Introduction
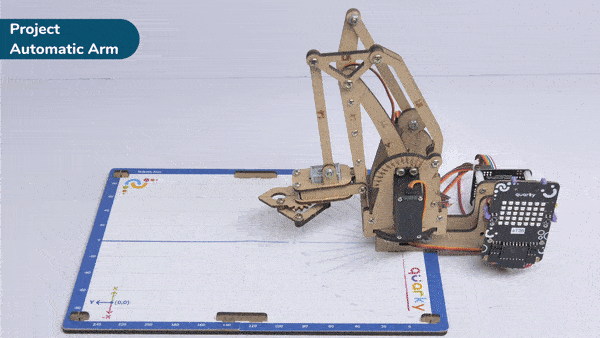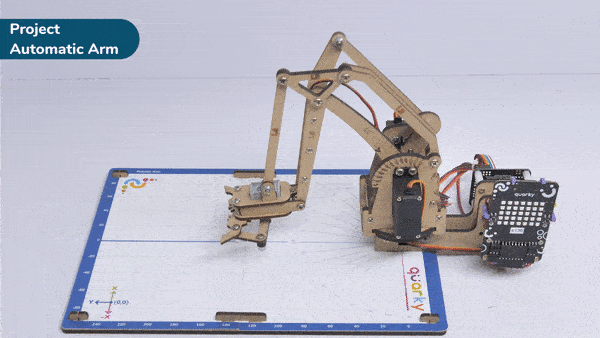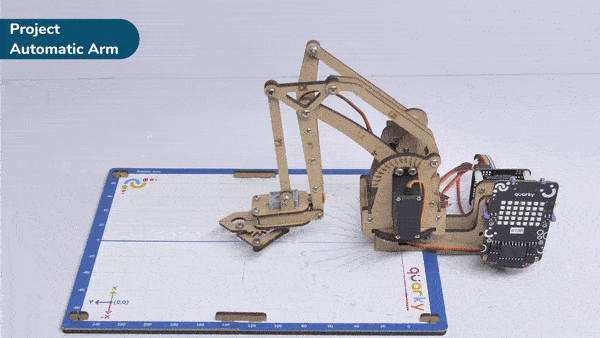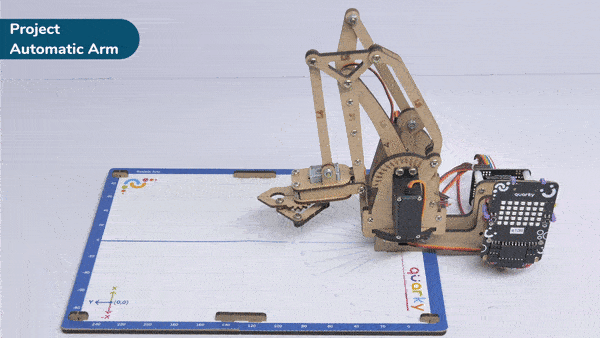
Automatic Robotic AMR stands for Automatic Mobile Robots for Autonomous Material Handling. It refers to a class of robots that are designed to autonomously transport and handle materials in various environments, such as warehouses, factories, hospitals, and distribution centers.
Code
sprite = Sprite('Tobi')
import time
roboticArm = RoboticArm(1,2,3,4,)
roboticArm.setgripperangle(90,145)
roboticArm.sethome()
while True:
roboticArm.controlgripper("open")
roboticArm.movexyzonebyone(0,200,15,1000)
roboticArm.gotoinoneaxis(180,"Y",1000)
roboticArm.controlgripper("close")
roboticArm.gotoinoneaxis(150,"X",1000)
roboticArm.controlgripper("open")
roboticArm.sethome()
roboticArm.controlgripper("close")
time.sleep(1)
roboticArm.controlgripper("open")
roboticArm.movexyzonebyone(-60,160,10,1000)
roboticArm.gotoinoneaxis(200,"Y",1000)
roboticArm.gotoinoneaxis(15,"Z",1000)
roboticArm.gripperaction("close")
roboticArm.gotoinoneaxis(150,"X",1000)
roboticArm.gripperaction("open")
roboticArm.sethome()
roboticArm.gripperaction("close")
time.sleep(0.2)Logic
- Open the Pictoblox application.
- Select the Python-based environment.
- The code starts by importing the required modules, including the “quarky” module and the “RoboticArm” class from the “expansion_addon” module. These modules provide the necessary functionalities for controlling the robotic arm.

- An instance of the RoboticArm class is created with four parameters (1, 2, 3, 4). These parameters likely represent some configuration values or settings for the robotic arm.
- The gripper angle of the robotic arm is set to 90 and 145 degrees using the setgripperangle() method.
- The sethome() method is used to set the home position() of the robotic arm.
- The code enters a while loop that runs indefinitely (until the program is manually terminated. Inside the loop, various actions are performed using the robotic arm.
- The gripper of the robotic arm is opened and closed using the gripperaction() method with the parameters “open” and “close” respectively.
- The robotic arm is instructed to move in the XY plane using the movexyzonebyone() method. The parameters provided are the initial and final X coordinates (0 and 200), the Y coordinate (15), and the speed (1000).
- The robotic arm is commanded to move to a specific position in a single axis (X, Y, or Z) using the gotoinoneaxis() method. The parameters include the target position, the axis, and the speed.
- The program includes a few additional time.sleep(0.2) statements, which introduce short delays before the program repeats the looP.
- Press Run to run the code.
Output