This function returns the specified parameter of the hand landmark detected:
- Position Parameter Value 1 – X Position of the landmark.
- Position Parameter Value 2 – Y Position of the landmark.
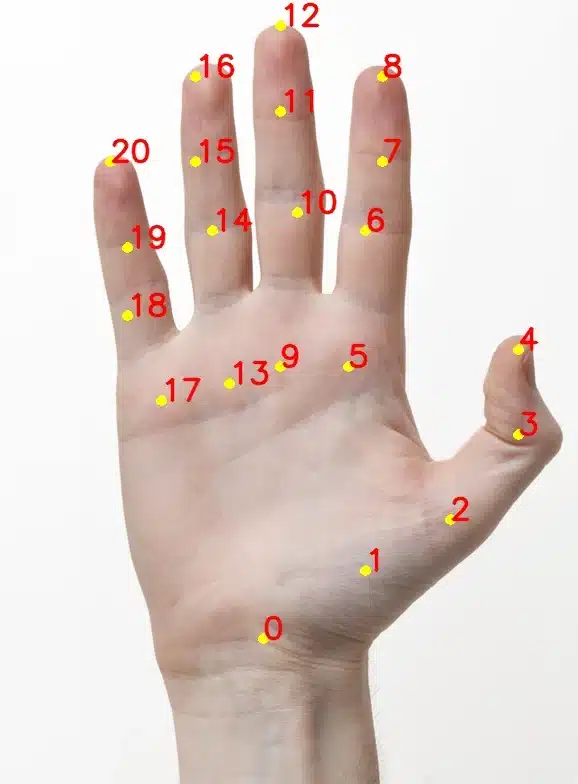

Function Definition: gethandposition(parameter = 1, landmark_number = 4)
| Name | Type | Description | Expected Values | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| parameter | int | The parameter value: 1 for X value 2 for Y value | 1, and 2 | 1 |
| landmark_number | int | The landmark number for which the value is required. | 0-20 | 4 |
This function returns the specified parameter of the hand landmark detected:

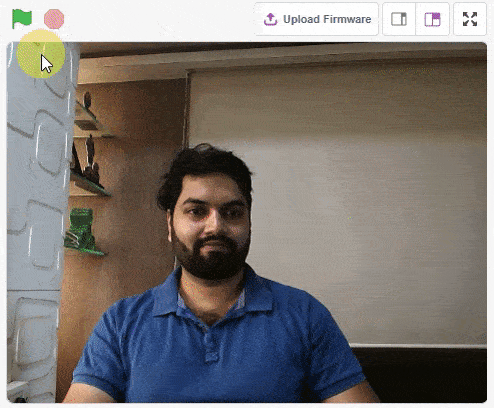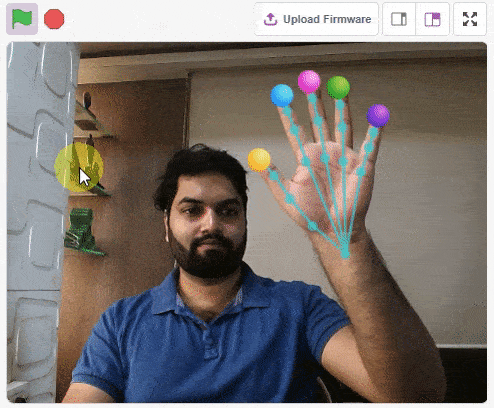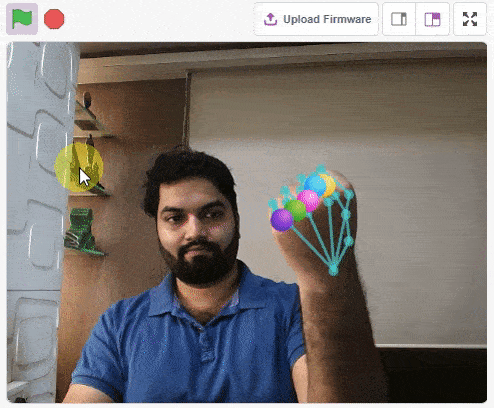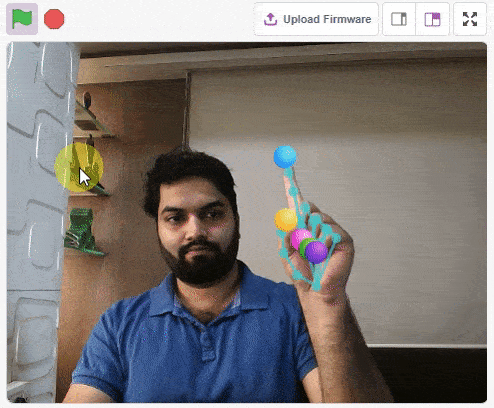
thumb = Sprite('Thumb')
index = Sprite('Index')
middle = Sprite('Middle')
ring = Sprite('Ring')
pinky = Sprite('Pinky')
hand = Posenet()
hand.video("on", 0)
hand.enablebox()
thumb.switchcostume("ball-a")
thumb.setsize(50)
index.switchcostume("ball-b")
index.setsize(50)
middle.switchcostume("ball-c")
middle.setsize(50)
ring.switchcostume("ball-d")
ring.setsize(50)
pinky.switchcostume("ball-e")
pinky.setsize(50)
while True:
hand.analysehand()
if hand.ishanddetected():
thumb.setx(hand.gethandposition(1, 4))
thumb.sety(hand.gethandposition(2, 4))
thumb.show()
index.setx(hand.gethandposition(1, 8))
index.sety(hand.gethandposition(2, 8))
index.show()
middle.setx(hand.gethandposition(1, 12))
middle.sety(hand.gethandposition(2, 12))
middle.show()
ring.setx(hand.gethandposition(1, 16))
ring.sety(hand.gethandposition(2, 16))
ring.show()
pinky.setx(hand.gethandposition(1, 20))
pinky.sety(hand.gethandposition(2, 20))
pinky.show()
else:
thumb.hide()
index.hide()
middle.hide()
ring.hide()
pinky.hide()

This project demonstrates how to use Machine Learning Environment to make a machine–learning model that identifies the hand gestures and makes the Mecanum move accordingly.
We are going to use the Hand Classifier of the Machine Learning Environment. The model works by analyzing your hand position with the help of 21 data points. We will add in total 8 different classes to operate the different motions of the Mecanum Robot with the help of the ML Environment of the Pictoblox Software.
Follow the steps below:

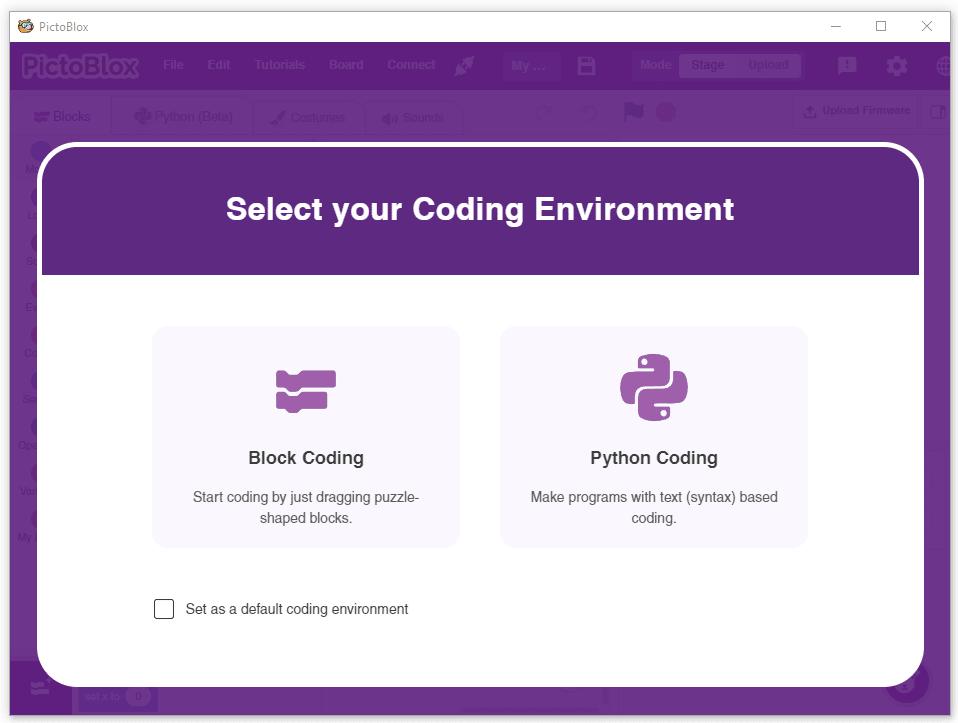

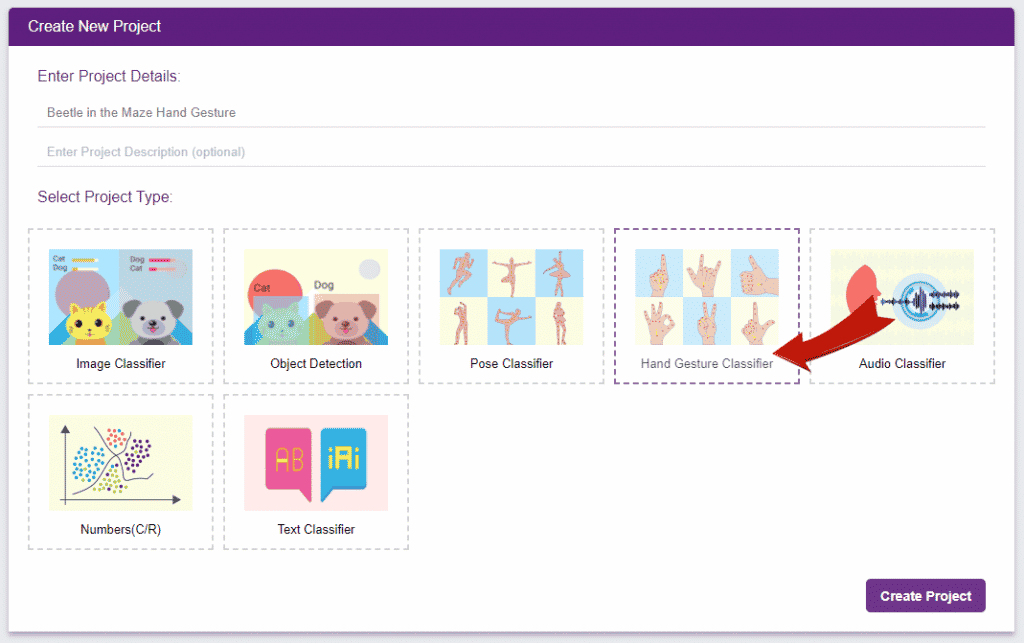
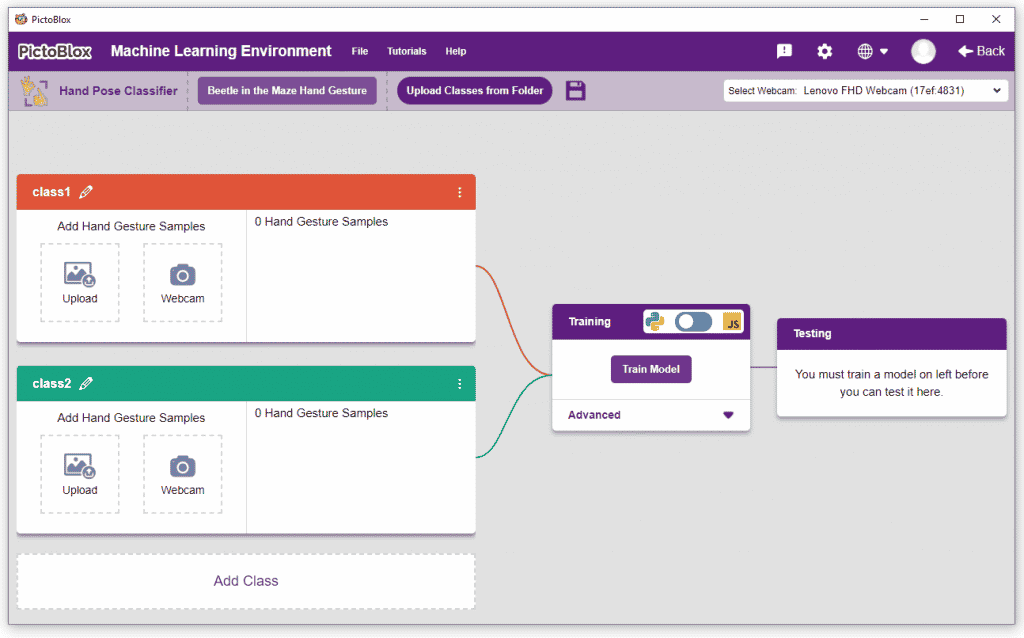
There are 2 things that you have to provide in a class:


You can perform the following operations to manipulate the data into a class.
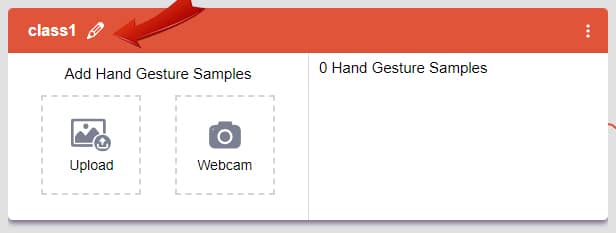
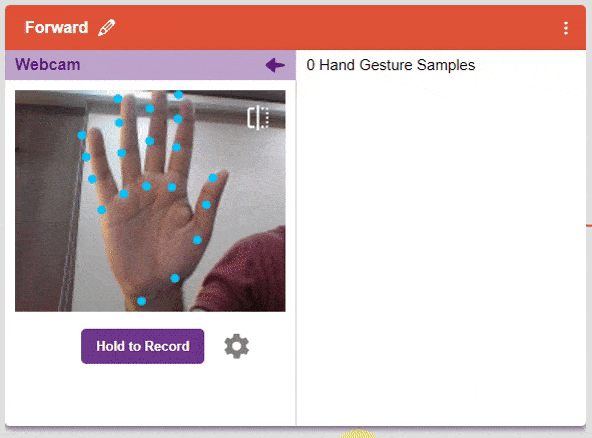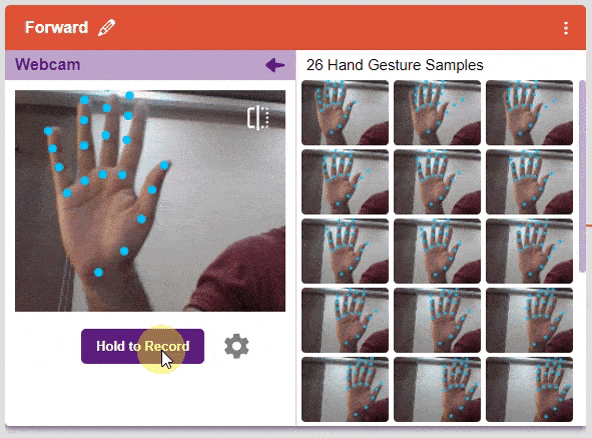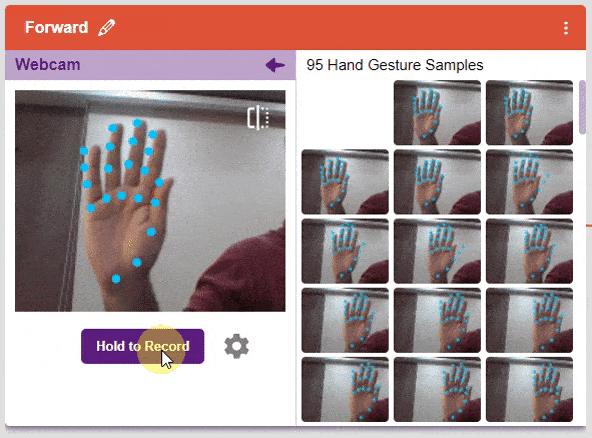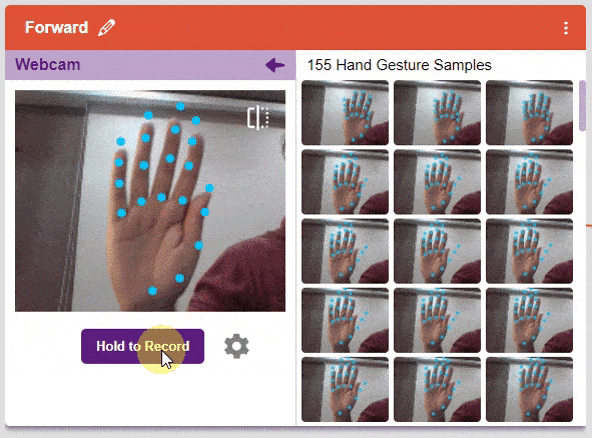

After data is added, it’s fit to be used in model training. In order to do this, we have to train the model. By training the model, we extract meaningful information from the hand pose, and that in turn updates the weights. Once these weights are saved, we can use our model to make predictions on data previously unseen.

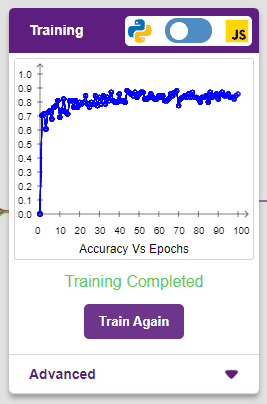
The accuracy of the model should increase over time. The x-axis of the graph shows the epochs, and the y-axis represents the accuracy at the corresponding epoch. Remember, the higher the reading in the accuracy graph, the better the model. The range of the accuracy is 0 to 1.
To test the model, simply enter the input values in the “Testing” panel and click on the “Predict” button.
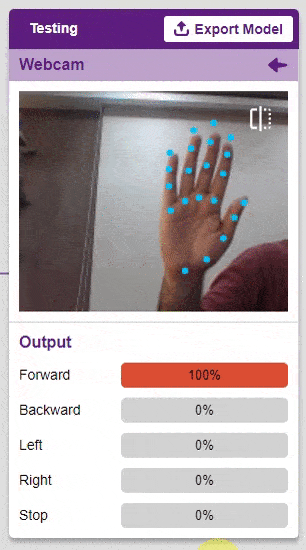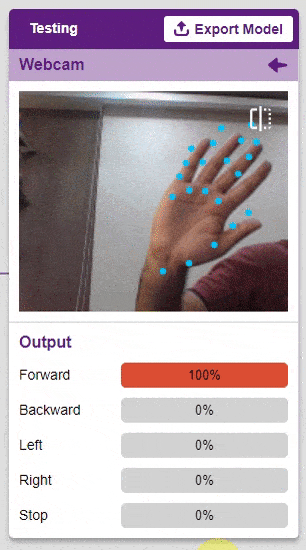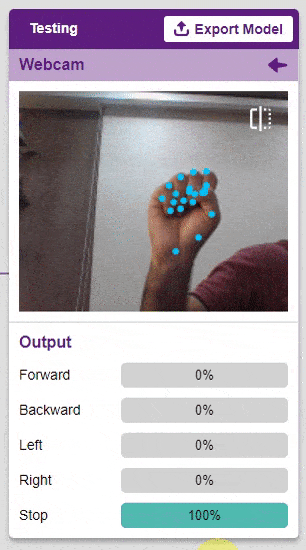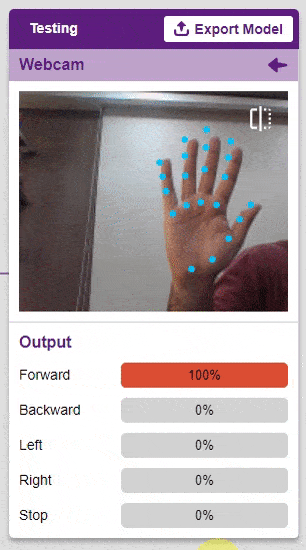
The model will return the probability of the input belonging to the classes.
Click on the “Export Model” button on the top right of the Testing box, and PictoBlox will load your model into the Python Coding Environment if you have opened the ML Environment in the Python Coding.
The mecanum will move according to the following logic:
The following code appears in the Python Editor of the selected sprite.
####################imports####################
# Do not change
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import time
# Do not change
####################imports####################
#Following are the model and video capture configurations
# Do not change
model=tf.keras.models.load_model(
"num_model.h5",
custom_objects=None,
compile=True,
options=None)
pose = Posenet() # Initializing Posenet
pose.enablebox() # Enabling video capture box
pose.video("on",0) # Taking video input
class_list=['Forward','Backward','Stop','LateralRight','LateralLeft','NormalRight','NormalLeft','CircularMotion'] # List of all the classes
meca=Mecanum(1,2,7,8)
def runmecanum(predicted_class):
if pose.ishanddetected():
if predicted_class=="Forward":
meca.runtimedrobot("forward",100,2)
if predicted_class=="Backward":
meca.runtimedrobot("backward",100,2)
if predicted_class=="Stop":
meca.stoprobot()
if predicted_class=="LateralRight":
meca.runtimedrobot("lateral right",100,2)
if predicted_class=="LateralLeft":
meca.runtimedrobot("lateral left",100,2)
if predicted_class=="NormalRight":
meca.runtimedrobot("circular right",100,1)
if predicted_class=="NormalLeft":
meca.runtimedrobot("circular left",100,1)
if predicted_class=="CircularMotion":
meca.runtimedrobot("lateral arc",100,1)
# Do not change
###############################################
#This is the while loop block, computations happen here
# Do not change
while True:
pose.analysehand() # Using Posenet to analyse hand pose
coordinate_xy=[]
# for loop to iterate through 21 points of recognition
for i in range(21):
if(pose.gethandposition(1,i,0)!="NULL" or pose.gethandposition(2,i,0)!="NULL"):
coordinate_xy.append(int(240+float(pose.gethandposition(1,i,0))))
coordinate_xy.append(int(180-float(pose.gethandposition(2,i,0))))
else:
coordinate_xy.append(0)
coordinate_xy.append(0)
coordinate_xy_tensor = tf.expand_dims(coordinate_xy, 0) # Expanding the dimension of the coordinate list
predict=model.predict(coordinate_xy_tensor) # Making an initial prediction using the model
predict_index=np.argmax(predict[0], axis=0) # Generating index out of the prediction
predicted_class=class_list[predict_index] # Tallying the index with class list
print(predicted_class)
runmecanum(predicted_class)
# Do not changedef runmecanum(predicted_class):
if pose.ishanddetected():
if predicted_class=="Forward":
meca.runtimedrobot("forward",100,2)
if predicted_class=="Backward":
meca.runtimedrobot("backward",100,2)
if predicted_class=="Stop":
meca.stoprobot()
if predicted_class=="LateralRight":
meca.runtimedrobot("lateral right",100,2)
if predicted_class=="LateralLeft":
meca.runtimedrobot("lateral left",100,2)
if predicted_class=="NormalRight":
meca.runtimedrobot("circular right",100,1)
if predicted_class=="NormalLeft":
meca.runtimedrobot("circular left",100,1)
if predicted_class=="CircularMotion":
meca.runtimedrobot("lateral arc",100,1)Forward-Backward Motions:

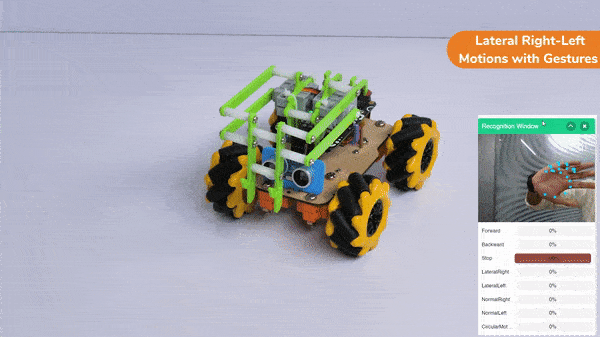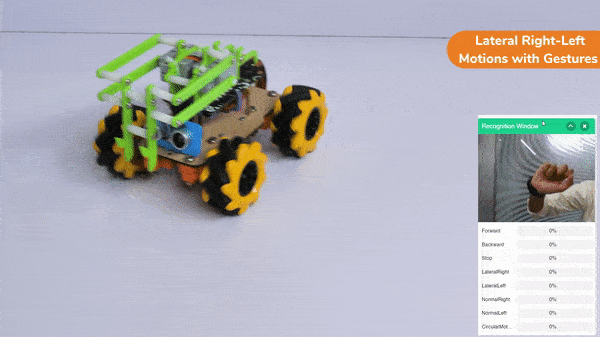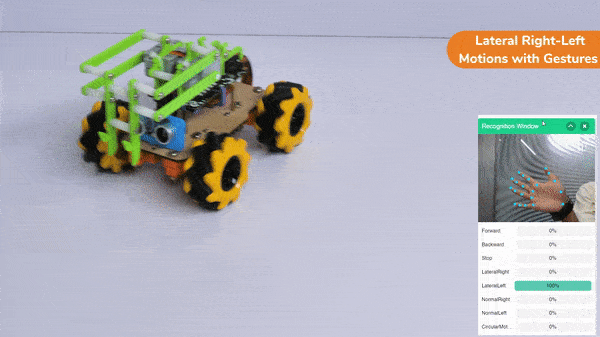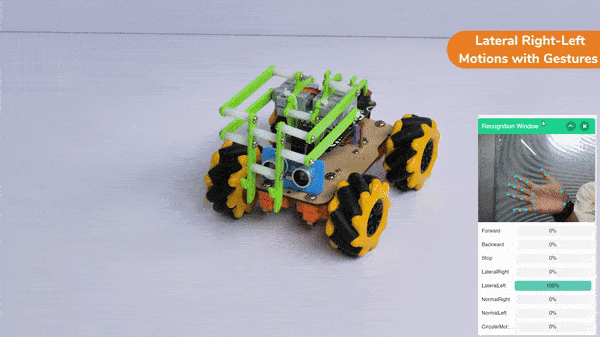
Lateral Right-Left Motions:

Circular Right-Left Motions:
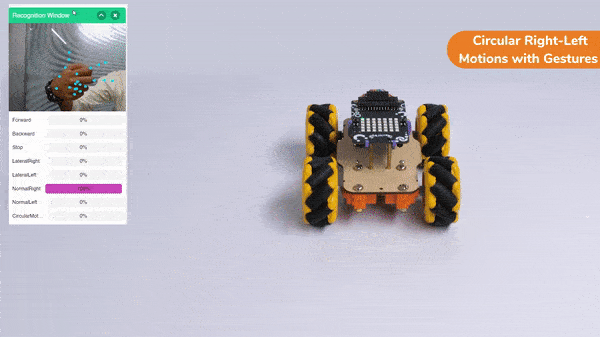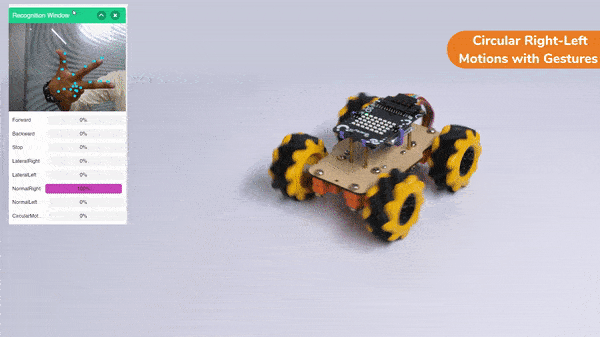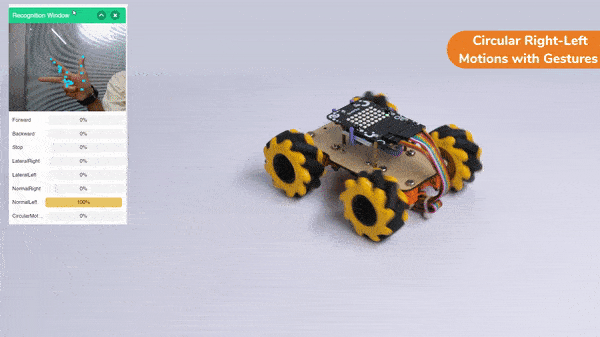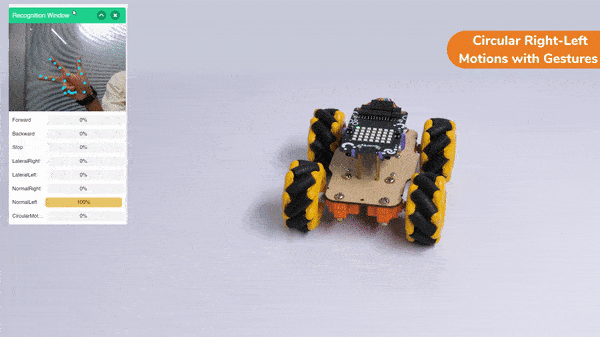
Lateral Arc Motion:

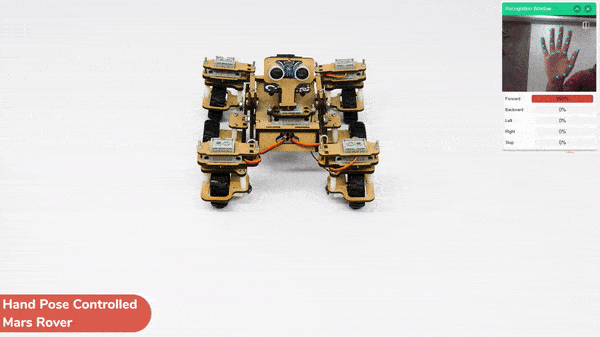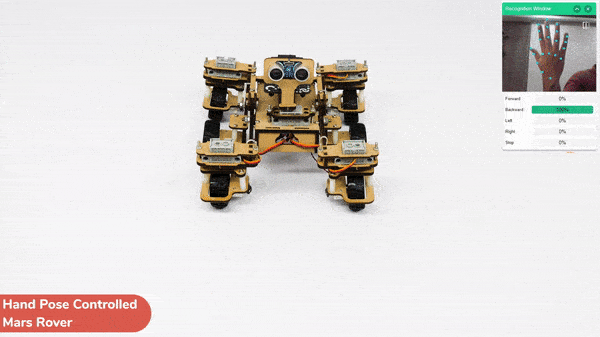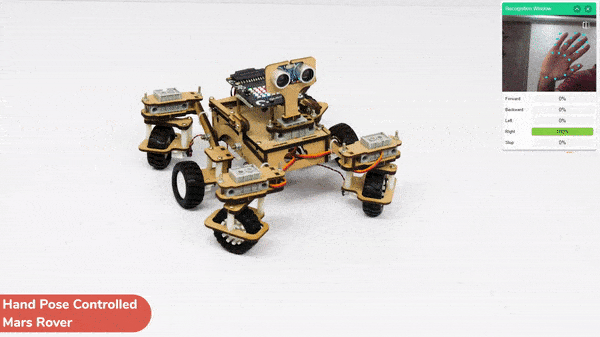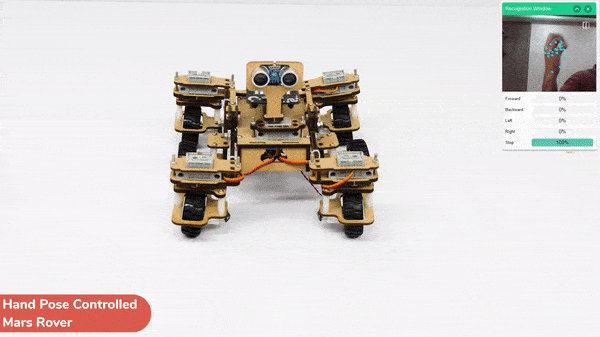
This project demonstrates how to use Machine Learning Environment to make a machine–learning model that identifies hand gestures and makes the Mars Rover move accordingly.
We are going to use the Hand Classifier of the Machine Learning Environment. The model works by analyzing your hand position with the help of 21 data points.
Follow the steps below:





There are 2 things that you have to provide in a class:


You can perform the following operations to manipulate the data into a class.



After data is added, it’s fit to be used in model training. In order to do this, we have to train the model. By training the model, we extract meaningful information from the hand pose, and that in turn updates the weights. Once these weights are saved, we can use our model to make predictions on data previously unseen.

The accuracy of the model should increase over time. The x-axis of the graph shows the epochs, and the y-axis represents the accuracy at the corresponding epoch. Remember, the higher the reading in the accuracy graph, the better the model. The range of the accuracy is 0 to 1.


To test the model, simply enter the input values in the “Testing” panel and click on the “Predict” button.

The model will return the probability of the input belonging to the classes.
Click on the “Export Model” button on the top right of the Testing box, and PictoBlox will load your model into the Python Coding Environment if you have opened the ML Environment in Python Coding.

The following code appears in the Python Editor of the selected sprite.
####################imports####################
# Do not change
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import time
sprite=Sprite('Tobi')
import time
quarky = Quarky()
rover = MarsRover(4, 1, 7, 2, 6)
# Do not change
####################imports####################
#Following are the model and video capture configurations
# Do not change
model=tf.keras.models.load_model(
"num_model.h5",
custom_objects=None,
compile=True,
options=None)
pose = Posenet() # Initializing Posenet
pose.enablebox() # Enabling video capture box
pose.video("on",0) # Taking video input
class_list=['forward','backward','left','right','stop'] # List of all the classes
def runQuarky(predicted_class):
if pose.ishanddetected():
if predicted_class == "forward":
rover.home()
rover.setinangle(0)
quarky.runtimedrobot("F",100,3)
if predicted_class == "backward":
rover.home()
rover.setinangle(0)
quarky.runtimedrobot("B",100,3)
if predicted_class == "left":
rover.home()
rover.setinangle(40)
quarky.runtimedrobot("L",100,3)
if predicted_class == "right":
rover.home()
rover.setinangle(40)
quarky.runtimedrobot("R",100,3)
if predicted_class == "stop":
quarky.stoprobot()
else:
quarky.stoprobot()
# Do not change
###############################################
#This is the while loop block, computations happen here
# Do not change
while True:
pose.analysehand() # Using Posenet to analyse hand pose
coordinate_xy=[]
# for loop to iterate through 21 points of recognition
for i in range(21):
if(pose.gethandposition(1,i,0)!="NULL" or pose.gethandposition(2,i,0)!="NULL"):
coordinate_xy.append(int(240+float(pose.gethandposition(1,i,0))))
coordinate_xy.append(int(180-float(pose.gethandposition(2,i,0))))
else:
coordinate_xy.append(0)
coordinate_xy.append(0)
coordinate_xy_tensor = tf.expand_dims(coordinate_xy, 0) # Expanding the dimension of the coordinate list
predict=model.predict(coordinate_xy_tensor) # Making an initial prediction using the model
predict_index=np.argmax(predict[0], axis=0) # Generating index out of the prediction
predicted_class=class_list[predict_index] # Tallying the index with class list
print(predicted_class)
runQuarky(predicted_class)
# Do not change
def runQuarky(predicted_class):
if pose.ishanddetected():
if predicted_class == "forward":
rover.home()
rover.setinangle(0)
quarky.runtimedrobot("F",100,3)
if predicted_class == "backward":
rover.home()
rover.setinangle(0)
quarky.runtimedrobot("B",100,3)
if predicted_class == "left":
rover.home()
rover.setinangle(40)
quarky.runtimedrobot("L",100,3)
if predicted_class == "right":
rover.home()
rover.setinangle(40)
quarky.runtimedrobot("R",100,3)
if predicted_class == "stop":
quarky.stoprobot()
else:
quarky.stoprobot()

In this activity, we will try to create a new Machine Learning model that will be able to identify and detect different types of hand poses and that can help us to control the Mecanum Gripper Robot. This activity can be quite fun and by knowing the process, you can develop your own customized hand pose classifier model easily!
We will use the same model that we have created in the previous Hand Pose Controlled Mecanum model to avoid any misdirection and confusion.
Note: You can always create your own model and use it to perform any type of functions as per your choice. This example proves the same point and helps you understand well the concept of Machine Learning models and environment.
Follow the steps below:



There are 2 things that you have to provide in a class:


You can perform the following operations to manipulate the data into a class.



After data is added, it’s fit to be used in model training. In order to do this, we have to train the model. By training the model, we extract meaningful information from the hand pose, and that in turn updates the weights. Once these weights are saved, we can use our model to make predictions on data previously unseen.

The accuracy of the model should increase over time. The x-axis of the graph shows the epochs, and the y-axis represents the accuracy at the corresponding epoch. Remember, the higher the reading in the accuracy graph, the better the model. The range of the accuracy is 0 to 1.


To test the model, simply enter the input values in the “Testing” panel and click on the “Predict” button.

The model will return the probability of the input belonging to the classes.
Click on the “Export Model” button on the top right of the Testing box, and PictoBlox will load your model into the Python Coding Environment if you have opened the ML Environment in the Python Coding.

The mecanum will move according to the following logic:
Logical Code:
meca=Mecanum(1,2,7,8)
meca.initialisegripper(5)
meca.setcloseangle(90)
meca.setopenangle(0)
def runmecanum(predicted_class):
if pose.ishanddetected():
if predicted_class=="Forward":
meca.runtimedrobot("forward",100,2)
if predicted_class=="Backward":
meca.runtimedrobot("backward",100,2)
if predicted_class=="Stop":
meca.closearm()
if predicted_class=="LateralRight":
meca.runtimedrobot("lateral right",100,2)
if predicted_class=="LateralLeft":
meca.runtimedrobot("lateral left",100,2)
if predicted_class=="NormalRight":
meca.runtimedrobot("circular right",100,1)
if predicted_class=="NormalLeft":
meca.runtimedrobot("circular left",100,1)
if predicted_class=="CircularMotion":
meca.openarm()Final Code
####################imports####################
# Do not change
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import time
# Do not change
####################imports####################
#Following are the model and video capture configurations
# Do not change
model=tf.keras.models.load_model(
"num_model.h5",
custom_objects=None,
compile=True,
options=None)
pose = Posenet() # Initializing Posenet
pose.enablebox() # Enabling video capture box
pose.video("on",0) # Taking video input
class_list=['Forward','Backward','Stop','LateralRight','LateralLeft','NormalRight','NormalLeft','CircularMotion'] # List of all the classes
meca=Mecanum(1,2,7,8)
meca.initialisegripper(5)
meca.setcloseangle(90)
meca.setopenangle(0)
def runmecanum(predicted_class):
if pose.ishanddetected():
if predicted_class=="Forward":
meca.runtimedrobot("forward",100,2)
if predicted_class=="Backward":
meca.runtimedrobot("backward",100,2)
if predicted_class=="Stop":
meca.closearm()
if predicted_class=="LateralRight":
meca.runtimedrobot("lateral right",100,2)
if predicted_class=="LateralLeft":
meca.runtimedrobot("lateral left",100,2)
if predicted_class=="NormalRight":
meca.runtimedrobot("circular right",100,1)
if predicted_class=="NormalLeft":
meca.runtimedrobot("circular left",100,1)
if predicted_class=="CircularMotion":
meca.openarm()
# Do not change
###############################################
#This is the while loop block, computations happen here
# Do not change
while True:
pose.analysehand() # Using Posenet to analyse hand pose
coordinate_xy=[]
# for loop to iterate through 21 points of recognition
for i in range(21):
if(pose.gethandposition(1,i,0)!="NULL" or pose.gethandposition(2,i,0)!="NULL"):
coordinate_xy.append(int(240+float(pose.gethandposition(1,i,0))))
coordinate_xy.append(int(180-float(pose.gethandposition(2,i,0))))
else:
coordinate_xy.append(0)
coordinate_xy.append(0)
coordinate_xy_tensor = tf.expand_dims(coordinate_xy, 0) # Expanding the dimension of the coordinate list
predict=model.predict(coordinate_xy_tensor) # Making an initial prediction using the model
predict_index=np.argmax(predict[0], axis=0) # Generating index out of the prediction
predicted_class=class_list[predict_index] # Tallying the index with class list
print(predicted_class)
runmecanum(predicted_class)
# Do not change
Forward-Backward Motion:
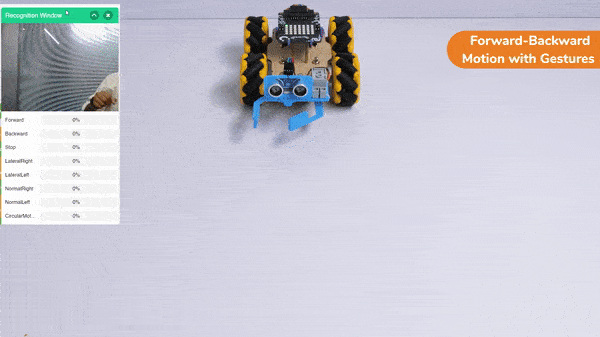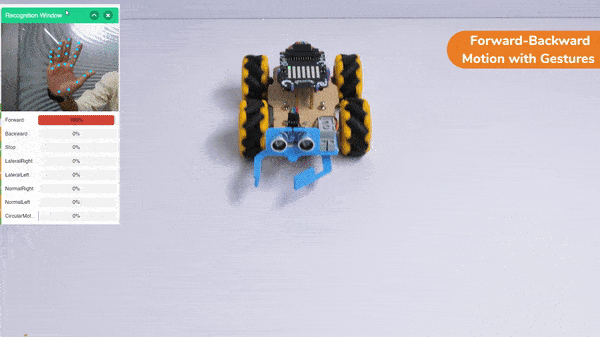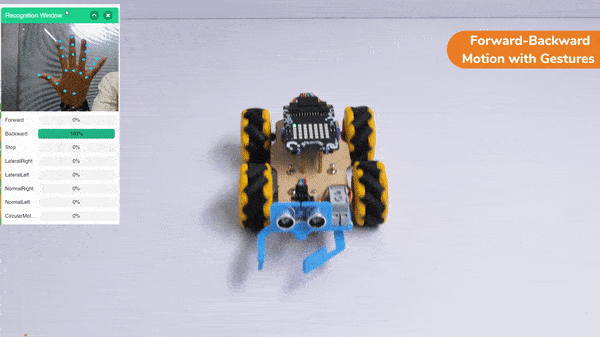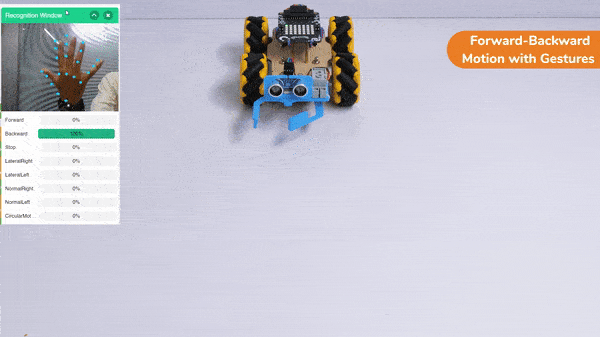
Circular Right-Left Motion:
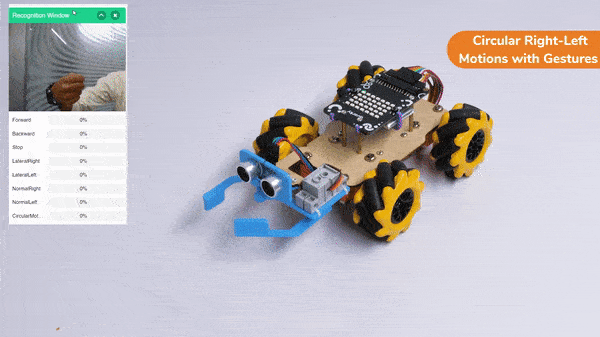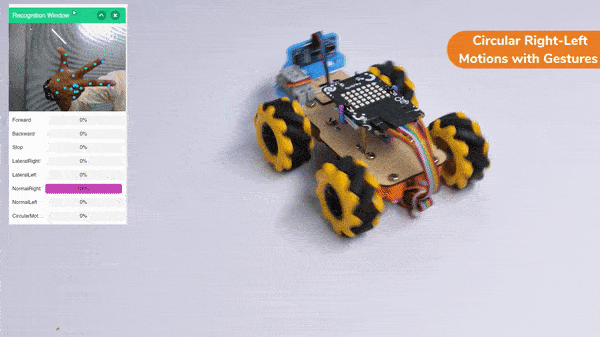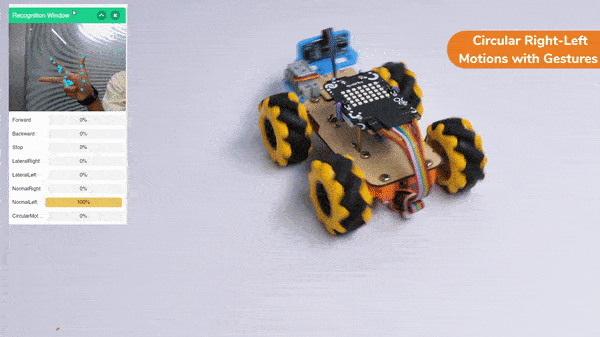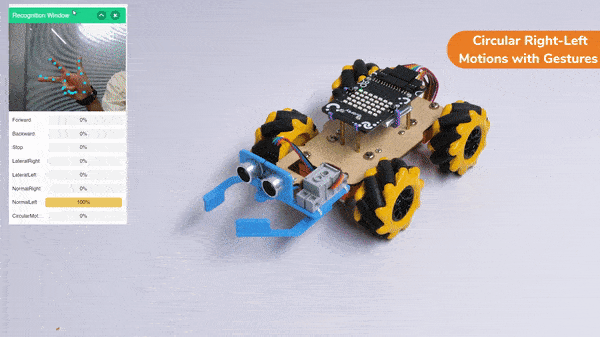
Lateral Right-Left Motions:
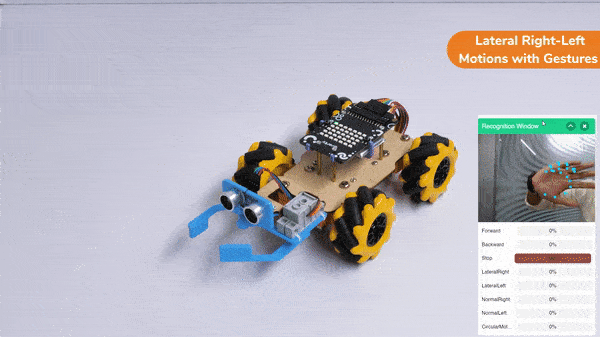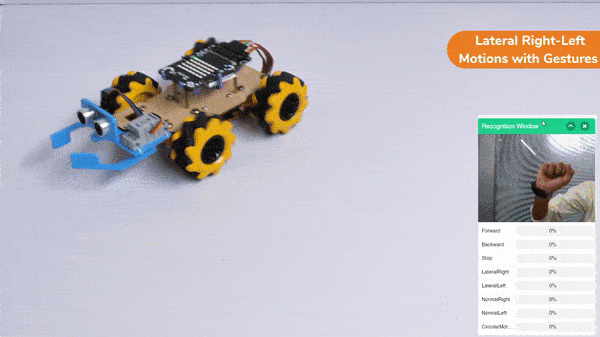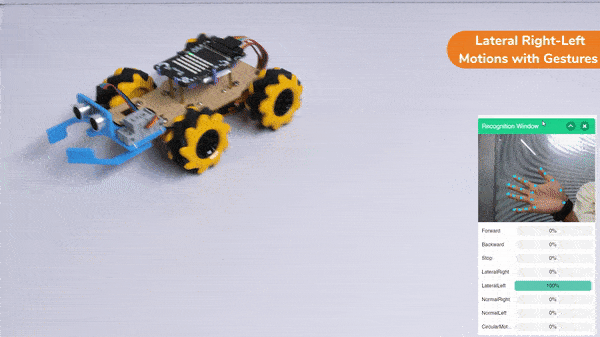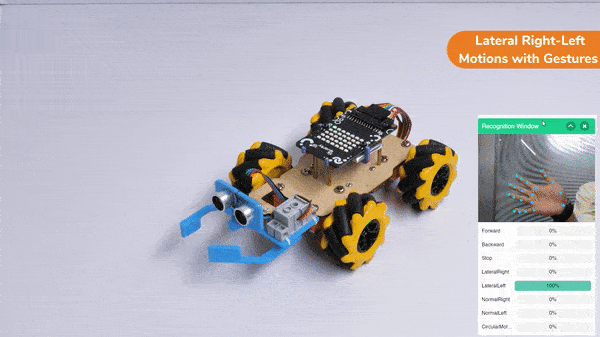
Gripper Mechanism with Hand Gestures:

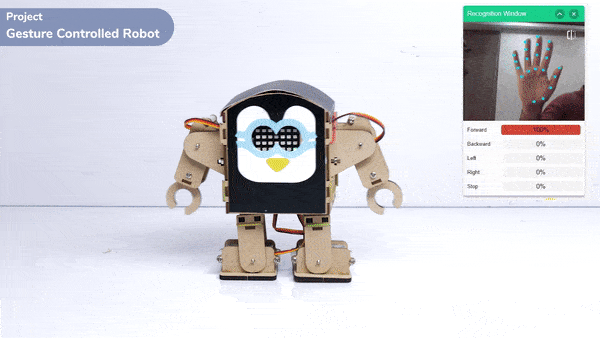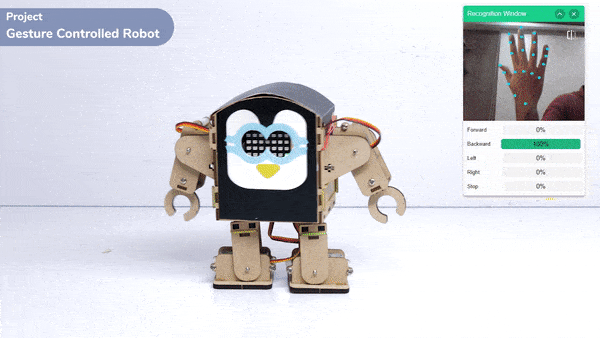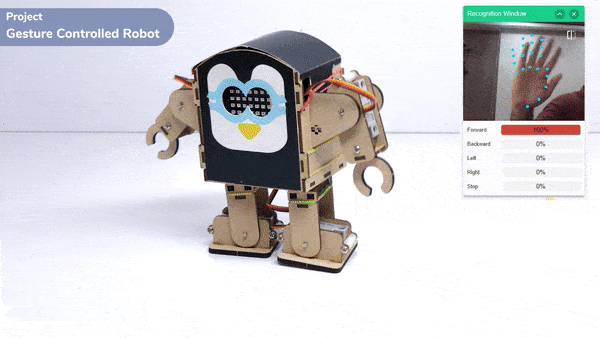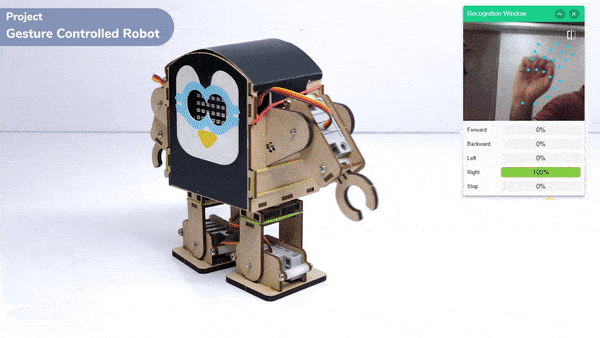
This project demonstrates how to use Machine Learning Environment to make a machine–learning model that identifies hand gestures and makes the humanoid move accordingly.
We are going to use the Hand Classifier of the Machine Learning Environment. The model works by analyzing your hand position with the help of 21 data points.
Follow the steps below:



There are 2 things that you have to provide in a class:


You can perform the following operations to manipulate the data into a class.



After data is added, it’s fit to be used in model training. In order to do this, we have to train the model. By training the model, we extract meaningful information from the hand pose, and that in turn updates the weights. Once these weights are saved, we can use our model to make predictions on data previously unseen.

The accuracy of the model should increase over time. The x-axis of the graph shows the epochs, and the y-axis represents the accuracy at the corresponding epoch. Remember, the higher the reading in the accuracy graph, the better the model. The range of the accuracy is 0 to 1.


To test the model, simply enter the input values in the “Testing” panel and click on the “Predict” button.

The model will return the probability of the input belonging to the classes.
Click on the “Export Model” button on the top right of the Testing box, and PictoBlox will load your model into the Python Coding Environment if you have opened the ML Environment in Python Coding.

The following code appears in the Python Editor of the selected sprite.
####################imports####################
# Do not change
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
sprite=Sprite('Tobi')
import time
quarky = Quarky()
import time
humanoid = Humanoid(7, 2, 6, 3, 8, 1)
# Do not change
####################imports####################
#Following are the model and video capture configurations
# Do not change
model=tf.keras.models.load_model(
"num_model.h5",
custom_objects=None,
compile=True,
options=None)
pose = Posenet() # Initializing Posenet
pose.enablebox() # Enabling video capture box
pose.video("on",0) # Taking video input
class_list=['forward','backward','left','right','stop'] # List of all the classes
def runQuarky(predicted_class):
if pose.ishanddetected():
if predicted_class == "forward":
humanoid.move("forward", 1000, 1)
if predicted_class == "backward":
humanoid.move("backward", 1000, 1)
if predicted_class == "left":
humanoid.move("left", 1000, 1)
if predicted_class == "right":
humanoid.move("right", 1000, 1)
if predicted_class == "stop":
humanoid.home()
else:
quarky.stoprobot()
# Do not change
###############################################
#This is the while loop block, computations happen here
# Do not change
while True:
pose.analysehand() # Using Posenet to analyse hand pose
coordinate_xy=[]
# for loop to iterate through 21 points of recognition
for i in range(21):
if(pose.gethandposition(1,i,0)!="NULL" or pose.gethandposition(2,i,0)!="NULL"):
coordinate_xy.append(int(240+float(pose.gethandposition(1,i,0))))
coordinate_xy.append(int(180-float(pose.gethandposition(2,i,0))))
else:
coordinate_xy.append(0)
coordinate_xy.append(0)
coordinate_xy_tensor = tf.expand_dims(coordinate_xy, 0) # Expanding the dimension of the coordinate list
predict=model.predict(coordinate_xy_tensor) # Making an initial prediction using the model
predict_index=np.argmax(predict[0], axis=0) # Generating index out of the prediction
predicted_class=class_list[predict_index] # Tallying the index with class list
print(predicted_class)
runQuarky(predicted_class)

if pose.ishanddetected():
if predicted_class == "forward":
humanoid.move("forward", 1000, 1)
if predicted_class == "backward":
humanoid.move("backward", 1000, 1)
if predicted_class == "left":
humanoid.move("left", 1000, 1)
if predicted_class == "right":
humanoid.move("right", 1000, 1)
if predicted_class == "stop":
humanoid.home()
else:
quarky.stoprobot()
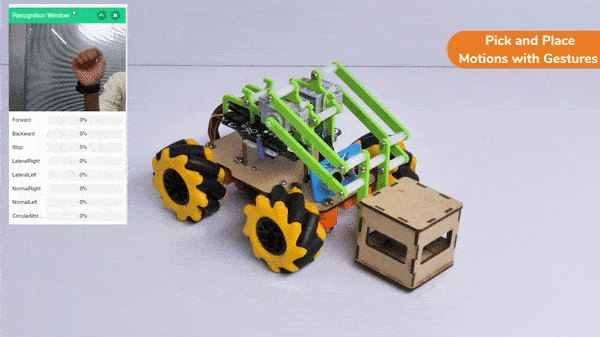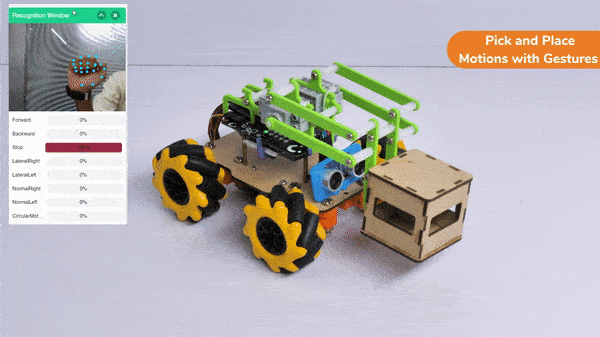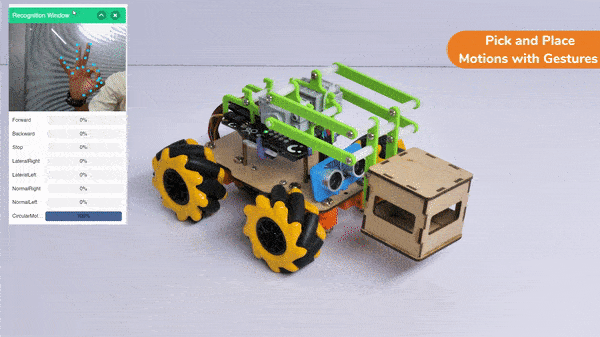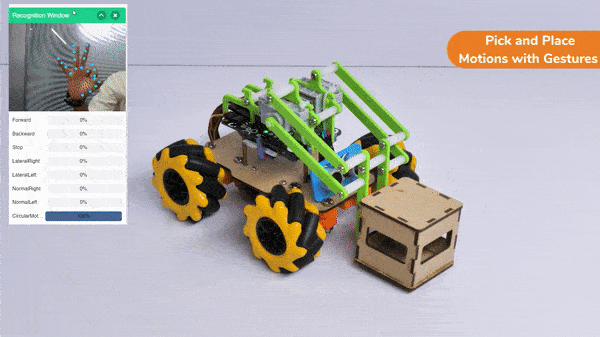
In this activity, we will try to create a new Machine Learning model that will be able to identify and detect different types of hand poses and that can help us to control the Mecanum Pick and Place Robot. This activity can be quite fun and by knowing the process, you can develop your own customized hand pose classifier model easily!
We will use the same model that we have created in the previous Hand Pose Controlled Mecanum model to avoid any misdirection and confusion.
Note: You can always create your own model and use it to perform any type of functions as per your choice. This example proves the same point and helps you understand well the concept of Machine Learning models and environment.
Follow the steps below:





There are 2 things that you have to provide in a class:


You can perform the following operations to manipulate the data into a class.



After data is added, it’s fit to be used in model training. In order to do this, we have to train the model. By training the model, we extract meaningful information from the hand pose, and that in turn updates the weights. Once these weights are saved, we can use our model to make predictions on data previously unseen.

The accuracy of the model should increase over time. The x-axis of the graph shows the epochs, and the y-axis represents the accuracy at the corresponding epoch. Remember, the higher the reading in the accuracy graph, the better the model. The range of the accuracy is 0 to 1.


To test the model, simply enter the input values in the “Testing” panel and click on the “Predict” button.

The model will return the probability of the input belonging to the classes.
Click on the “Export Model” button on the top right of the Testing box, and PictoBlox will load your model into the Python Coding Environment if you have opened the ML Environment in the Python Coding.

The mecanum will move according to the following logic:
Logical Code
meca=Mecanum(1,2,7,8)
meca.initialisepickplace(5,4)
meca.setpickangle(40)
meca.setarmangle(90)
def runmecanum(predicted_class):
if pose.ishanddetected():
if predicted_class=="Forward":
meca.runtimedrobot("forward",100,2)
if predicted_class=="Backward":
meca.runtimedrobot("backward",100,2)
if predicted_class=="Stop":
meca.pick()
if predicted_class=="LateralRight":
meca.runtimedrobot("lateral right",100,2)
if predicted_class=="LateralLeft":
meca.runtimedrobot("lateral left",100,2)
if predicted_class=="NormalRight":
meca.runtimedrobot("circular right",100,1)
if predicted_class=="NormalLeft":
meca.runtimedrobot("circular left",100,1)
if predicted_class=="CircularMotion":
meca.place()Final Code
####################imports####################
# Do not change
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import time
# Do not change
####################imports####################
#Following are the model and video capture configurations
# Do not change
model=tf.keras.models.load_model(
"num_model.h5",
custom_objects=None,
compile=True,
options=None)
pose = Posenet() # Initializing Posenet
pose.enablebox() # Enabling video capture box
pose.video("on",0) # Taking video input
class_list=['Forward','Backward','Stop','LateralRight','LateralLeft','NormalRight','NormalLeft','CircularMotion'] # List of all the classes
meca=Mecanum(1,2,7,8)
meca.initialisepickplace(5,4)
meca.setpickangle(40)
meca.setarmangle(90)
def runmecanum(predicted_class):
if pose.ishanddetected():
if predicted_class=="Forward":
meca.runtimedrobot("forward",100,2)
if predicted_class=="Backward":
meca.runtimedrobot("backward",100,2)
if predicted_class=="Stop":
meca.pick()
if predicted_class=="LateralRight":
meca.runtimedrobot("lateral right",100,2)
if predicted_class=="LateralLeft":
meca.runtimedrobot("lateral left",100,2)
if predicted_class=="NormalRight":
meca.runtimedrobot("circular right",100,1)
if predicted_class=="NormalLeft":
meca.runtimedrobot("circular left",100,1)
if predicted_class=="CircularMotion":
meca.place()
# Do not change
###############################################
#This is the while loop block, computations happen here
# Do not change
while True:
pose.analysehand() # Using Posenet to analyse hand pose
coordinate_xy=[]
# for loop to iterate through 21 points of recognition
for i in range(21):
if(pose.gethandposition(1,i,0)!="NULL" or pose.gethandposition(2,i,0)!="NULL"):
coordinate_xy.append(int(240+float(pose.gethandposition(1,i,0))))
coordinate_xy.append(int(180-float(pose.gethandposition(2,i,0))))
else:
coordinate_xy.append(0)
coordinate_xy.append(0)
coordinate_xy_tensor = tf.expand_dims(coordinate_xy, 0) # Expanding the dimension of the coordinate list
predict=model.predict(coordinate_xy_tensor) # Making an initial prediction using the model
predict_index=np.argmax(predict[0], axis=0) # Generating index out of the prediction
predicted_class=class_list[predict_index] # Tallying the index with class list
print(predicted_class)
runmecanum(predicted_class)
# Do not change
Forward-Backward Motion:
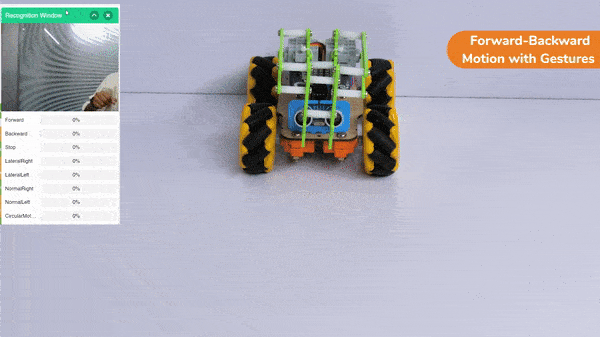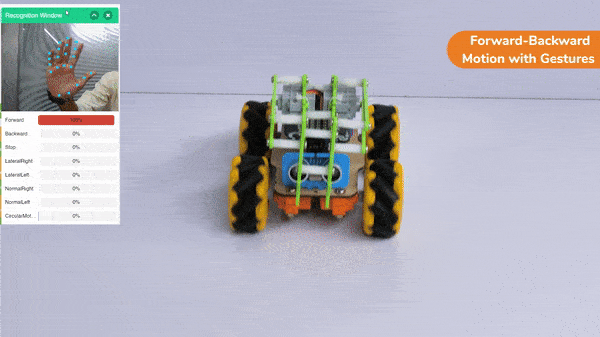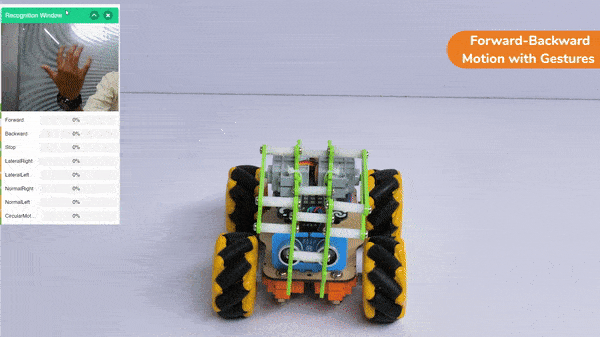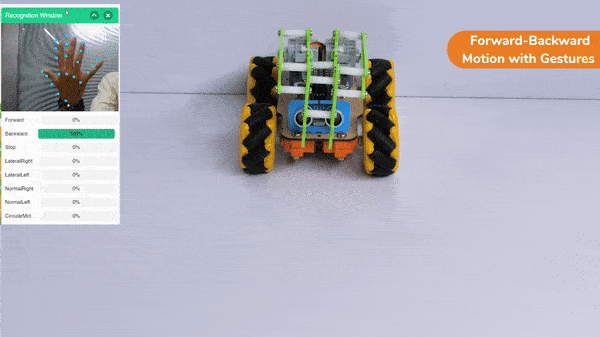
Circular Right-Left Motion:
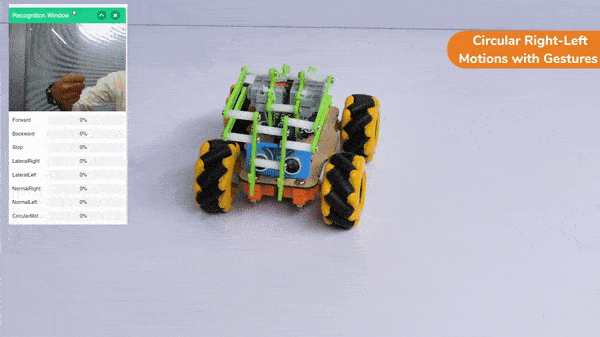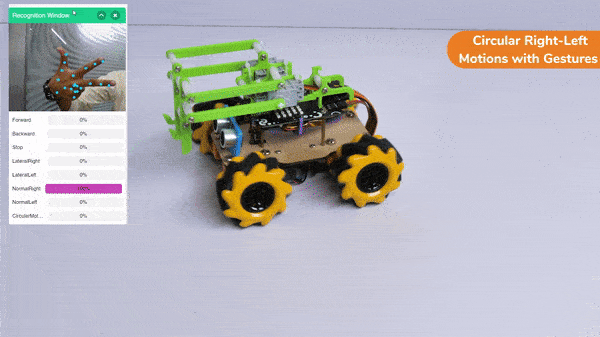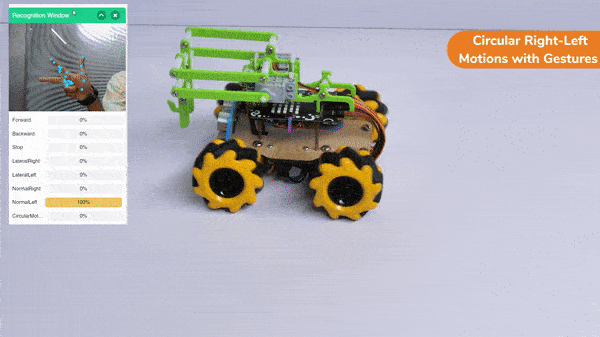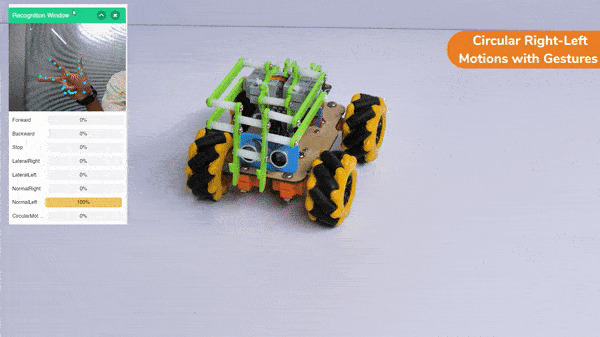
Lateral Right-Left Motion:
Pick and Place Mechanism with Hand Pose:


Copyright 2025 – Agilo Research Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved – Terms & Condition | Privacy Policy
