The function sets the threshold value of the specified IR sensor to the specified value. The value can be from 0 to 4095.
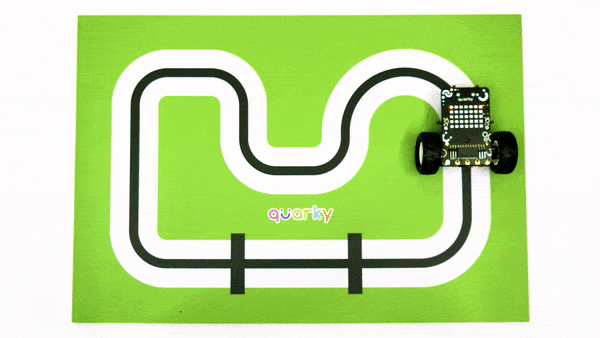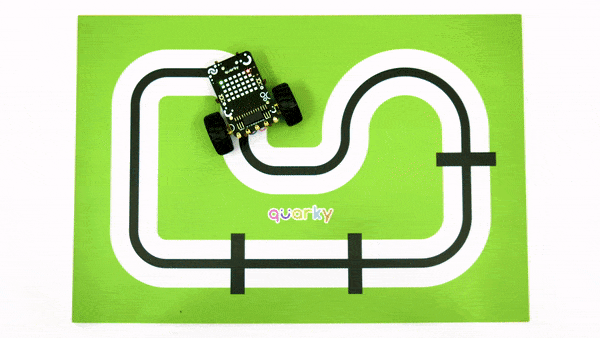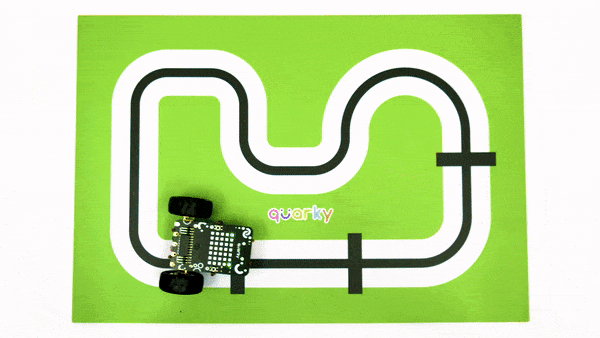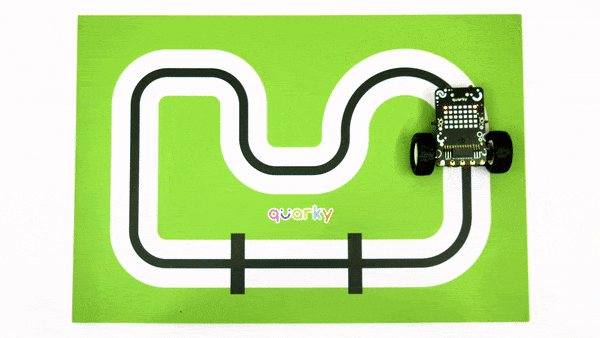
The example demonstrates how to calibrate the IR sensors to detect black lines on the white surface in Python Coding Environment.
Logic
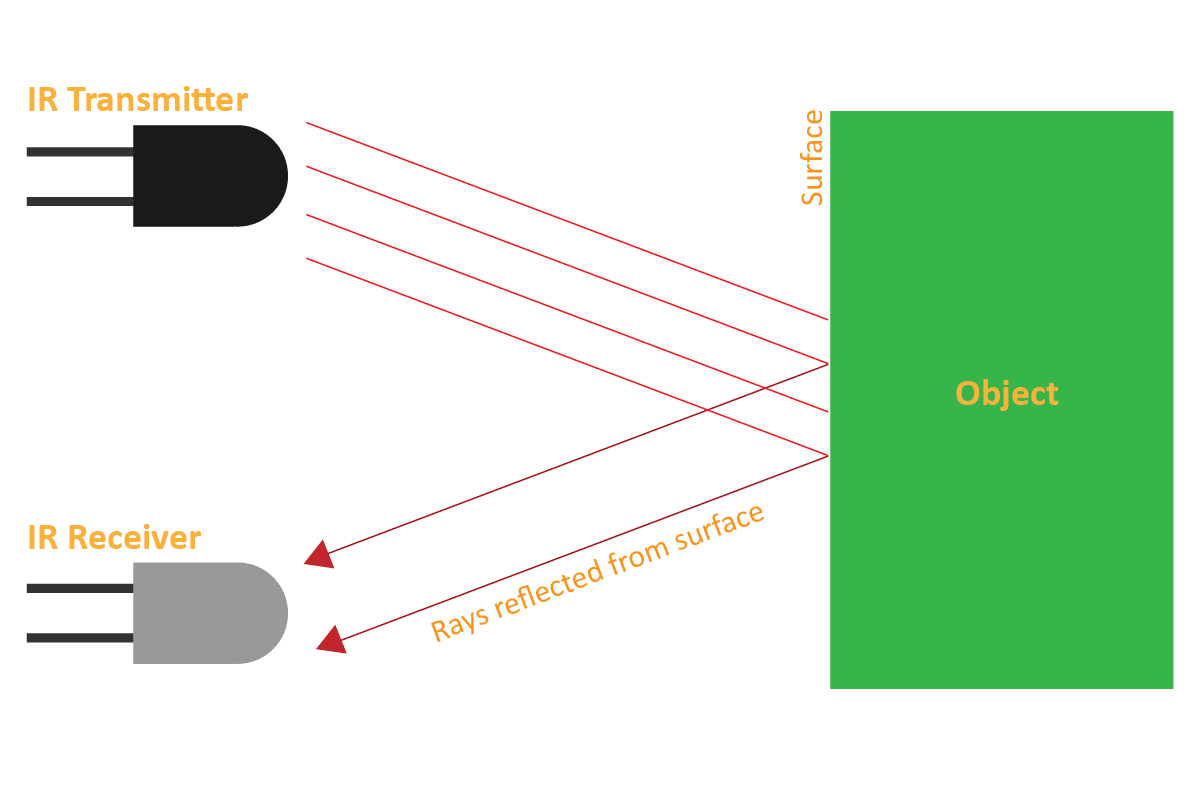
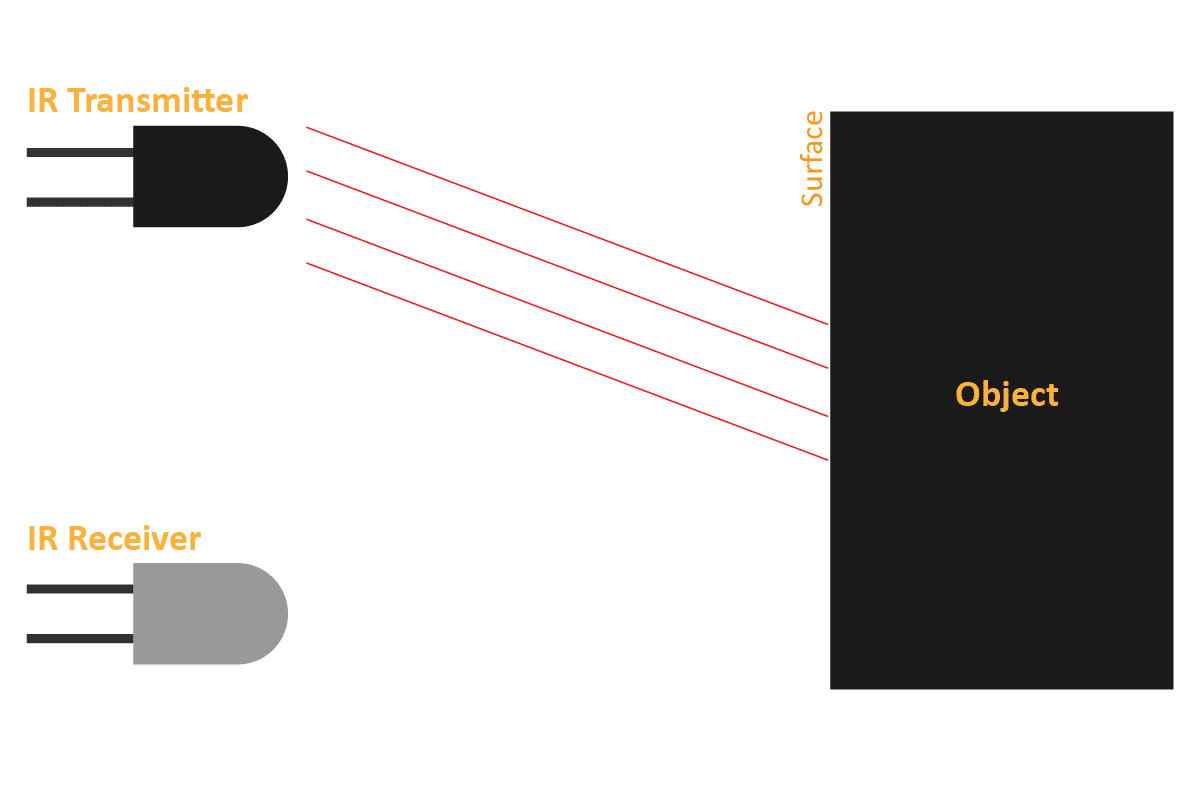
An IR sensor consists of 2 LEDs: one which transmits the IR light and one which receives the IR light. When the IR rays are transmitted, they bounce from the nearest surface and get back to the receiver LED. That’s how an IR sensor detects an object.
But to detect colors, we depend on the number of rays the surface reflects:
- The dark surface will absorb more IR rays and as a result, the receiver will get fewer IR rays.
- White or shiny objects will absorb fewer IR rays and as a result, the receiver will get more IR rays.
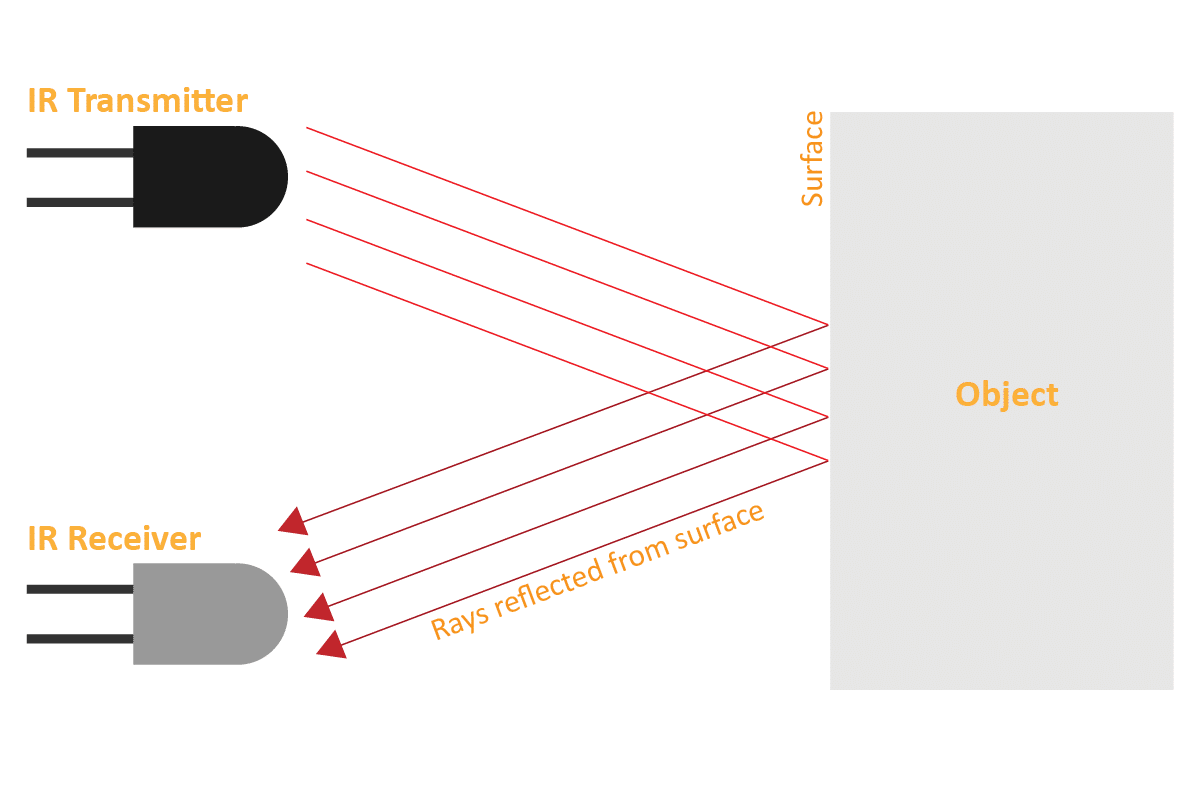
We can get the sensor values in PictoBlox and based on that value we can estimate whether the surface is black or white.
- If the sensor detects the black line, its output value is increased. This means that the sensor is active.
- If it detects the white area, its output value decreases. This means that the sensor is inactive.
We will call the threshold value above which the sensor detects the black line. If the sensor value is less than the threshold, it means that the sensor hasn’t detected the line yet.

Alert: IR sensors DON’T work in sunlight. IR rays from the sun increase the overall threshold of the sensors therefore they stay active all time. A closed environment or nighttime is the place/time to work with your line following robot.
Code
sprite = Sprite('Tobi')
quarky = Quarky()
quarky.cleardisplay()
quarky.setirthreshold("IRL", 3000)
quarky.setirthreshold("IRR", 3000)
while True:
if quarky.getirstate("IRL"):
quarky.setled(1, 1, [0, 255, 0], 20)
else:
quarky.setled(1, 1, [255, 0, 0], 20)
if quarky.getirstate("IRR"):
quarky.setled(7, 1, [0, 255, 0], 20)
else:
quarky.setled(7, 1, [255, 0, 0], 20)
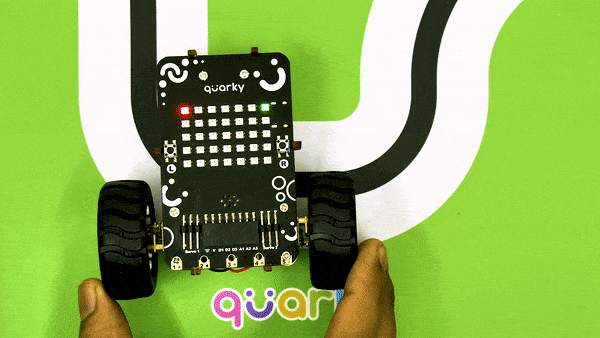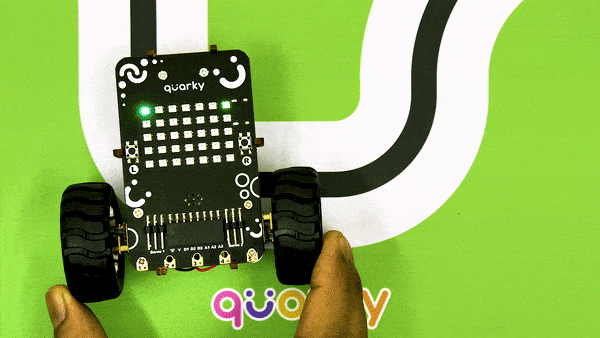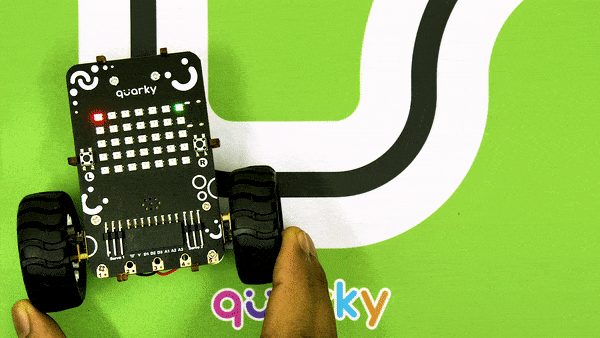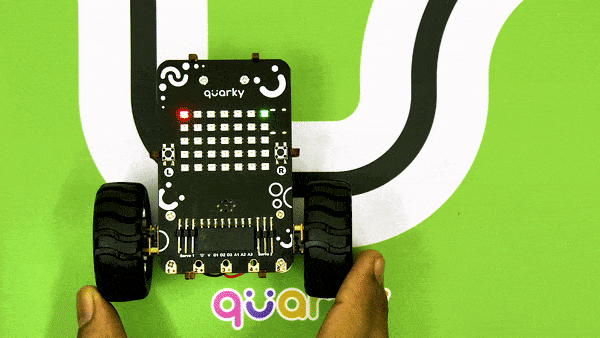
Calibrating the IR Sensors
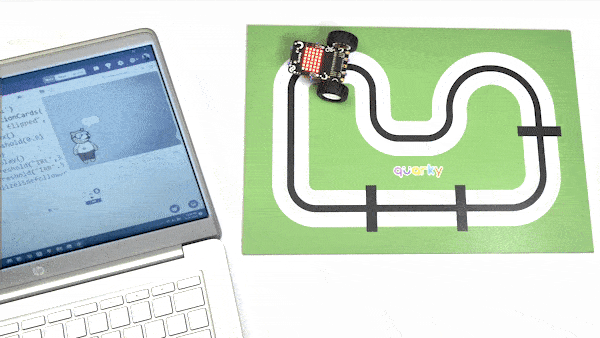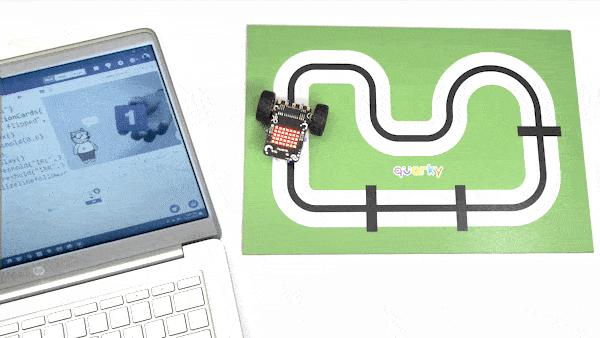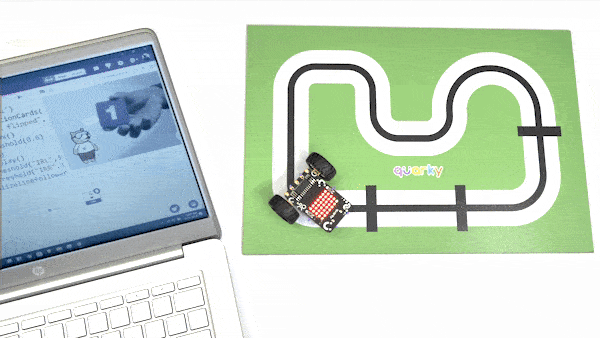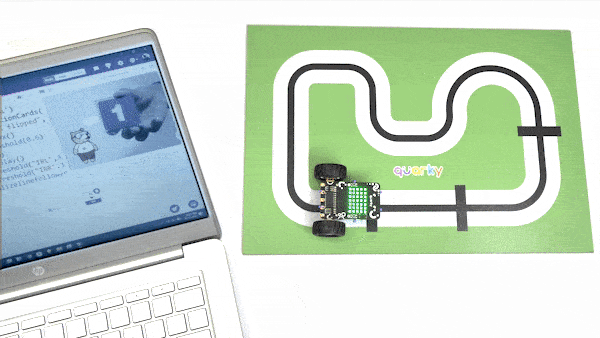
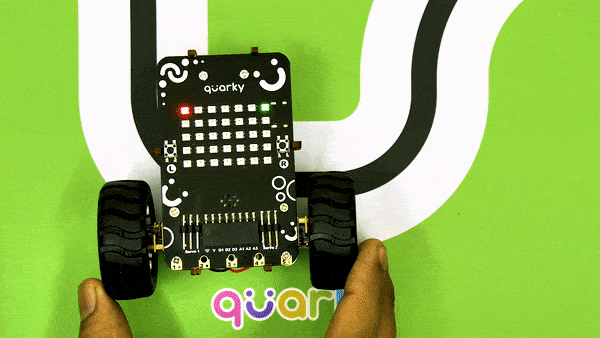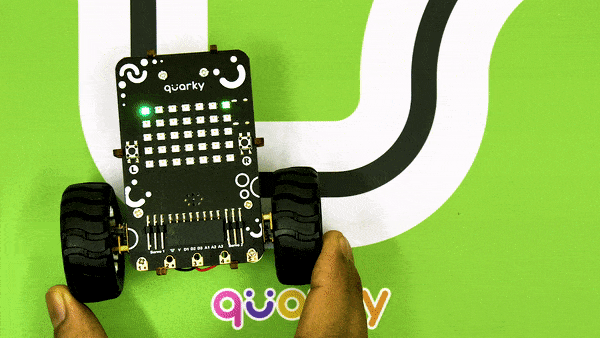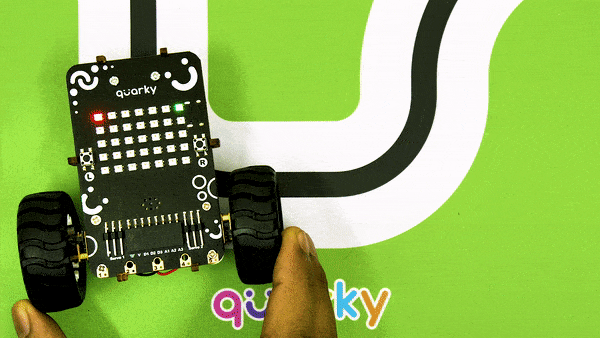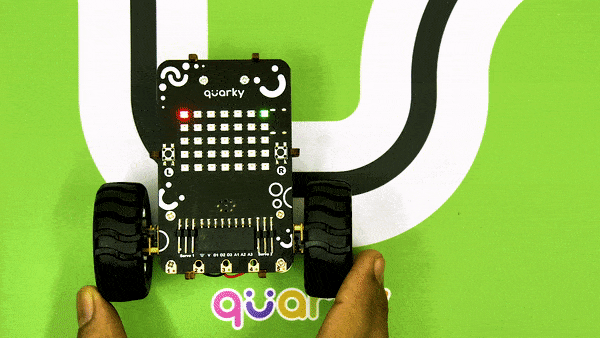
Now, run the code by clicking the green flag and bringing the black line of the track close to the IR sensor. One of the following three conditions will happen:
- Your calibration value is HIGH: The black region will not be detected in this case. Reduce the calibration value.

- Your calibration value is LOW: The white region will not be detected in this case. Therefore, increase the calibration value.

- Your calibration value is OK. The white and black regions are detected accurately.
Now modify the script to add the detection value for the right IR sensor.
Output

Read More