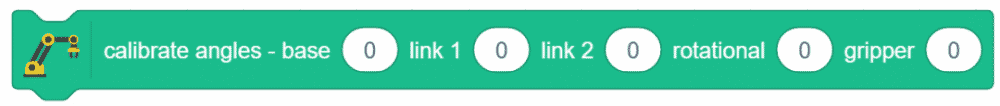
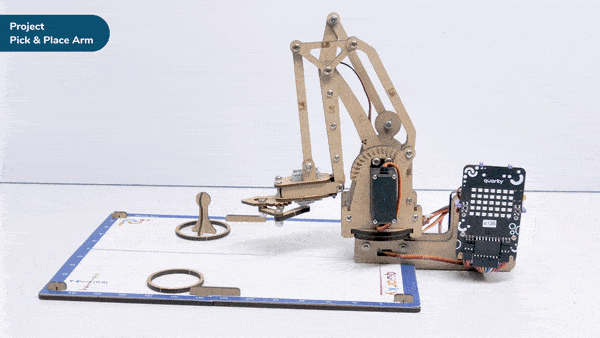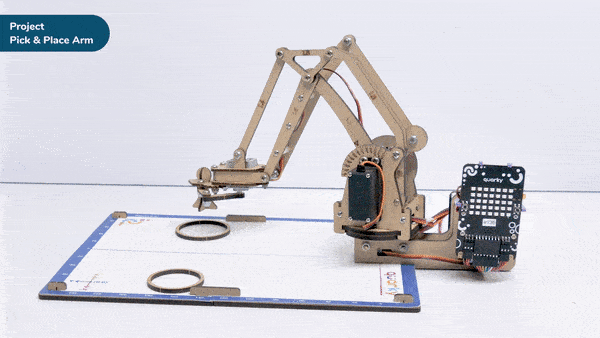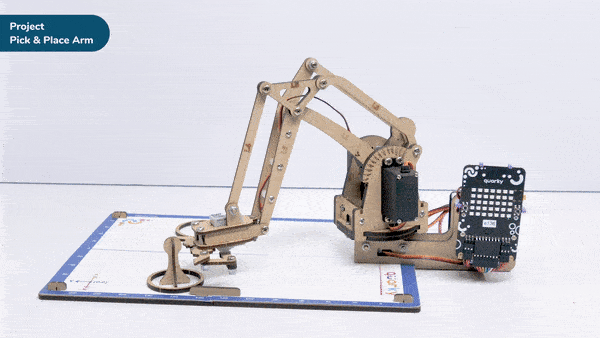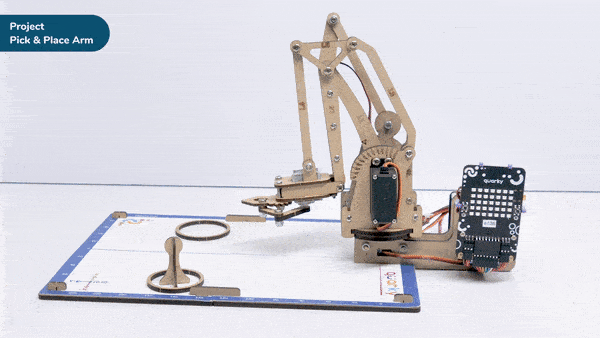
Calibrate angles – base () link 1 () link 2 () rotational () gripper () is a stack block available in Robotic Arm extension for evive and other Arduino boards. This block should be included every time you work with the robotic arm as this block calibrates the angles of the servo motors and saves it in the memory of evive.
Input Parameters
- Enter the error angle of base servo.
- Enter the error angle of link 1 servo.
- Enter the error angle of link 2 servo.
- Enter the error angle of the rotational servo.
- Enter the error angle of the gripper servo.

Note: This block is available in both Stage and Upload mode.
Example
Here, in the given script, we’ll be calibrating the entire robotic arm i.e. all the six servos before working it. Write the script given below to calibrate all the servo angles.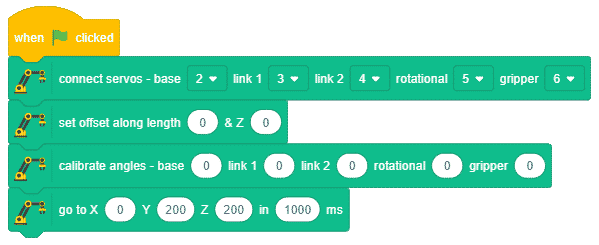
- Run the script by clicking on the green flag.
- If the robotic arm is straight, keep the base angle as 0° in the calibrate angles blocks. If it is not straight, then change the base offset angle and run the script. Use the trial and error method to calibrate the servos.on block. For example, if the base angle is about 15° towards the left, then set the base angle as -15° in the calibrate angles block.
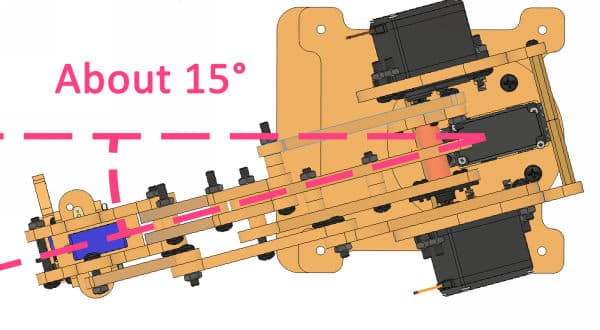
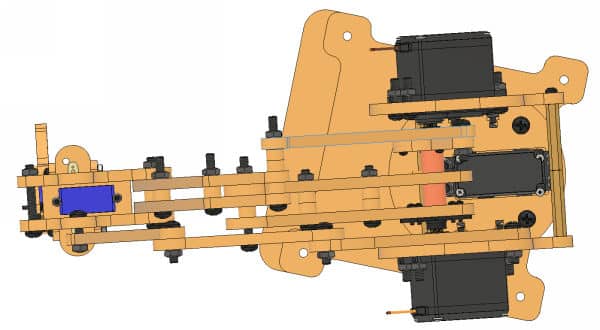
- Similarly, calibrate the rotational servos. If it is straight, keep the rotational angle as 0°. If not, then change the rotational servo offset block.
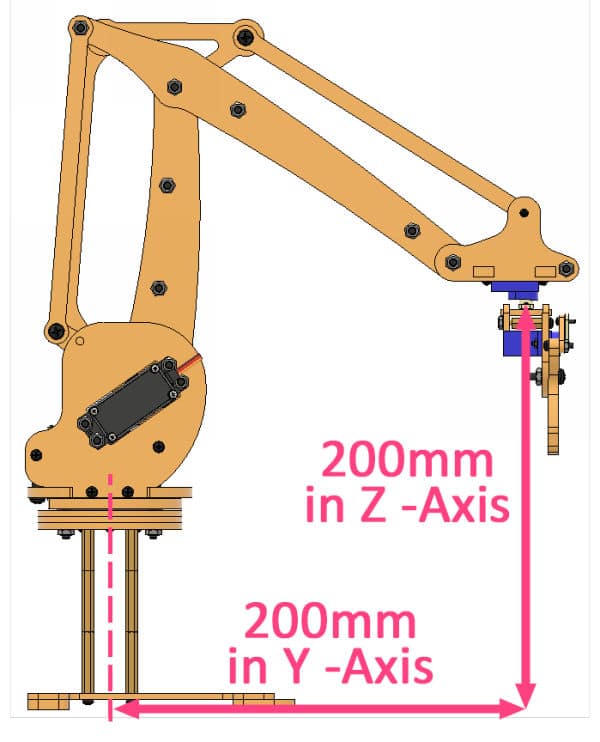
- Now, it’s time to calibrate the link servos. Using a scale, measure the distance of the end effector from the head of Rotational Servo to the base center in the Y and Z directions. If it is 200mm in both directions, then it’s ok; otherwise, change the link 1 and link 2 angles in the calibrate angles block, so that the distance is 200mm along both the axes.

If you need to change any angle by more than 25 degrees, then disassemble the Robotic Arm and carefully reassemble it.
Run the script every time you calibrate a part.