Introduction
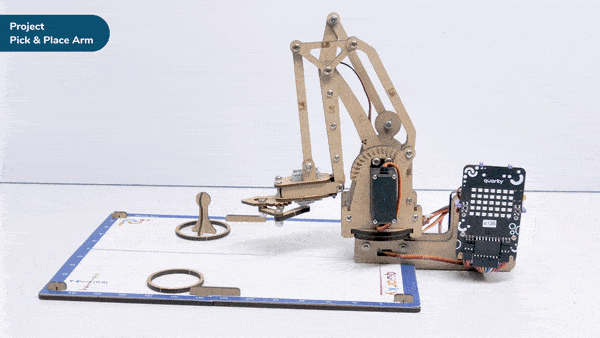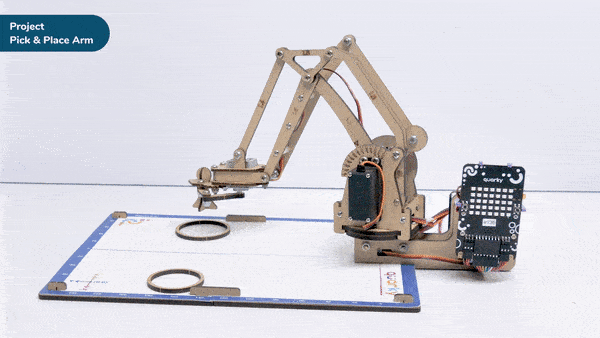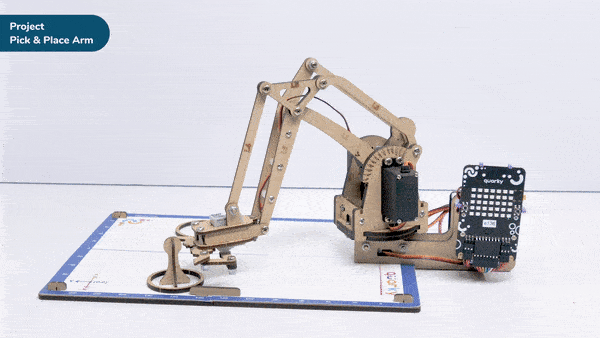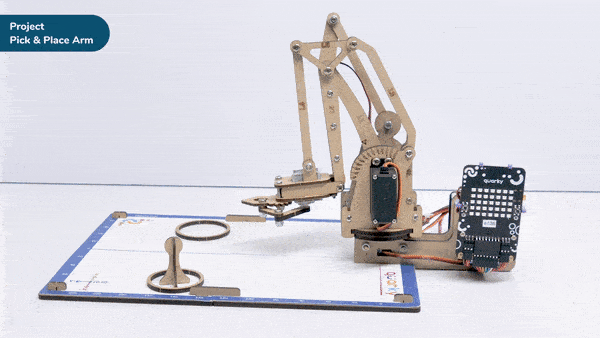
A pick-and-place robotic arm is a mechanical system designed to perform the task of picking up objects from one location and placing them in another. It consists of multiple segments connected, similar to a human arm, and is equipped with motors, sensors, and grippers.
The robotic arm is programmed to move in a precise and controlled manner. It can be guided by various input methods, such as a computer interface or remote control. The arm uses its grippers to grasp objects securely, and then it can move them to a different location.
Pick-and-place robotic arms are commonly used in industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and assembly lines. They automate repetitive tasks that involve moving objects, saving time and reducing the risk of human error. These robotic arms can handle a wide range of objects, from small components to larger items, with accuracy and efficiency.
Code
Logic
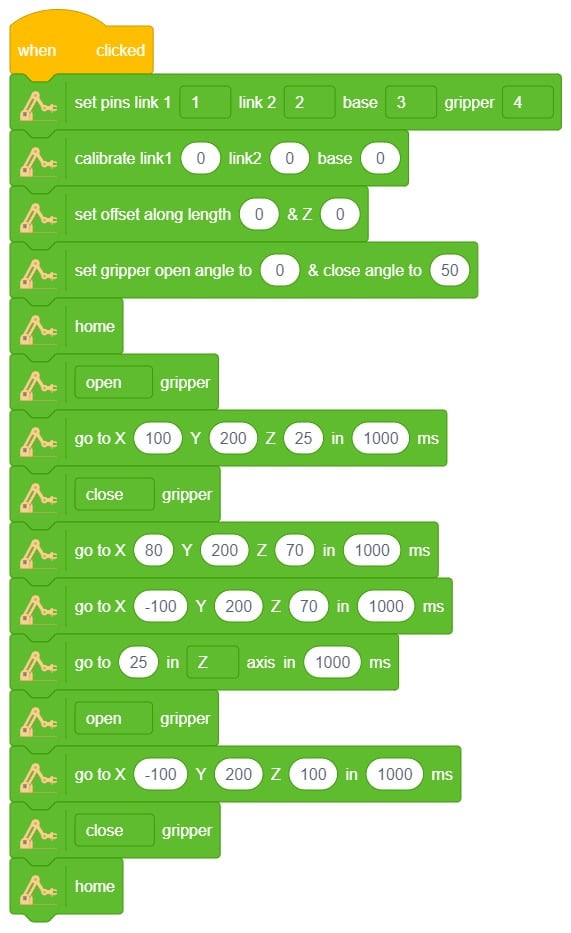
- Open the Pictoblox application.
- Select the block-based environment.
- Click on the robotic arm extension available in the left corner.

- Drag and drop the Set Pins Link1(), Link2(), Base(), and Gripper() block to define the robotic arm for each servo connection.
- Use the Calibrate Link1(), Link2(), and Base() block to set the angle.
- Drag and drop the Set Offset Along Length() and Set Offset along Z() blocks to adjust the position of the end effector in the z-direction.
- Select the home() block to set the home position for the robotic arm.
- Open the gripper to pick up a specific object.
- Close the gripper to grab the object securely.
- Move to the desired location, then open the gripper to release the object.
- Close the gripper afterward.
- Then The arm will move to its default or home position using home() block.
- Press Run to run the code.