This function is used to set the threshold for the confidence (accuracy) of object detection, 0 being low confidence and 1 being high confidence.
With the threshold value, you can set the level of confidence required for object detection.
Function Definition: setthreshold(threshold = 0.5)
| Name | Type | Description | Expected Values | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| threshold | float | Confidence value. 0 being low confidence and 1 being high confidence. | 0-1 | 0.5 |
This function is used to set the threshold for the confidence (accuracy) of object detection, 0 being low confidence and 1 being high confidence.
With the threshold value, you can set the level of confidence required for object detection.
sprite = Sprite('Tobi')
obj = ObjectDetection()
obj.enablebox()
sprite.gotoxy(-180, -110)
sprite.setsize(100)
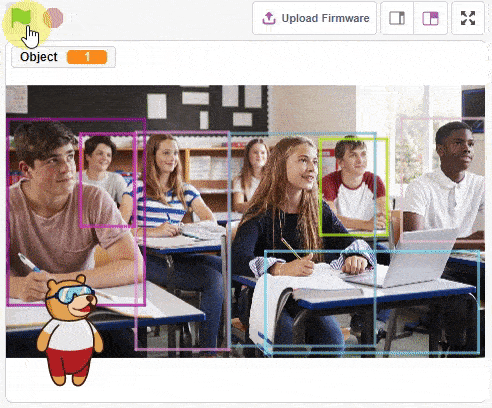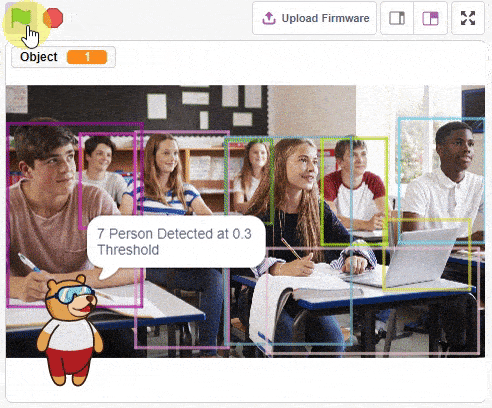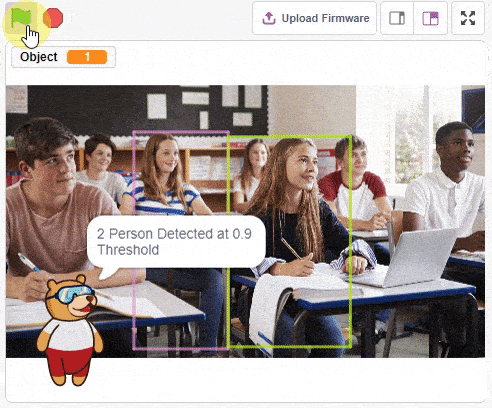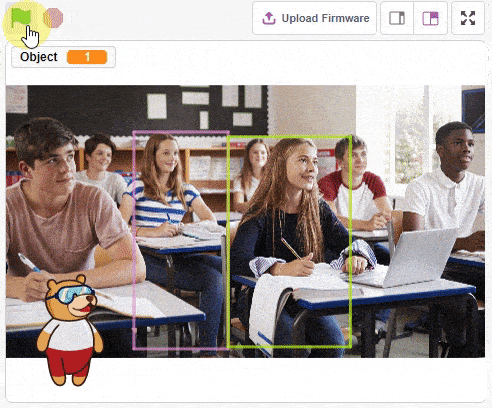
obj.setthreshold(0.3)
obj.analysestage()
sprite.say(str(obj.detectedcount("person")) + " Person Detected at 0.3 Threshold", 2)
obj.setthreshold(0.5)
obj.analysestage()
sprite.say(str(obj.detectedcount("person")) + " Person Detected at 0.5 Threshold", 2)
obj.setthreshold(0.9)
obj.analysestage()
sprite.say(str(obj.detectedcount("person")) + " Person Detected at 0.9 Threshold", 2)

A sign detector Mecanum robot is a robot that can recognize and interpret certain signs or signals, such as hand gestures or verbal commands, given by a human. The robot uses sensors, cameras, and machine learning algorithms to detect and understand the sign, and then performs a corresponding action based on the signal detected.
These robots are often used in manufacturing, healthcare, and customer service industries to assist with tasks that require human-like interaction and decision making.
sprite = Sprite('Tobi')
quarky = Quarky()
import time
meca=Mecanum(1,2,7,8)
recocards = RecognitionCards()
recocards.video("on flipped")
recocards.enablebox()
recocards.setthreshold(0.6)
while True:
recocards.analysecamera()
sign = recocards.classname()
sprite.say(sign + ' detected')
if recocards.count() > 1:
if 'Go' in sign:
meca.runtimedrobot("forward",100,2)
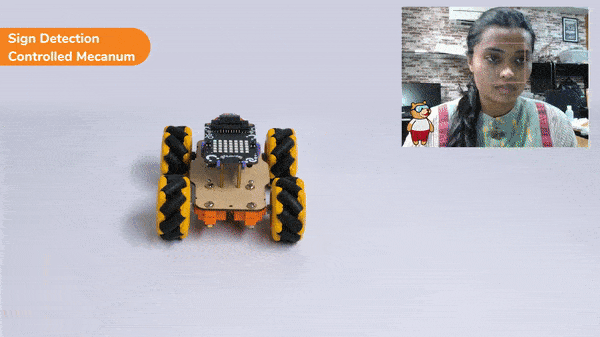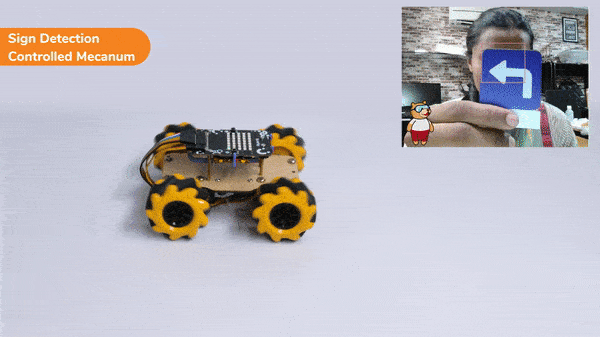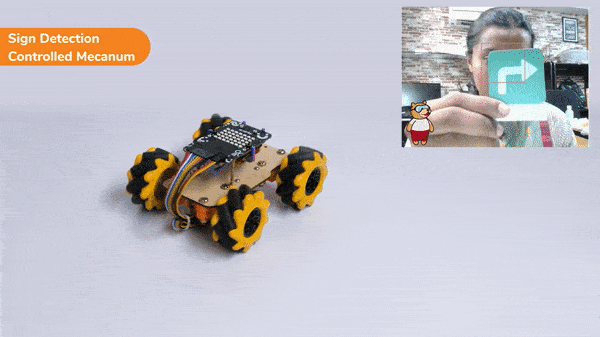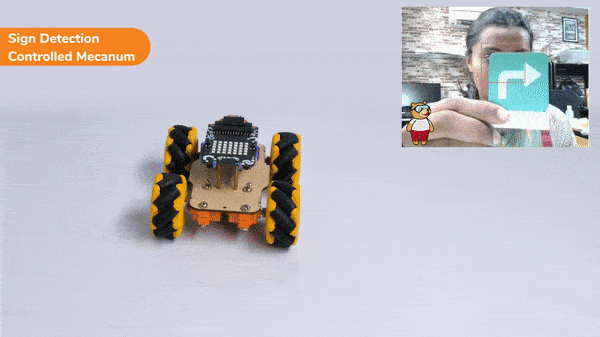
if 'Turn Left' in sign:
meca.runtimedrobot("lateral left",100,2)
if 'Turn Right' in sign:
meca.runtimedrobot("lateral right",100,2)
if 'U Turn' in sign:
meca.runtimedrobot("backward",100,2)Forward Motion:

Right-Left Motions:
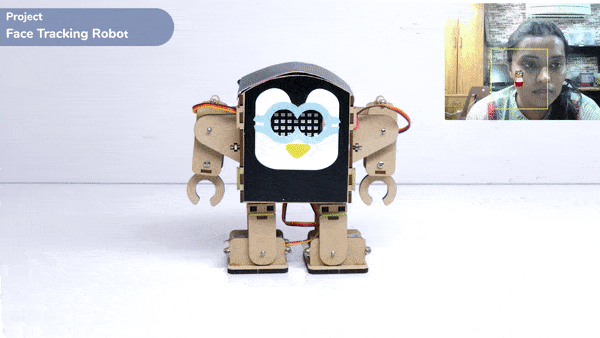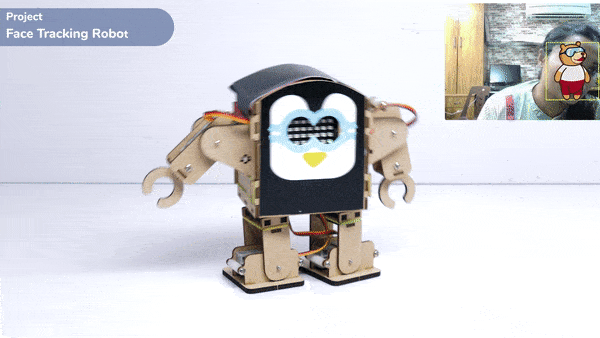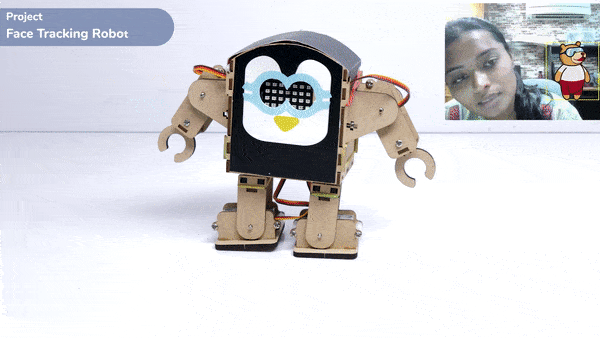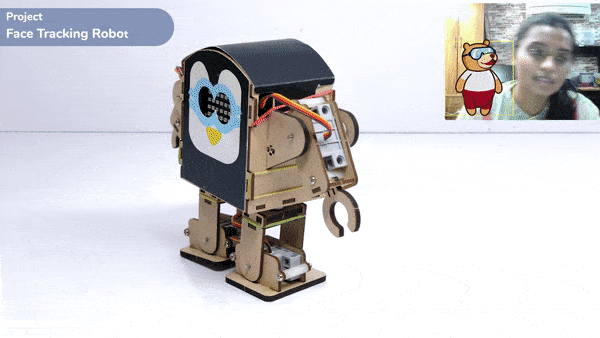
One of the most fascinating activities is face tracking, in which the Quarky can detect a face and move its head in the same direction as yours. How intriguing it sounds, so let’s get started with the coding for a face-tracking robot.
sprite = Sprite('Tobi')
quarky=Quarky()
import time
import math
humanoid = Humanoid(7,2,6,3,8,1)
fd = FaceDetection()
fd.video("on", 0)
fd.enablebox()
fd.setthreshold(0.5)
time.sleep(1)
Angle=0
while True:
fd.analysestage()
for i in range(fd.count()):
sprite.setx(fd.x(i + 1))
sprite.sety(fd.y(i + 1))
sprite.setsize(fd.width(i + 1))
Angle=fd.width(i + 1)
angle=int(float(Angle))
if angle>90:
humanoid.move("left",1000,3)
elif angle<90:
humanoid.move("right",1000,3)
time.sleep(1)
else:
humanoid.home()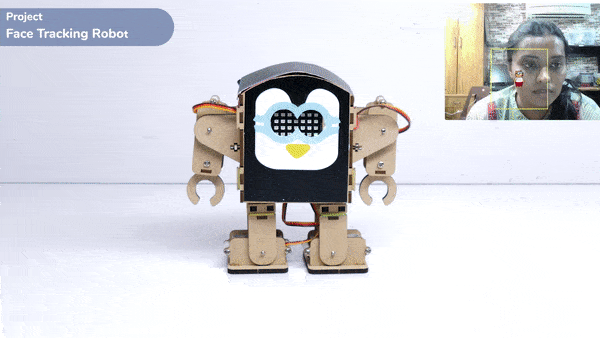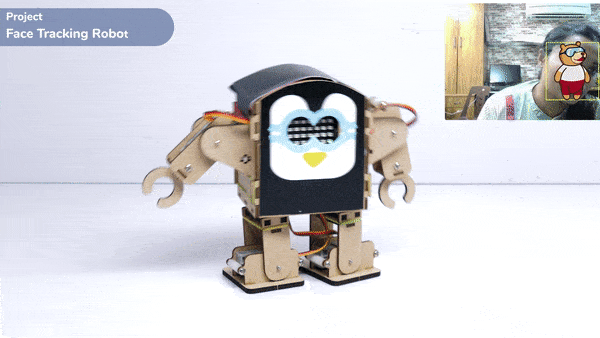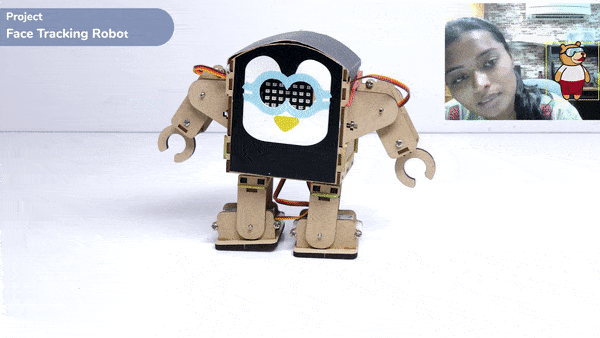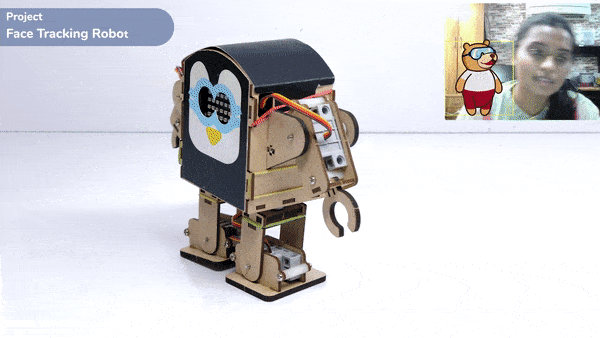

Copyright 2024 – Agilo Research Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved – Terms & Condition | Privacy Policy
