Introduction
In this example project, we are going to create a machine learning model that can classify different sign messages from the camera feed or image.
Hand Gesture Classifier in Machine Learning Environment
The Hand Gesture Classifier is the extension of the ML Environment used for classifying different hand poses into different classes.
Hand Gesture Classifier Workflow
- Open PictoBlox and create a new file.

- You can click on “Machine Learning Environment” to open it.
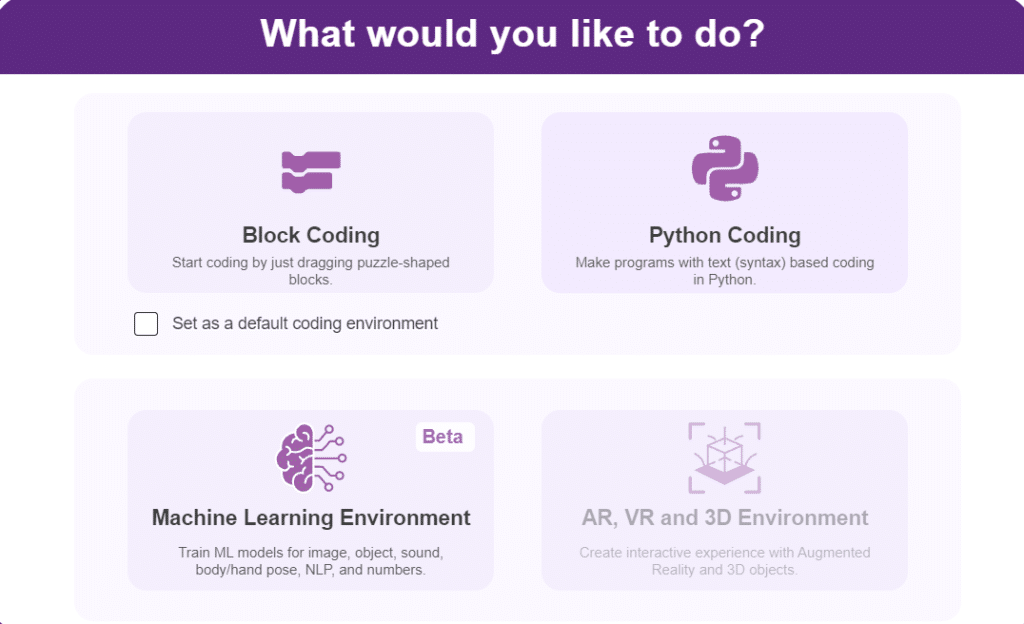
- Click on “Create New Project“.
- A window will open. Type in a project name of your choice and select the Hand Gesture Classifier” extension. Click the “Create Project” button to open the Pose Classifier window.
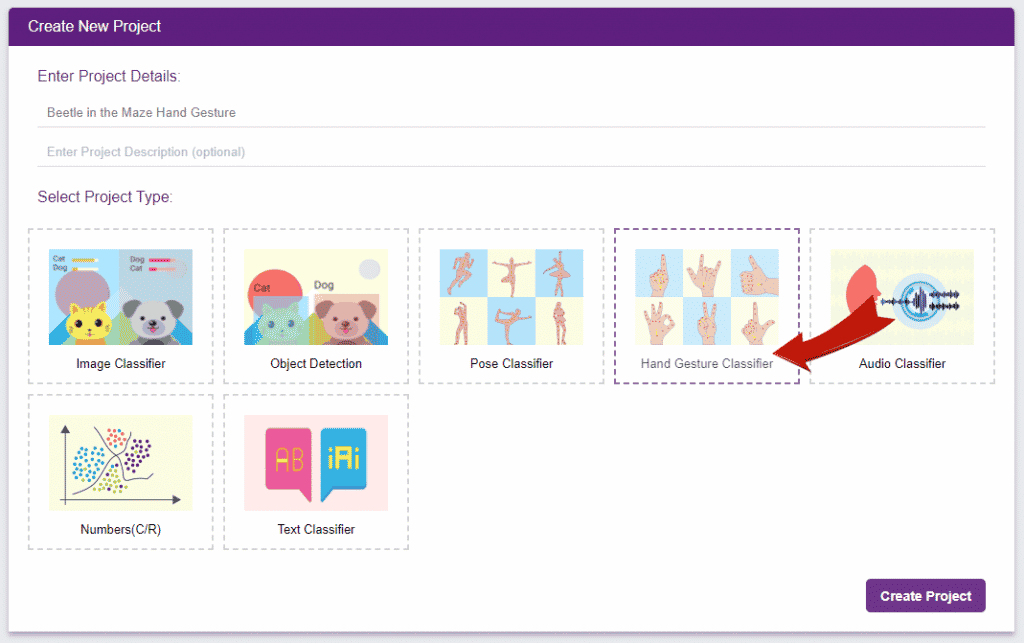
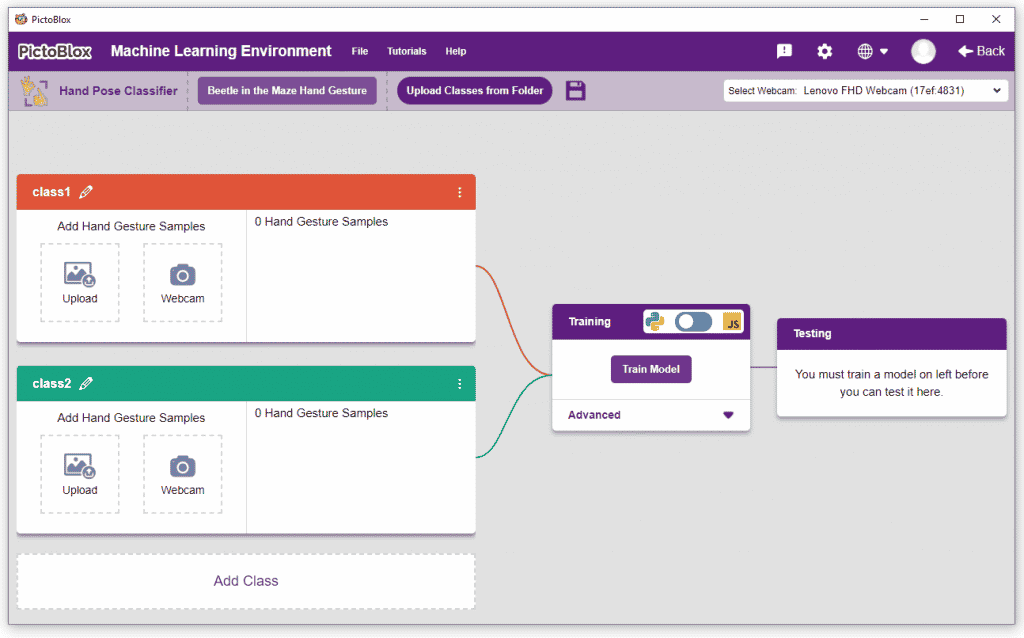
- You shall see the Gesture Pose Classifier workflow with two classes already made for you. Your environment is all set. Now it’s time to upload the data.
Class in Pose Classifier
Class is the category in which the Machine Learning model classifies the poses. Similar posts are put in one class.
Class in Hand Pose Classifier
Class is the category in which the Machine Learning model classifies the hand poses. Similar hand poses are put in one class.

Adding Data to Class
You can perform the following operations to manipulate the data into a class.
- Naming the Class: You can rename the class by clicking on the edit button.
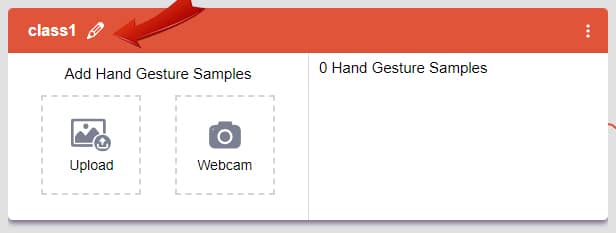
- Adding Data to the Class: You can add the data using the Webcam or by Uploading the files from the local folder.
- Webcam:
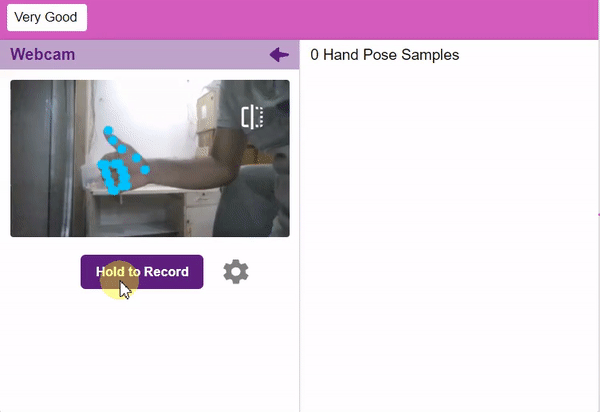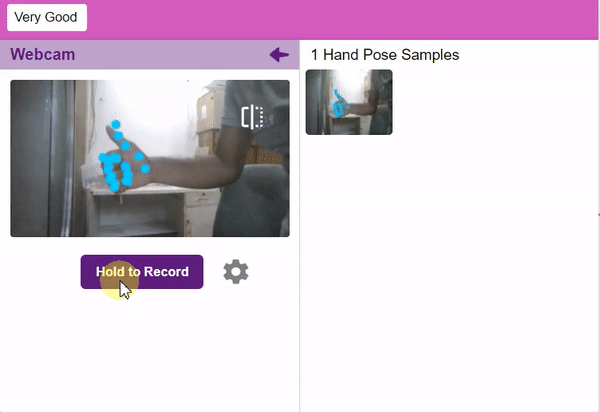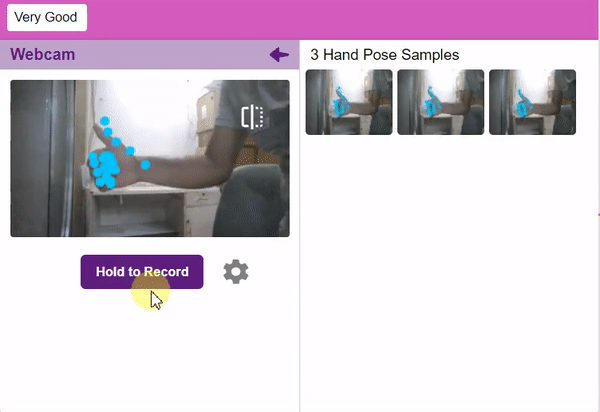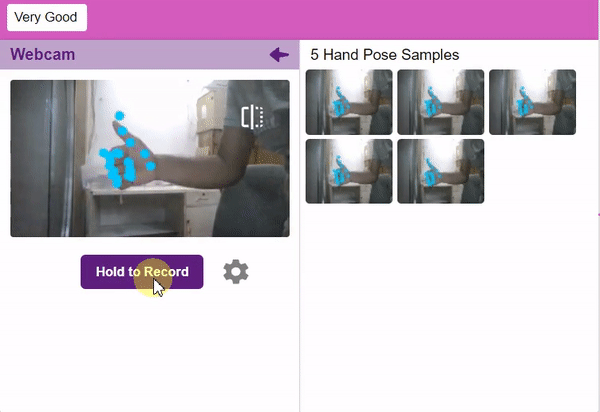
Note: You can edit the capture setting in the camera with the following. Hold to Record allows you to capture images with pose till the time button is pressed. Whereas when it is off you can set the start delay and duration of the sample collection.
If you want to change your camera feed, you can do it from the webcam selector in the top right corner.
Training the Model
After data is added, it’s fit to be used in model training. In order to do this, we have to train the model. By training the model, we extract meaningful information from the hand pose, and that in turn updates the weights. Once these weights are saved, we can use our model to make predictions on data previously unseen.

However, before training the model, there are a few hyperparameters that you should be aware of. Click on the “Advanced” tab to view them.
Note: These hyperparameters can affect the accuracy of your model to a great extent. Experiment with them to find what works best for your data.
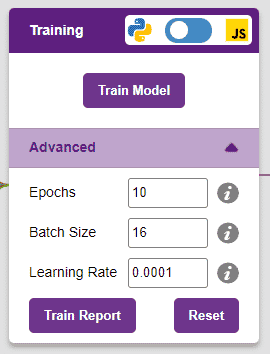
Note: Hover your mouse over the question mark next to the hyperparameters to see their description.
It’s a good idea to train a numeric classification model for a high number of epochs. The model can be trained in both JavaScript and Python. In order to choose between the two, click on the switch on top of the Training panel.
Alert: Dependencies must be downloaded to train the model in Python, JavaScript will be chosen by default.
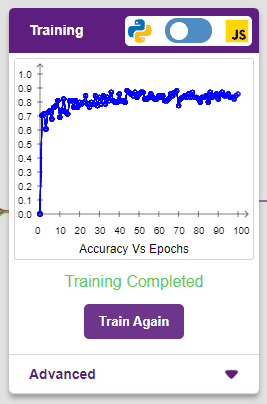
The accuracy of the model should increase over time. The x-axis of the graph shows the epochs, and the y-axis represents the accuracy at the corresponding epoch. Remember, the higher the reading in the accuracy graph, the better the model. The x-axis of the graph shows the epochs, and the y-axis represents the corresponding accuracy. The range of the accuracy is 0 to 1.
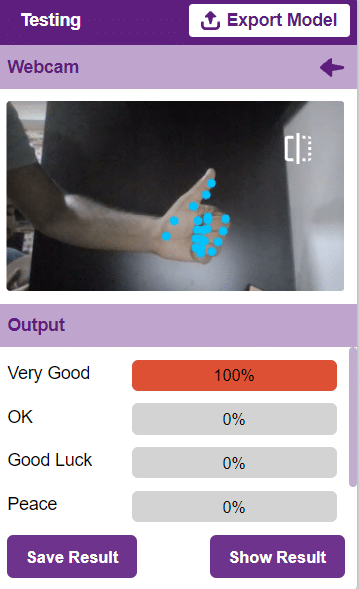
Testing the Model
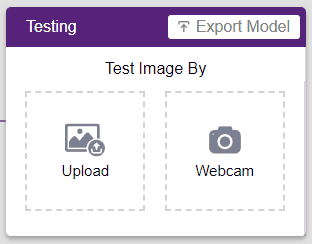
To test the model, simply enter the input values in the “Testing” panel and click on the “Predict” button.

The model will return the probability of the input belonging to the classes.
Export in Block Coding
Click on the “Export Model” button on the top right of the Testing box, and PictoBlox will load your model into the Block Coding Environment if you have opened the ML Environment in the Block Coding.
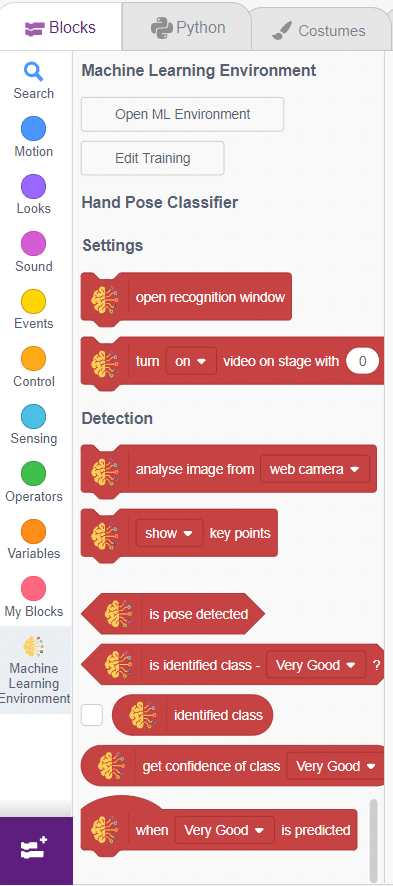
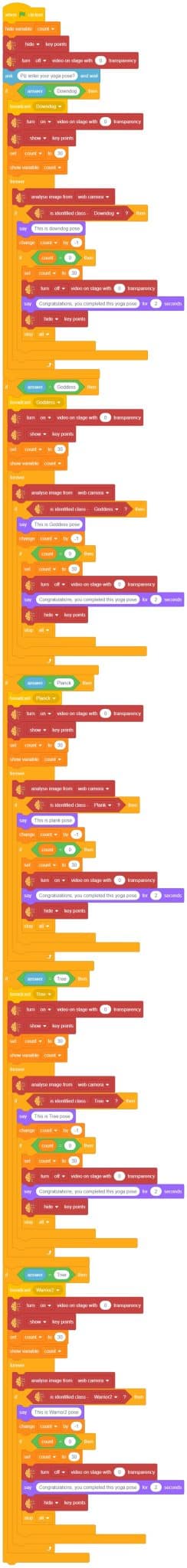
Script
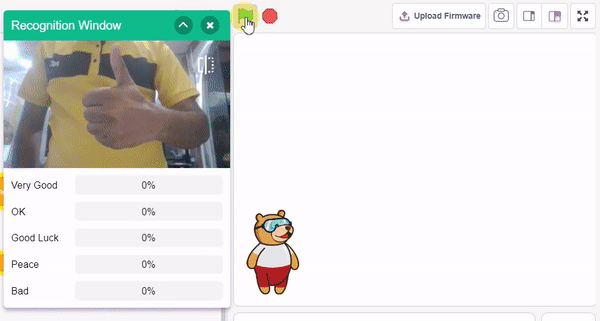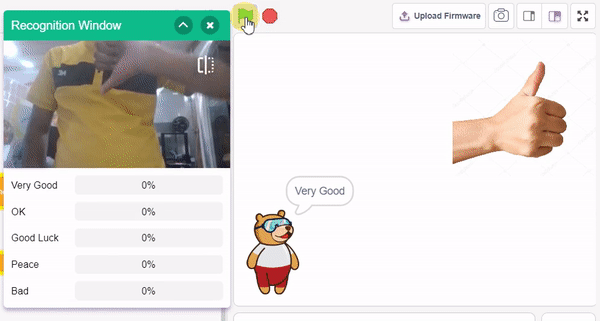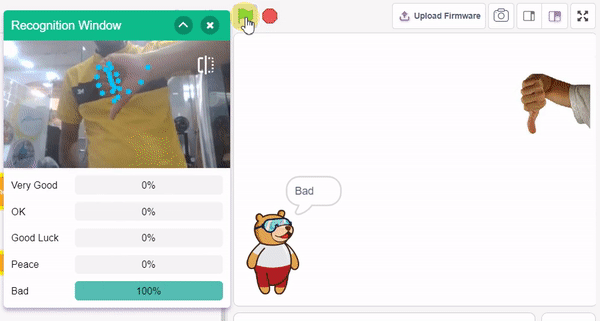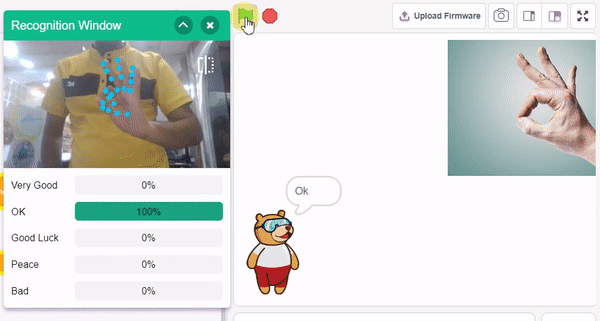
The idea is simple, we’ll add one image of each class in the “costume” column by making one new sprite which will we display on the stage according to input from user. we’ll also change name of the image according to sign class type.
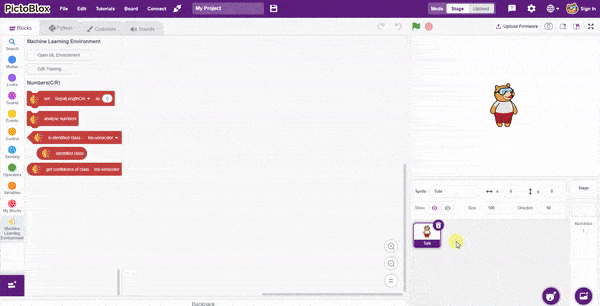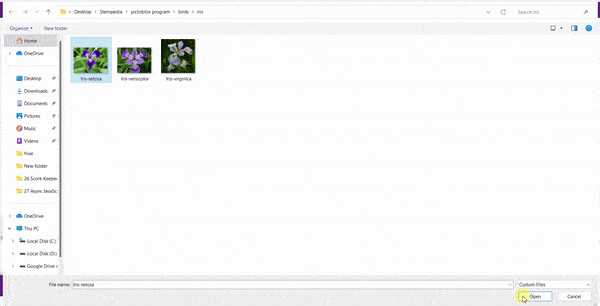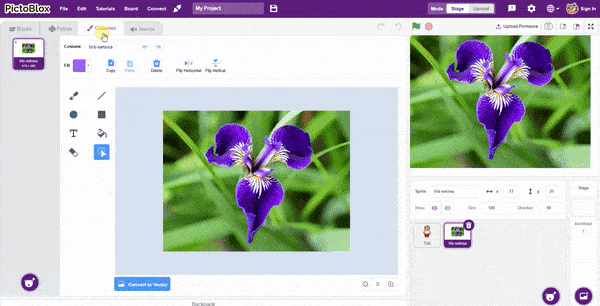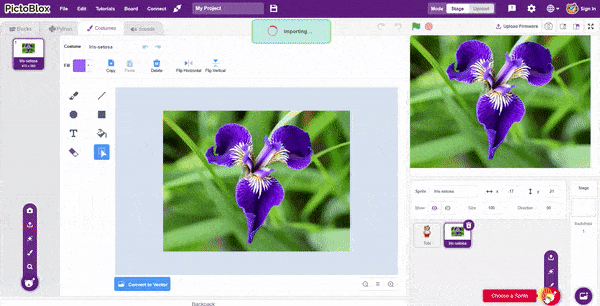
- Add one sign image as another sprite and upload at-least one image of all sign classes on costume.
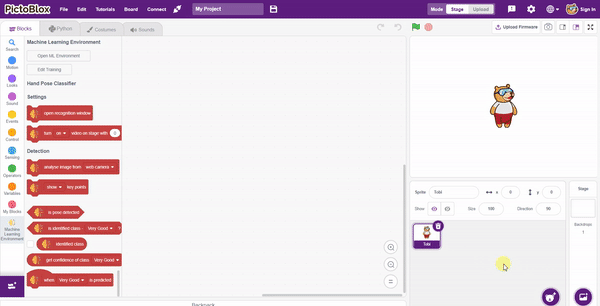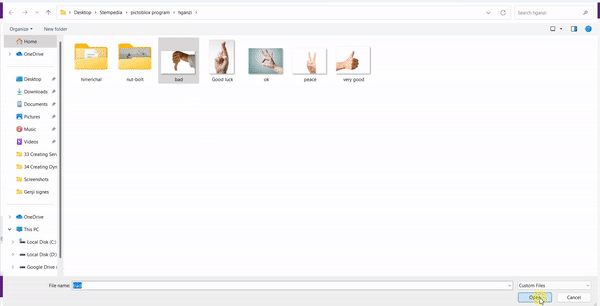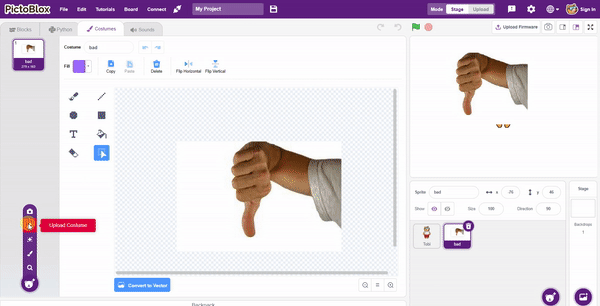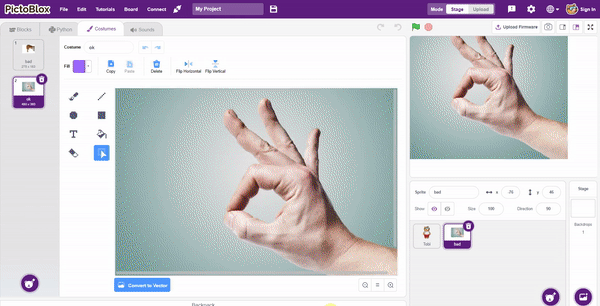
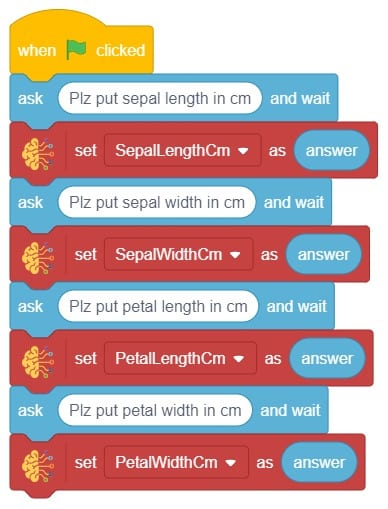
- Now, come back to the coding tab and select the Tobi sprite.
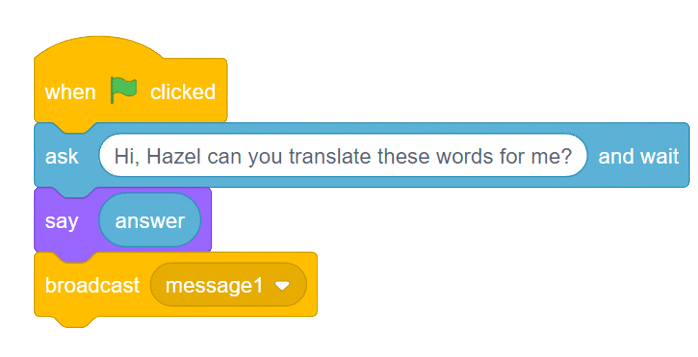
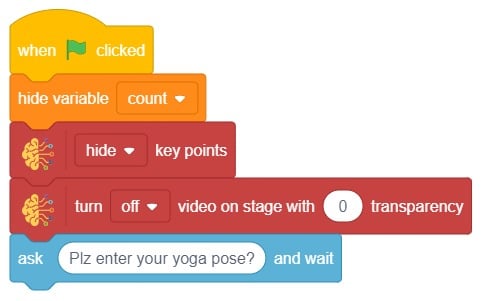
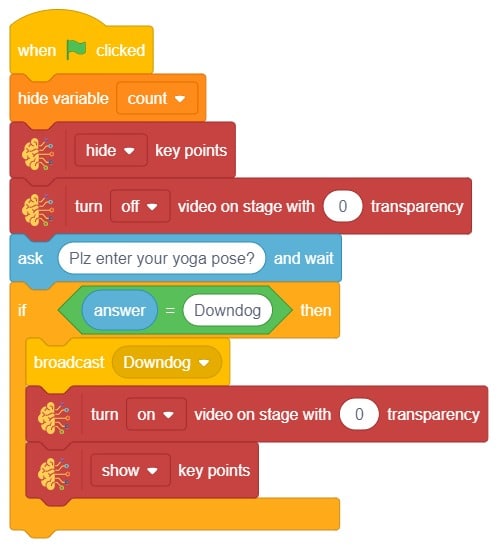
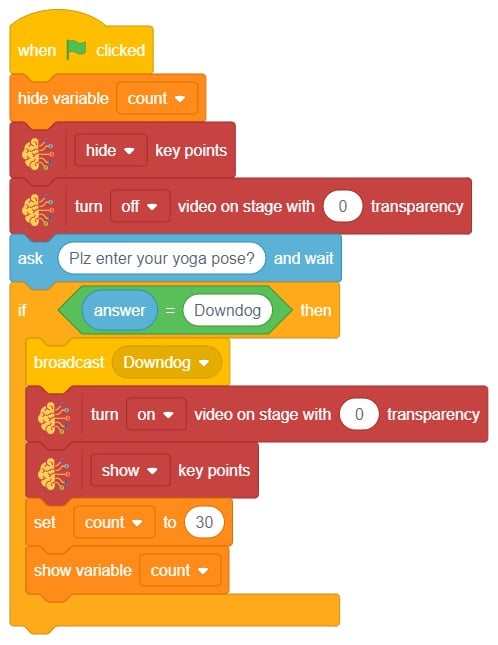
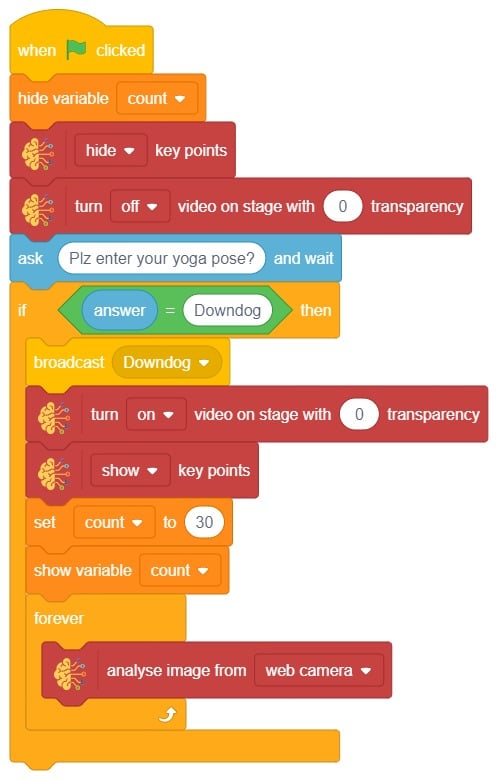
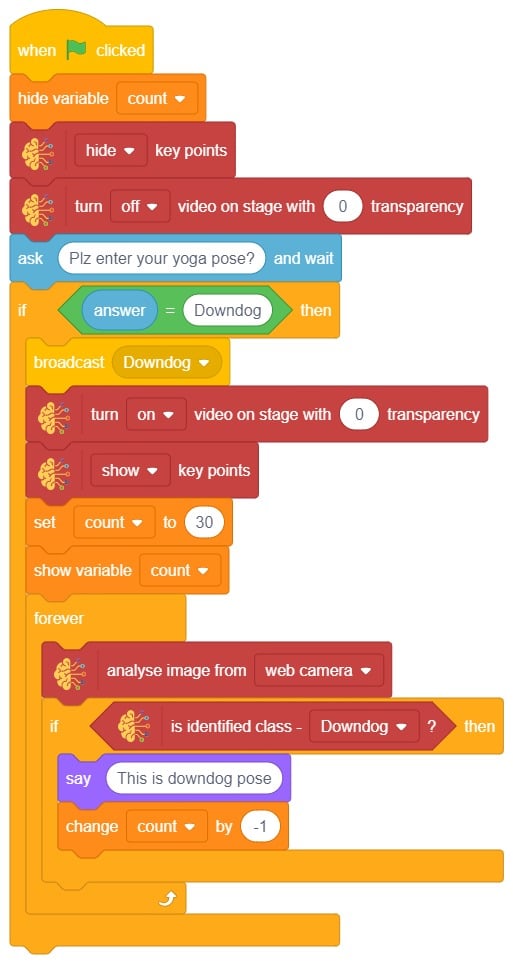
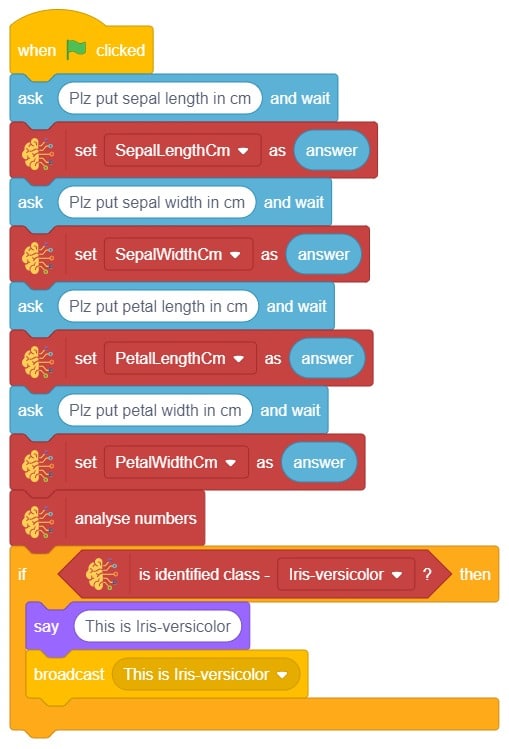
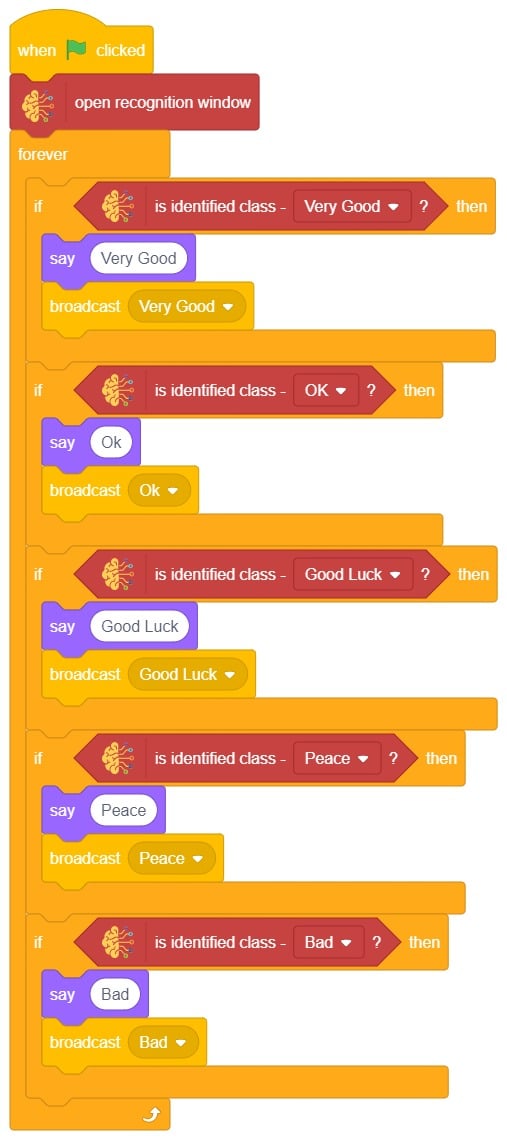
- We’ll start by adding a when flag clicked block from the Events palette.
- Add the “open recognition window” block from the Machine Learning palette.
- Add an “forever” block from the Control palette.
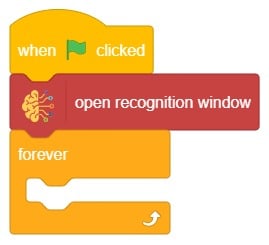
- Add the “if () then” block from the control palette for checking the user’s input.
- In the empty place of the “if () then” block, add an “is identified class ()” block from the Machine Learning palette. Select the appropriate class from the options.
- Inside the “if () then” block, add an “say ()” block from the Looks palette block. Write an appropriate statement in an empty place.
- Inside the “if () then” block, add a “broadcast ()” block from the Events palette block. Select the “New message” option and write an appropriate statement for broadcasting a message to another sprite.
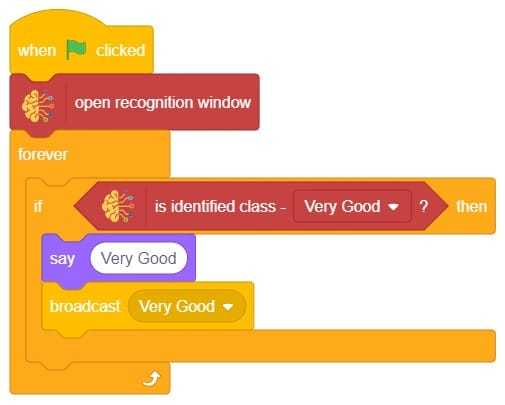
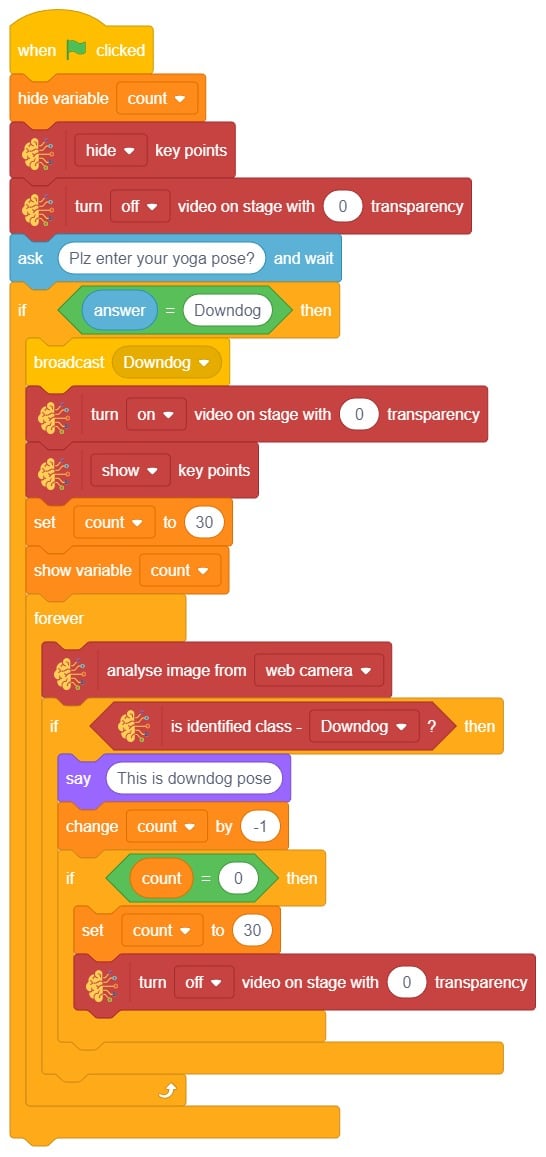
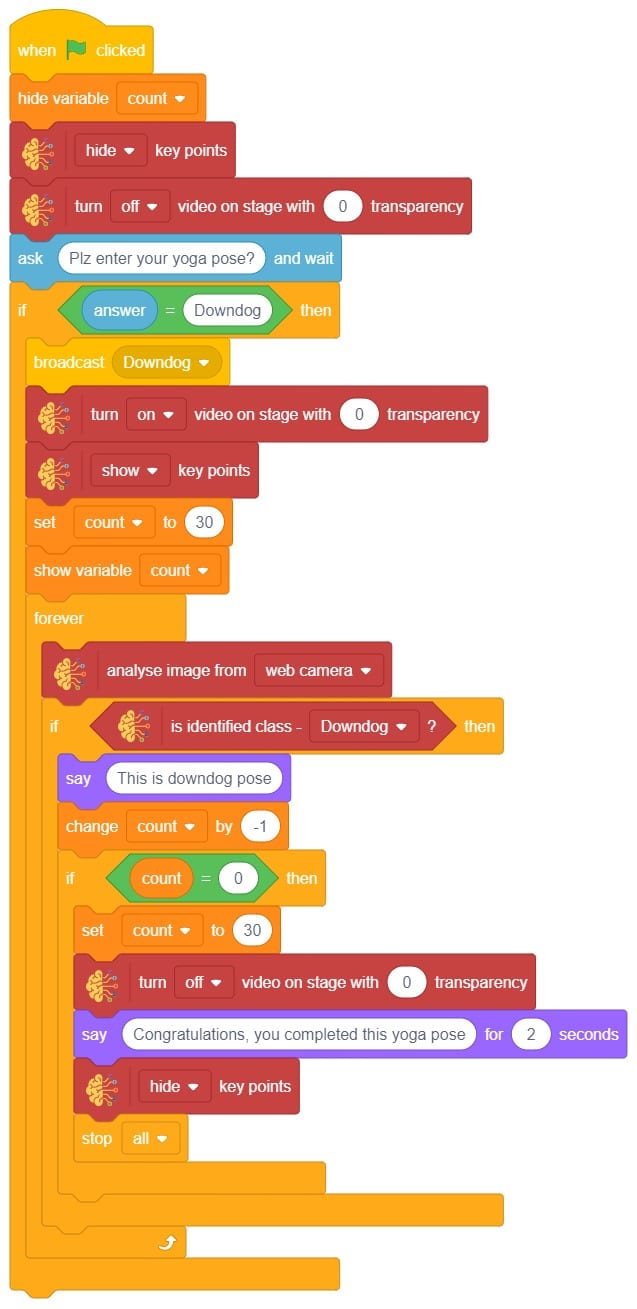
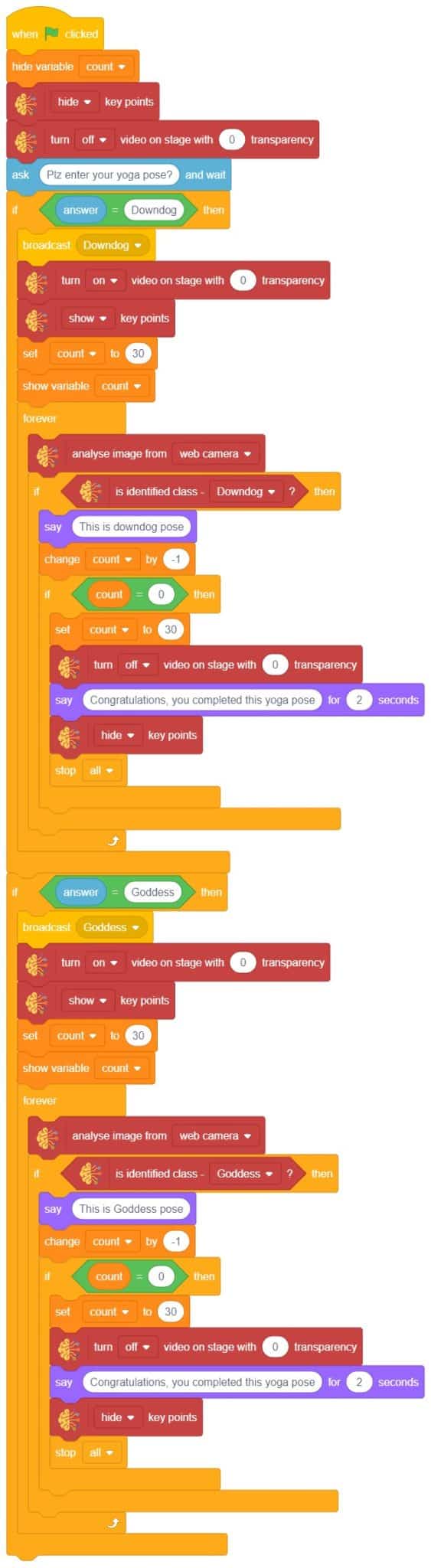
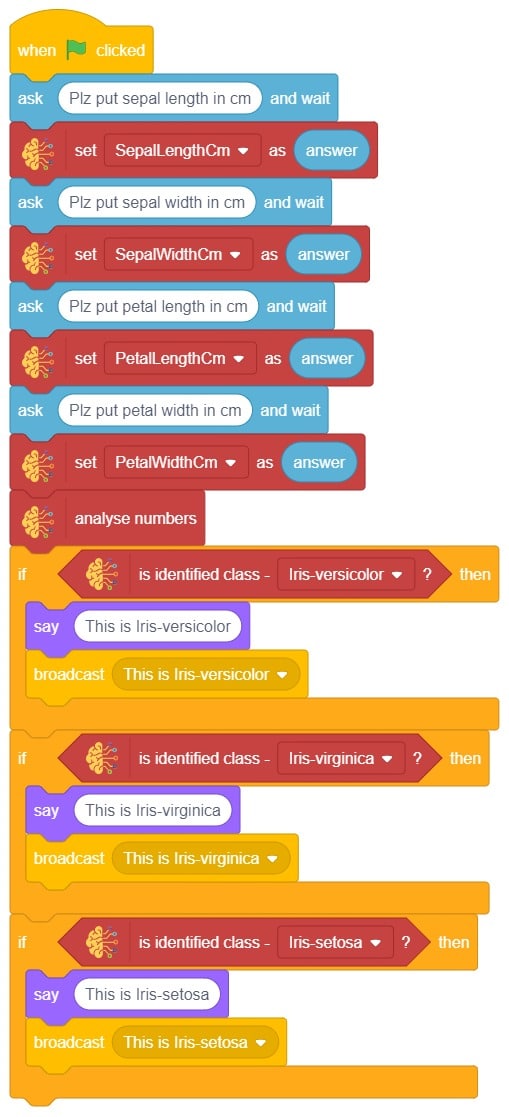
- Repeat “if () then” block code for other classes, make appropriate changes in copying block code according to other classes, and add code just below it.
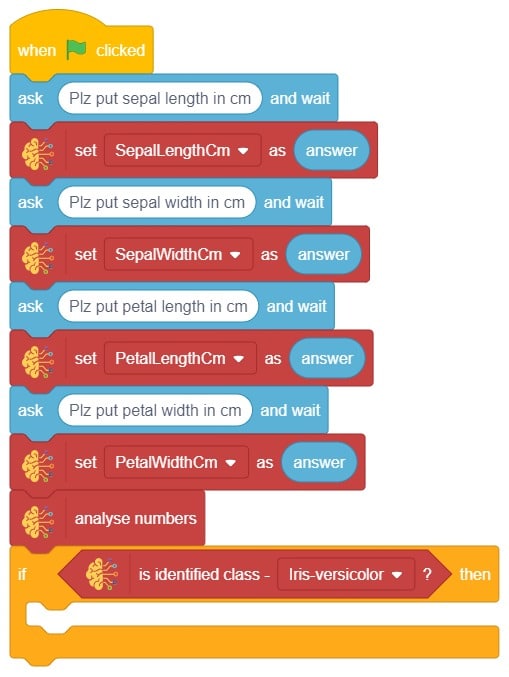
- Final code of “Tobi” sprite is
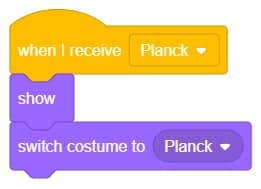
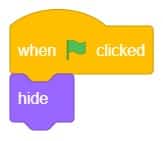
- Now click on another sprite and write code.
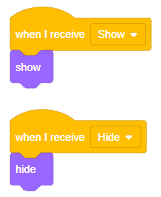
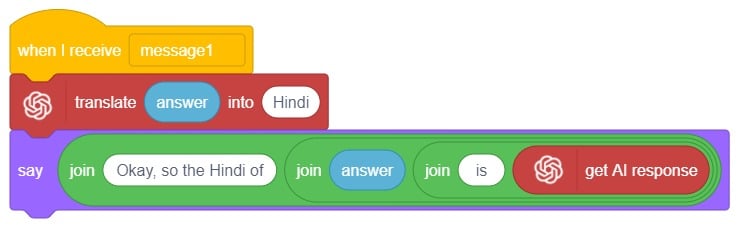
- We’ll start writing code for this sprite by adding a when flag is clicked block from the Events palette.
- Add the “hide” block from the Looks pallet.
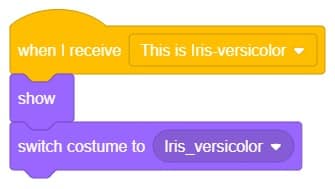
- Write a new code in the same sprite according to class and add the “when I receive ()” block from the Events palette. Select the appropriate class from the options.
- Add the “show” block from the Looks pallet.
- Add the “switch costume to ()” block from the Looks palette. Select the appropriate class from the options.
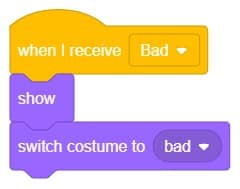
- Repeat the same code for other classes and make changes according to the class.
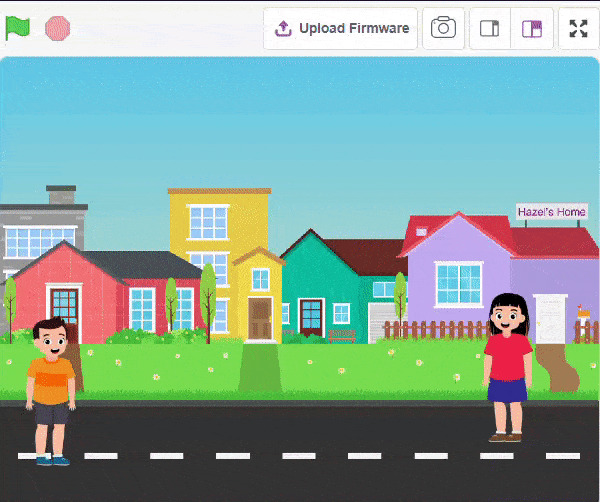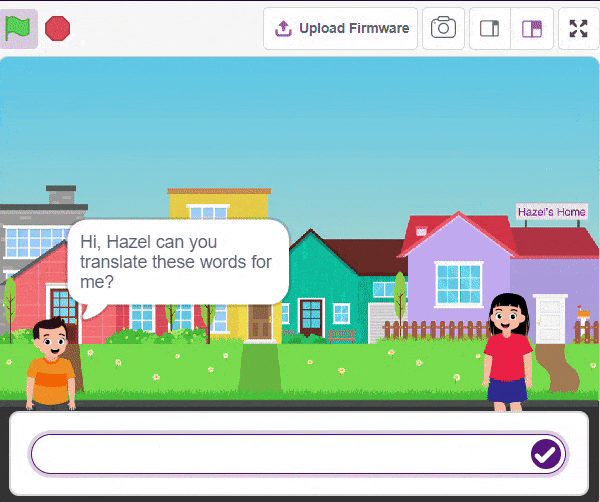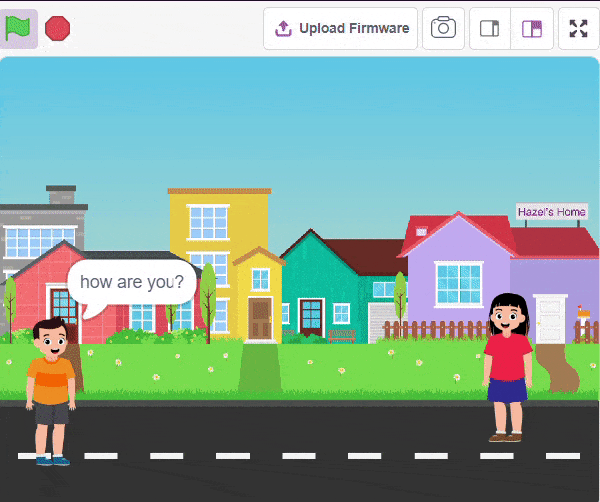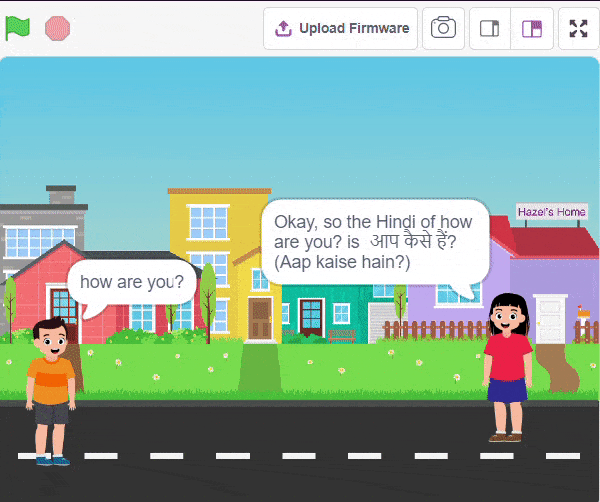
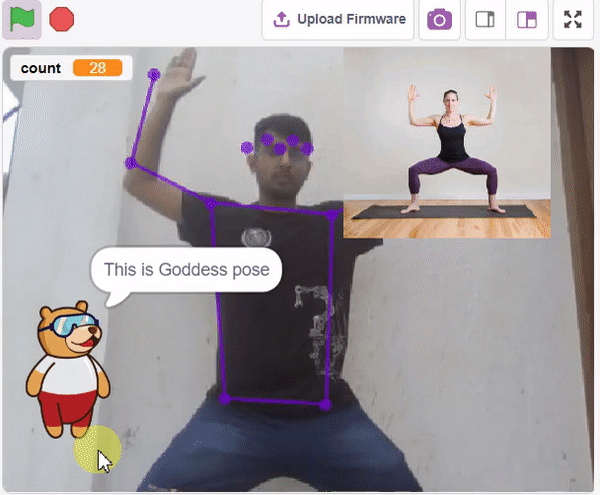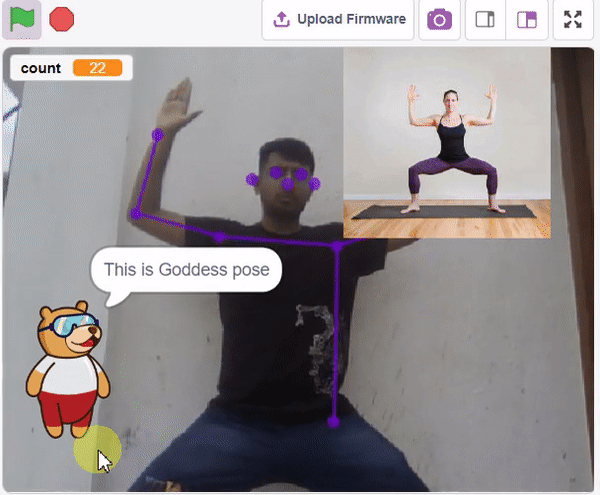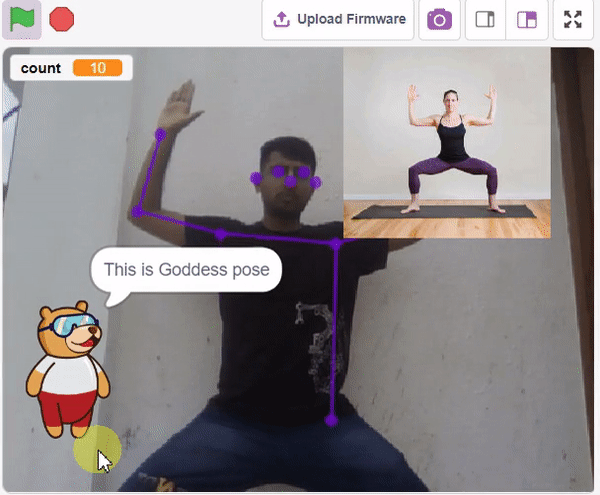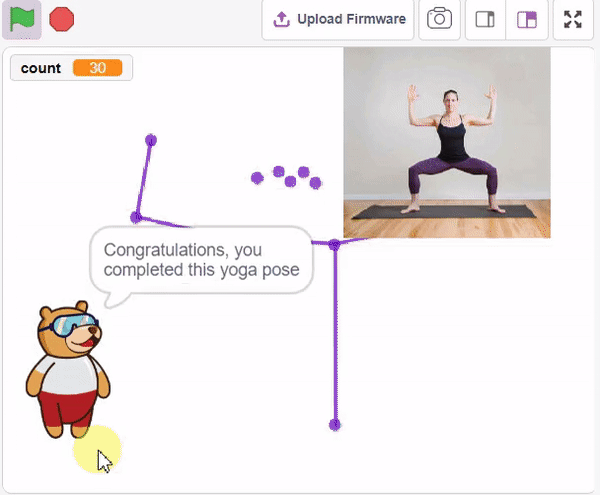
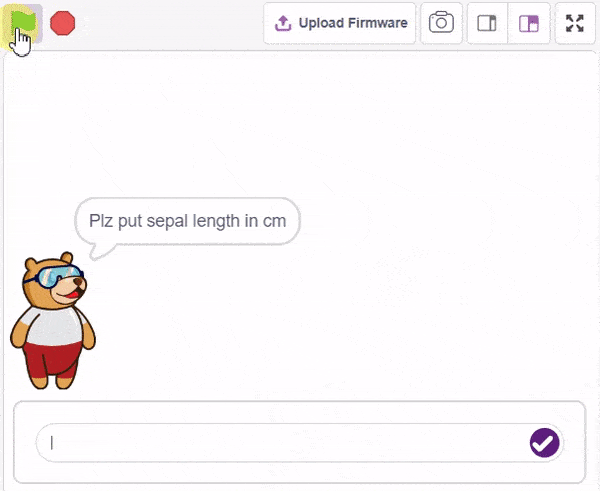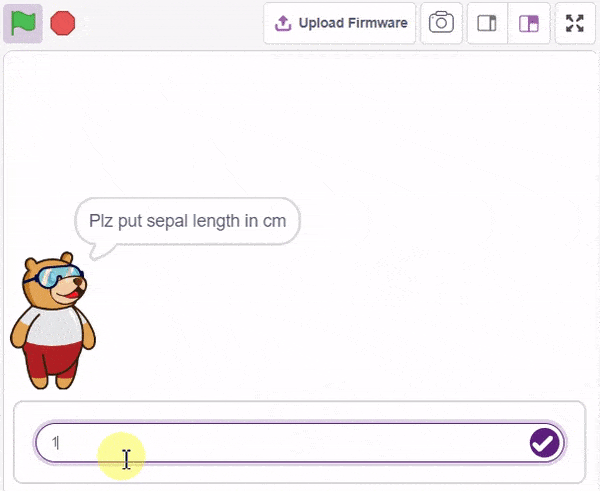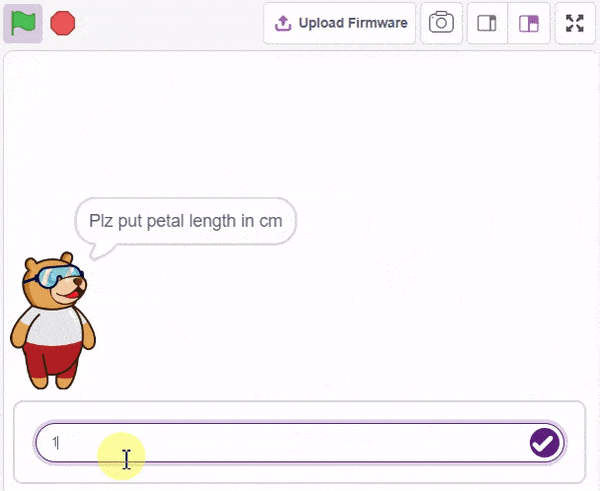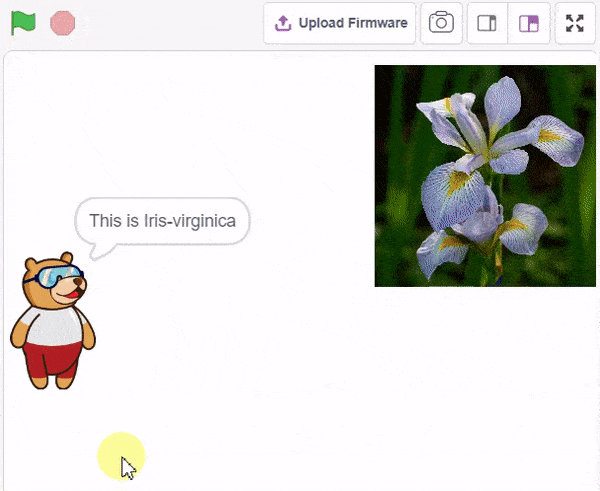
Final Output