3D and XR Studio Physics

-
 Available in: Block Coding, Python Coding
Available in: Block Coding, Python Coding
-
 Mode: Stage Mode
Mode: Stage Mode
-
 WiFi Required: No
WiFi Required: No
-
 Compatible Hardware in Block Coding: evive, Quarky, Wizbot, Arduino Uno, Arduino Mega, Arduino Nano, ESP32, T-Watch, Boffin, micro:bit, TECbits, LEGO EV3, LEGO Boost, LEGO WeDo 2.0, Go DFA
Compatible Hardware in Block Coding: evive, Quarky, Wizbot, Arduino Uno, Arduino Mega, Arduino Nano, ESP32, T-Watch, Boffin, micro:bit, TECbits, LEGO EV3, LEGO Boost, LEGO WeDo 2.0, Go DFA
-
 Compatible Hardware in Python: evive, Quarky, Wizbot, Arduino Uno, Arduino Mega, Arduino Nano, ESP32, T-Watch, Boffin, micro:bit, TECbits, LEGO EV3, LEGO Boost, LEGO WeDo 2.0, Go DFA
Compatible Hardware in Python: evive, Quarky, Wizbot, Arduino Uno, Arduino Mega, Arduino Nano, ESP32, T-Watch, Boffin, micro:bit, TECbits, LEGO EV3, LEGO Boost, LEGO WeDo 2.0, Go DFA
-
 Object Declaration in Python: .
Object Declaration in Python: .
-
 Extension Catergory: 3D and XR Studio
Extension Catergory: 3D and XR Studio
Introduction
Physics offers comprehensive control over the physical properties and behavior of objects and the world itself. Here’s a breakdown of each aspect:
1. World Physics Properties:
– World Type: Users can define the type of physics world, such as 2D or 3D, to match the dimensions of their environment.
– Gravity: Users have the ability to set the direction and magnitude of gravity within the physics world, influencing the behavior of objects subjected to gravitational forces.
2. Object Body Properties:
– Body Type: Users can specify the body type of objects, such as static, dynamic, or kinematic, determining how they interact with the physics simulation.
– Mass: Users can set the mass of objects, influencing their response to external forces and collisions.
– Friction: Users can adjust the friction coefficient of objects, controlling the resistance to motion when in contact with other surfaces.
– Damping: Users can define damping properties to simulate air resistance or other dissipative forces, affecting the object’s motion over time.
– Pressure: Users have the option to specify pressure properties for objects, influencing their deformation or buoyancy behavior in fluid simulations.
3. Motion Control:
Simple Motion:
1. Push Object Towards Another Object: Users can make one object move towards another with a specified speed, useful for creating collisions or interactions.
2. Move Forward/Backward: Users can move objects in a straight line, either forward or backward, with a set speed.
Advanced Motion:
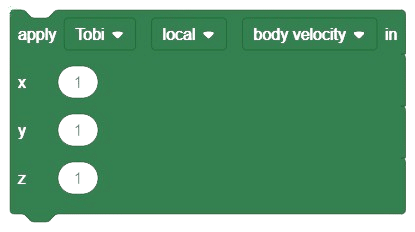
1. Body Velocity: Users can set the speed and direction of objects’ movement.
2. Body Angular Velocity: Users control how fast objects rotate.
3. Apply Impulse: Users can give objects a sudden push, simulating impacts or abrupt movements.
4. Apply Force: Users can continuously push objects, affecting their movement over time.
5. Gravity: Users can adjust how much gravity affects objects, controlling their falling speed or direction.
These motion options allow users to create a variety of dynamic effects in their scenes, from basic movements to complex physics simulations.