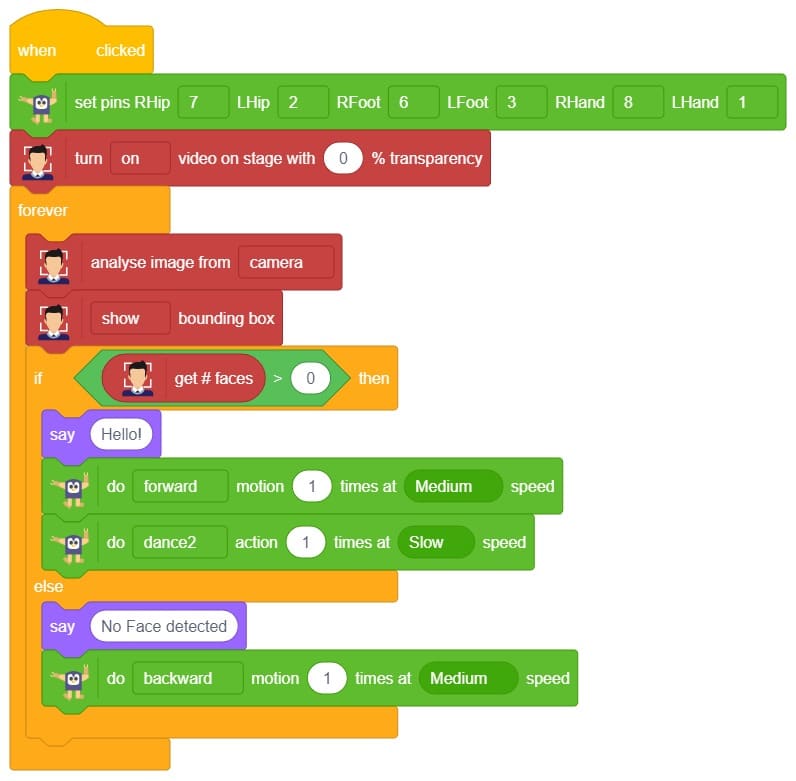
The example demonstrates how to use face detection with a camera feed. Following are the key steps happening:
- Creates a sprite object named ‘Tobi’. A sprite is typically a graphical element that can be animated or displayed on a screen.also creates a Quarky object.
- Creates a face detection object named ‘fd’. This object is responsible for detecting faces in images or video using fd = FaceDetection()
- Imports the ‘time’ module, which provides functions to work with time-related operations using import time.
- Creates a humanoid object with specific pins assigned to control various actions of the humanoid robot.
- Turns on the video display with 0% transparency for the face detection module using fd.video(“ON”, 0).
- Enables the face detection module to draw boxes around detected faces using fd.enablebox().
- The code enters an infinite loop using while 1, which means it will keep running indefinitely until interrupted.
- Analyzes the image from the camera for face detection using fd.analysecamera().
- The sprite says the detected face expressions obtained from the face detection module using sprite.say(fd.ex * pression()).
- The code checks for different face expressions using if statements and performs corresponding actions.
- For example, if the face expression is determined to be “happy“, the Quarky device shows a “happy” emotion, and the humanoid performs a dance action.
- Similarly, other face expressions like “sad”, “surprised”, and “angry” trigger specific emotional displays on Quarky and corresponding actions on the humanoid.
- If none of the predefined face expressions match, the humanoid goes back to its default or “home” position.
Output