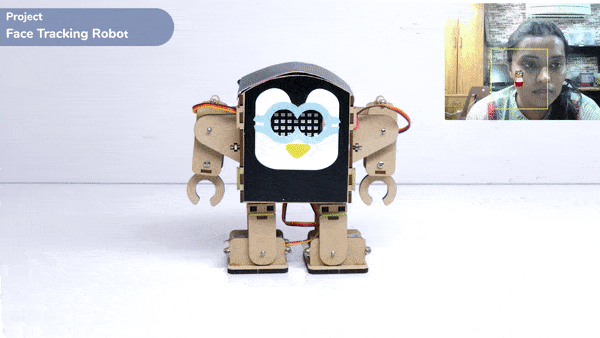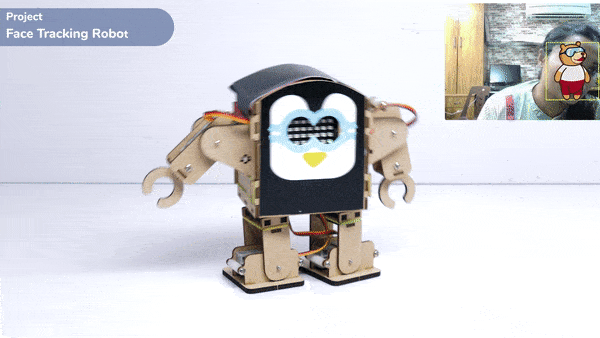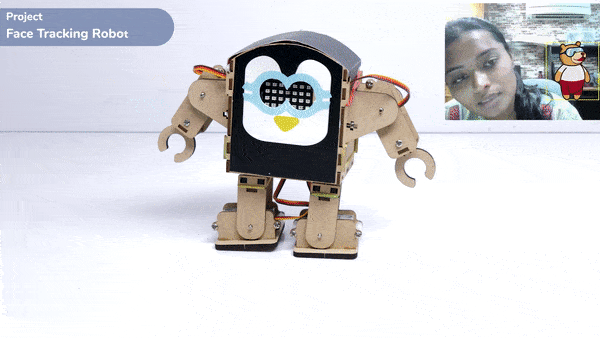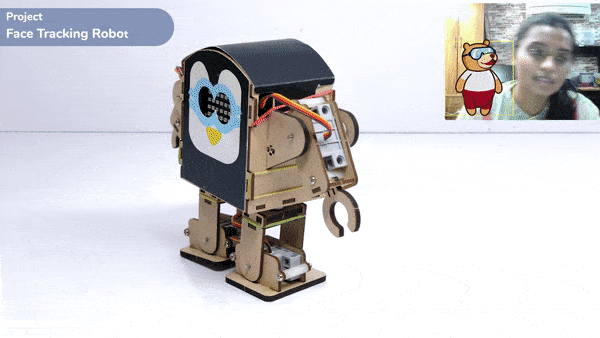
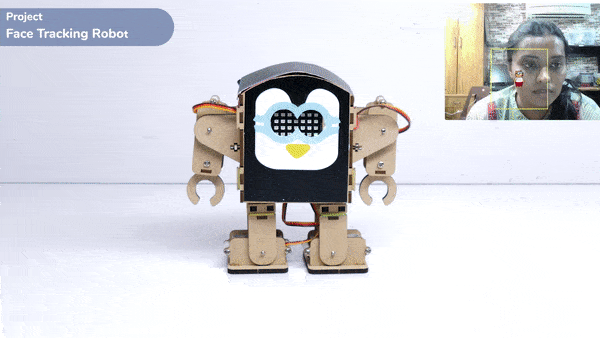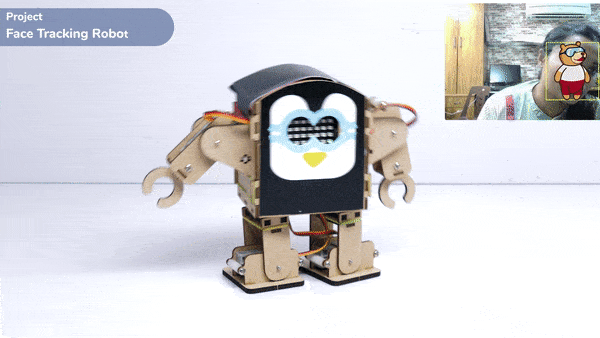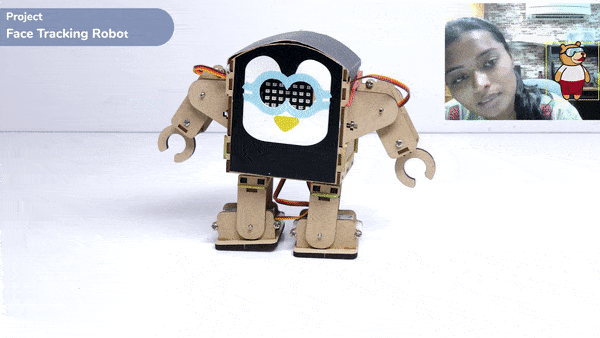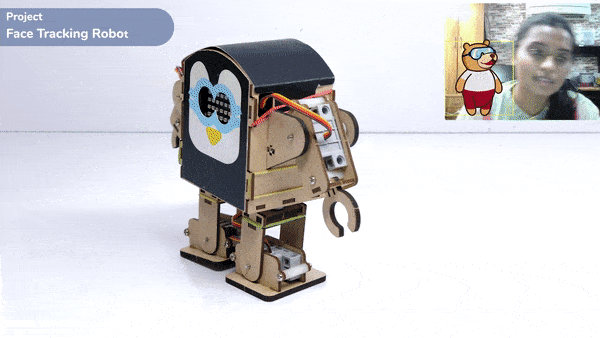
This function is used to analyze the image received as input from the stage, for the feature.
By analyzing the images for image features, you can recognize the following things:
- Brands: Brand detection uses a database of thousands of global logos to identify commercial brands in images. The Computer Vision service detects if there are brand logos in a given image; if so, it returns the brand name; else, it returns NULL.

- Celebrity: Celebrity detection uses a database to identify celebrities in images. The Computer Vision service detects if there is a celebrity in a given image; if so, it returns their name; else, it returns NULL.

- Objects: Computer vision detects if there are objects in a given image; if so, it returns their name; else, it returns NULL.

- Landmarks: Landmark detection uses a database of thousands of global landmarks to identify them in images, e.g., the Taj Mahal.

- Image Tags: Computer vision returns the taxonomy-based categories detected in an image. Computer Vision can categorize an image broadly or specifically according to the 86 categories given in the following diagram:

- Image Description: Human-readable sentence that describes the contents of the image.
Alert: This block processes the image input and updates the values in the other functions hence it needs to be put inside loops while making projects.