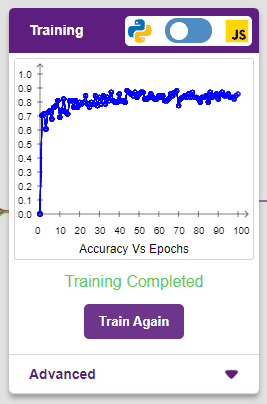
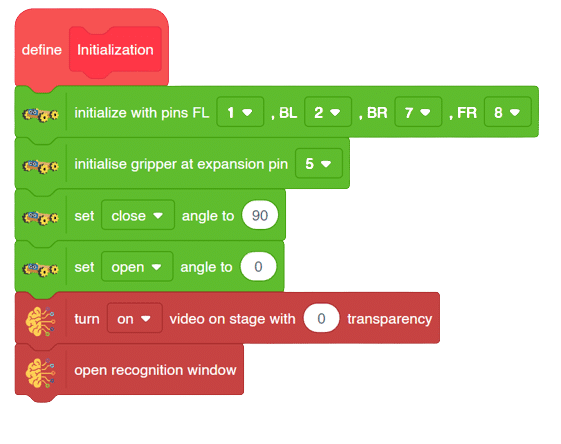
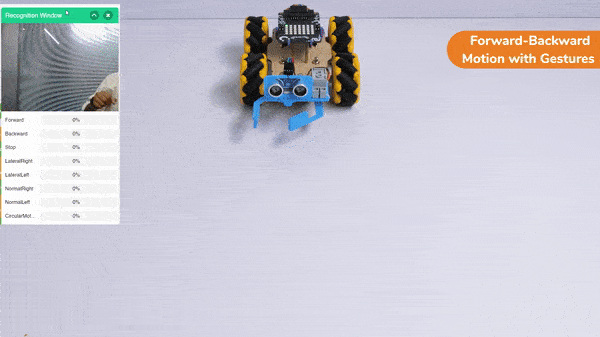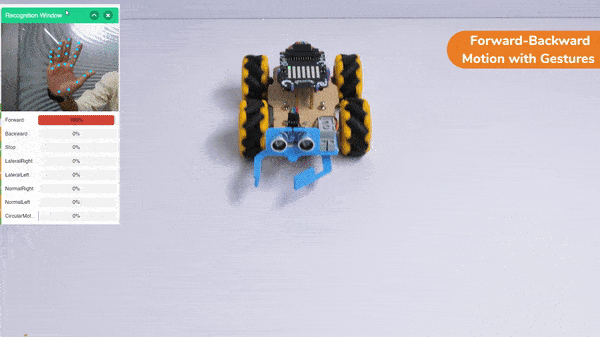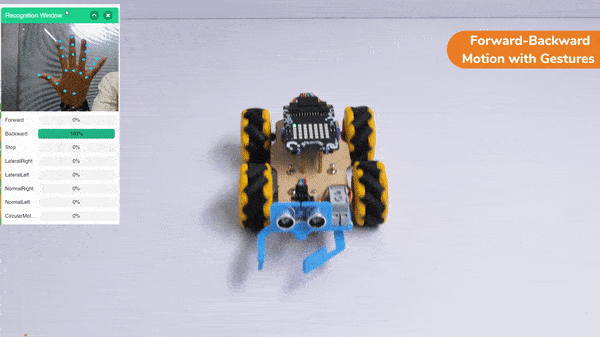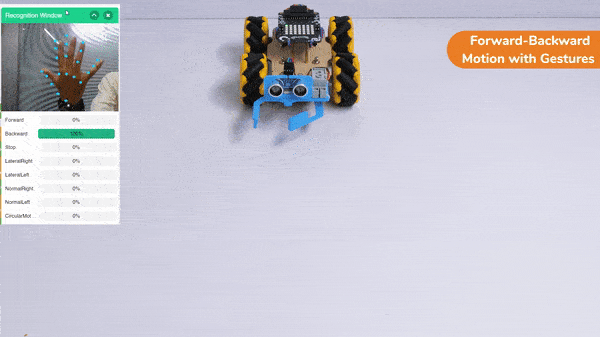
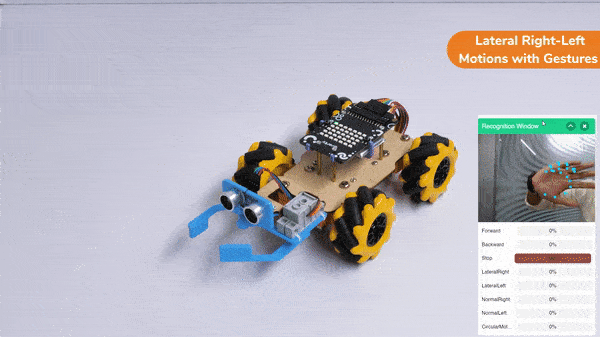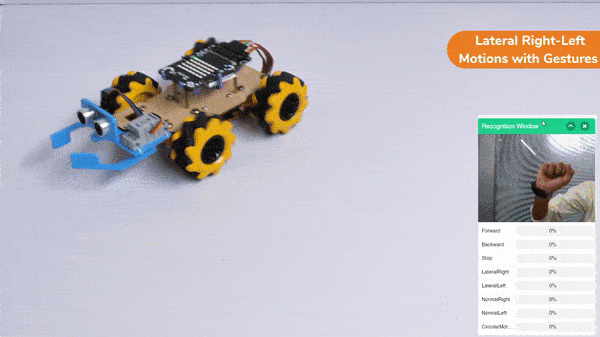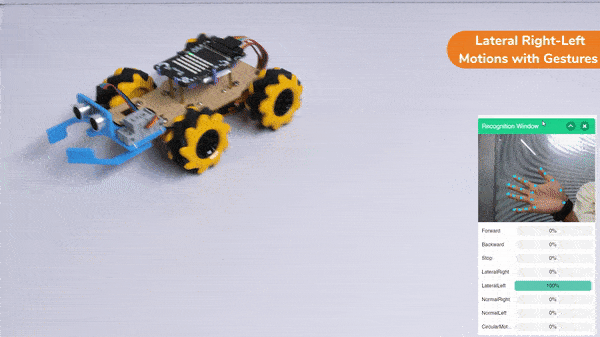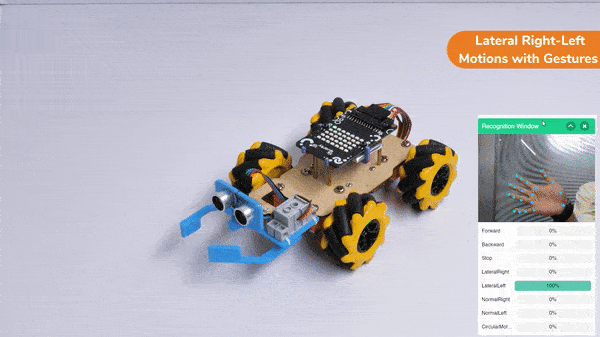
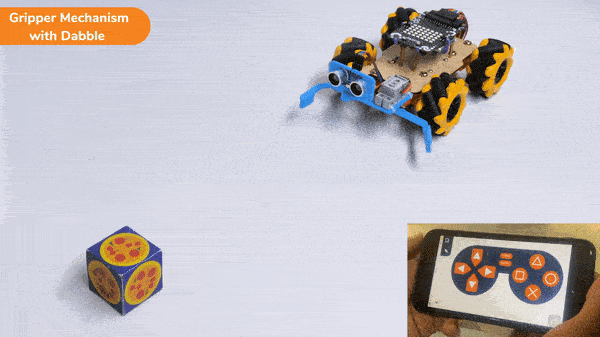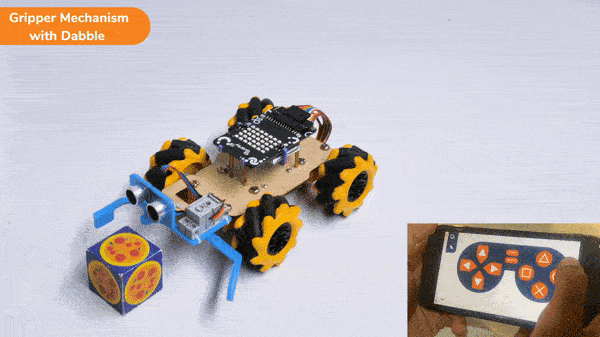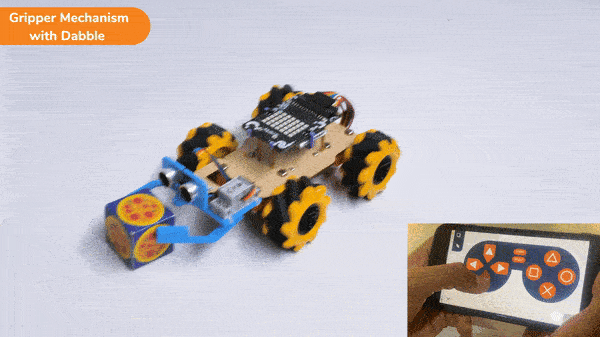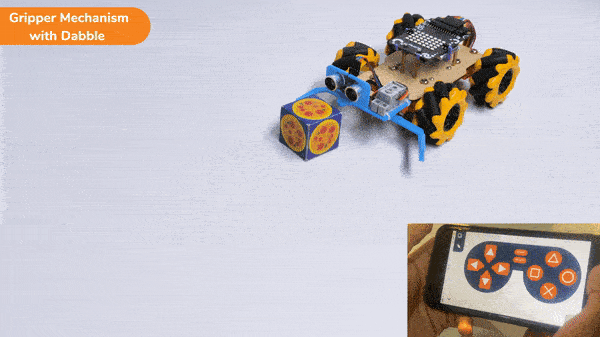
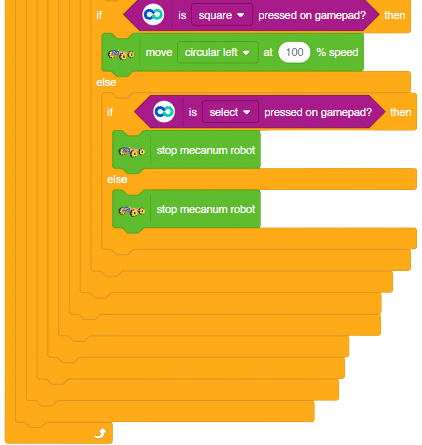
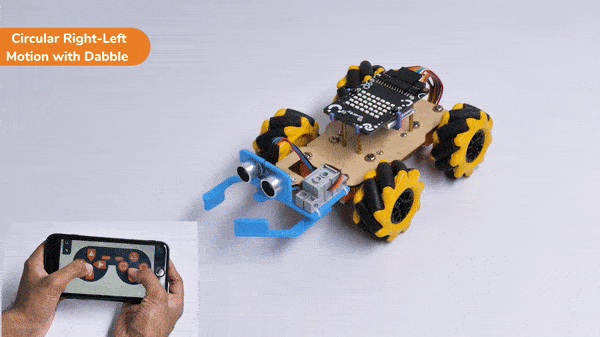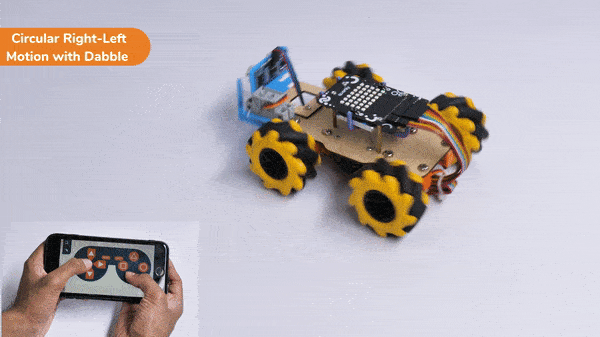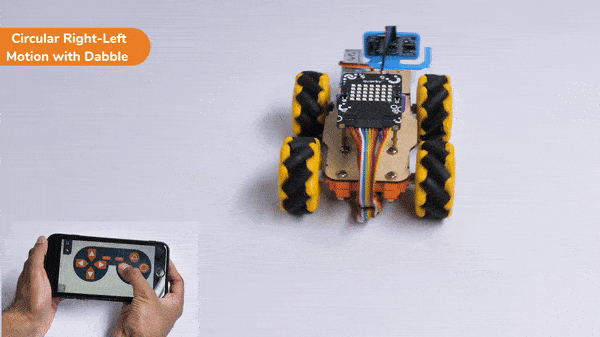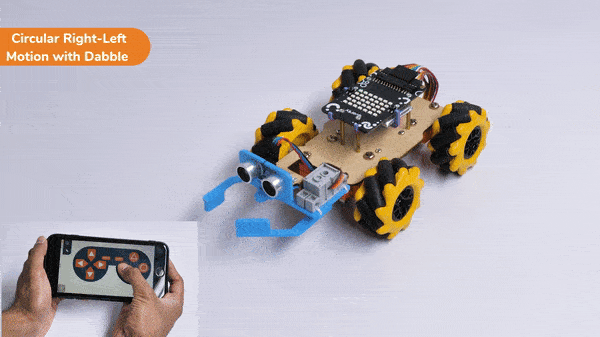
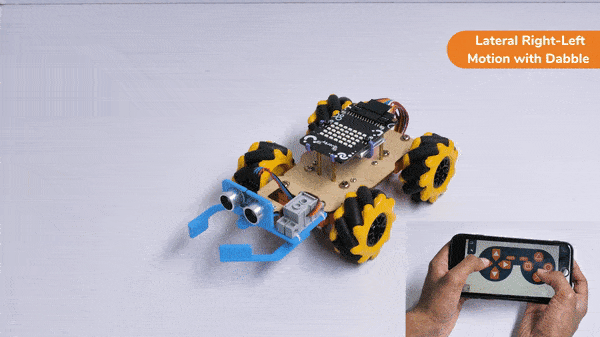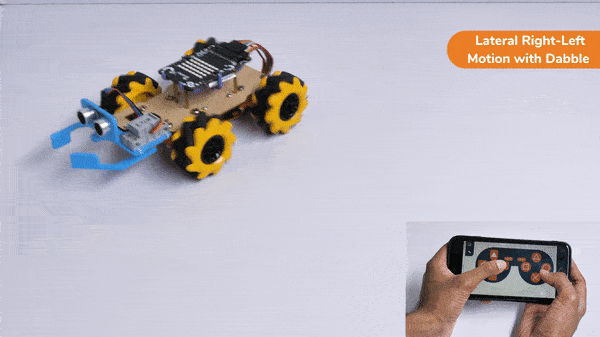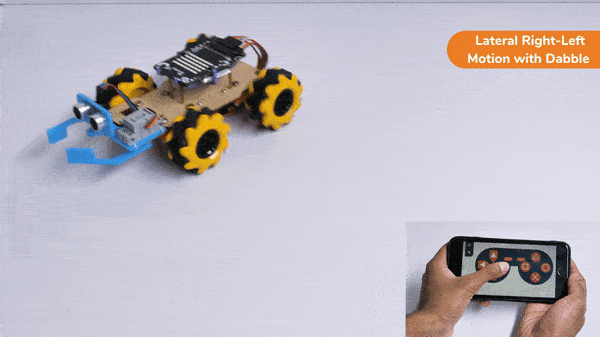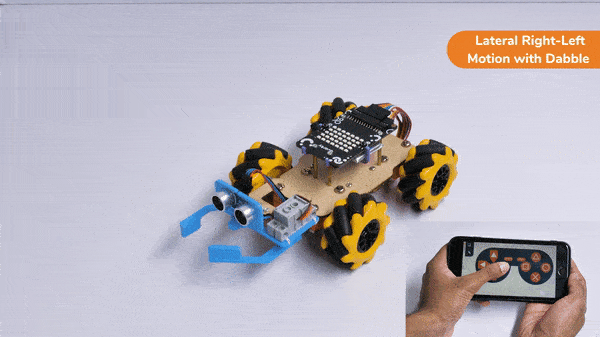
The block sets the Gripper Robot’s gripper servo motor angle for the open or the close position to the specified value.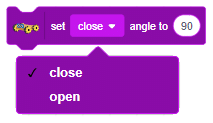
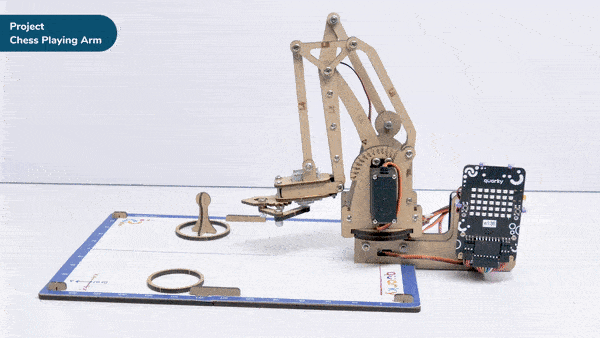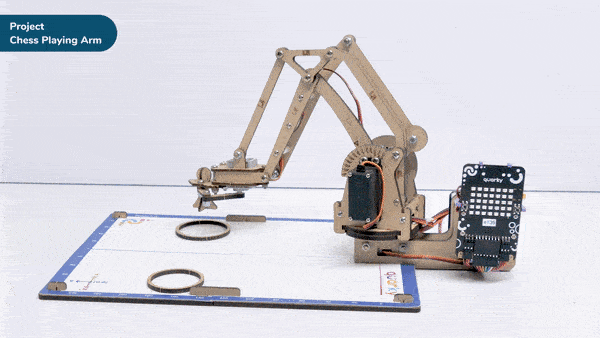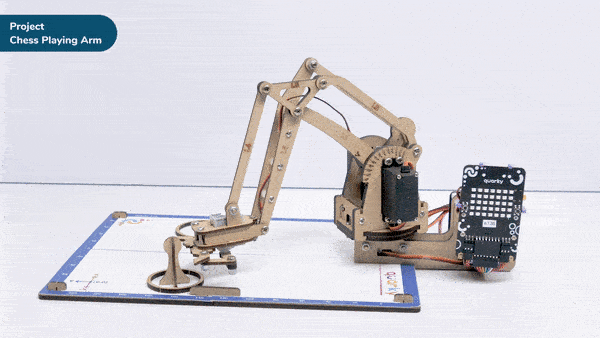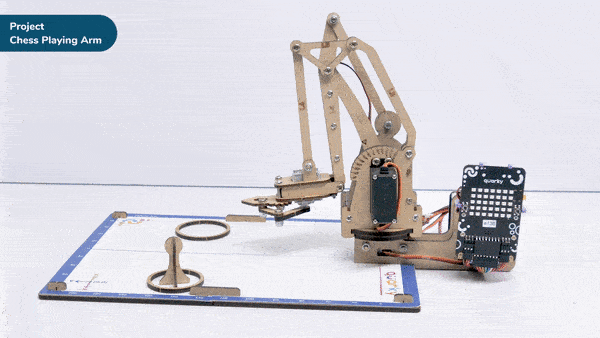
Discover how a robotic arm playing chess showcases the synergy between robots and AI.
Introduction
robotic arm playing chess is a great example of how robots and AI can work together to do complex tasks. Chess is a game that needs smart thinking and careful moves. The robotic arm is like a human arm and can move pieces on the chessboard.
The robotic arm has different parts like joints, actuators, sensors, and a gripper. The joints let the arm move in different ways, just like a human arm. The actuators control the arm’s movements, so it can make precise and planned moves during the game.
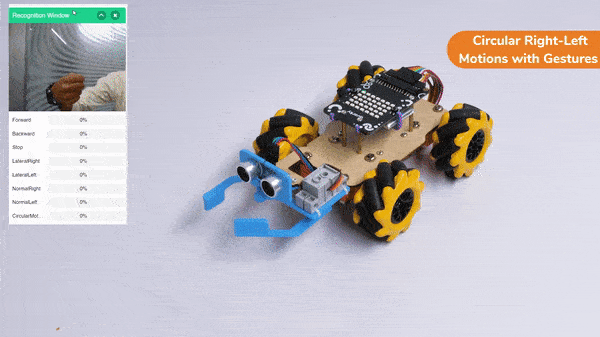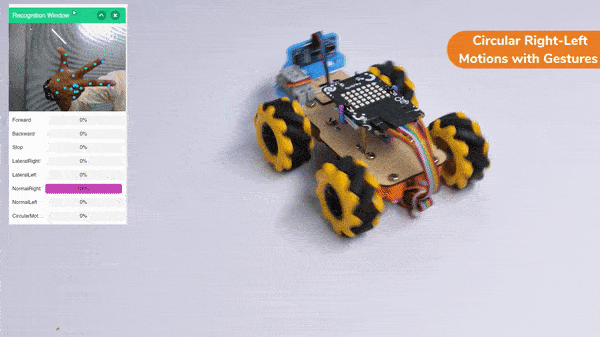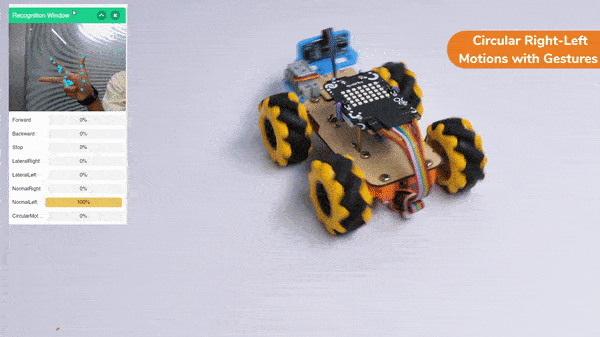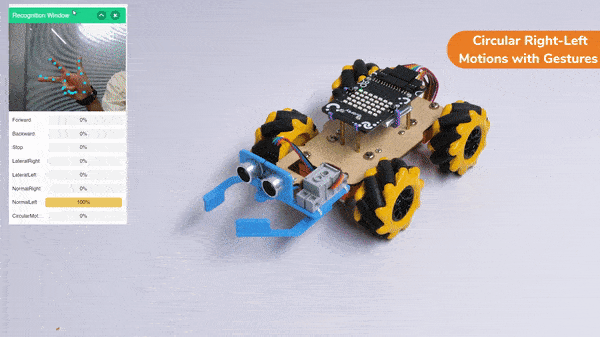
The robotic arm uses AI and computer vision to play chess. The AI algorithms study the chessboard, figure out where the pieces are, and decide on the best moves. They consider things like how valuable each piece is and where they are on the board. The arm’s sensors tell it where it is, so it can pick up the pieces and put them in the right places accurately.
When the AI finds the best move, the robotic arm carefully grabs the chosen piece, lifts it up, and puts it on the right square of the chessboard. The gripper has sensors to handle the pieces gently and not damage them.
The robotic arm playing chess is an amazing example of how robots, AI, and computer vision can work together. It shows how we can use complex algorithms and physical abilities to do tasks that people usually do. This technology can be useful in many fields like manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare, where we need precise and automated movements.
In summary, a robotic arm playing chess is a cool combination of robotics, AI, and computer vision. It can make smart and accurate moves on a chessboard. It’s a big achievement in robotics and shows how automation and AI can do complex tasks in different industries.
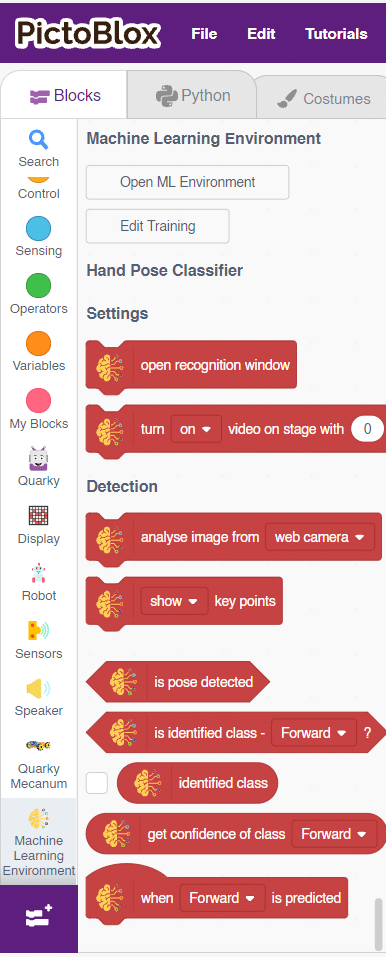
Code
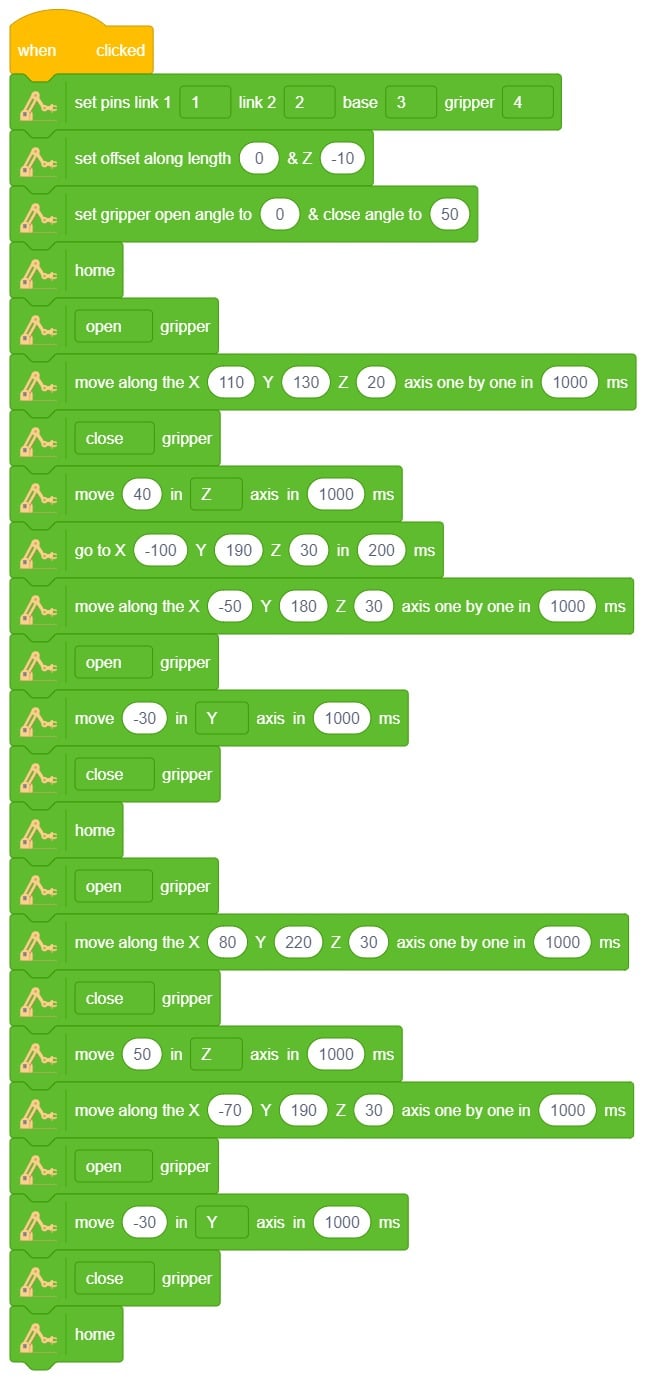
Logic
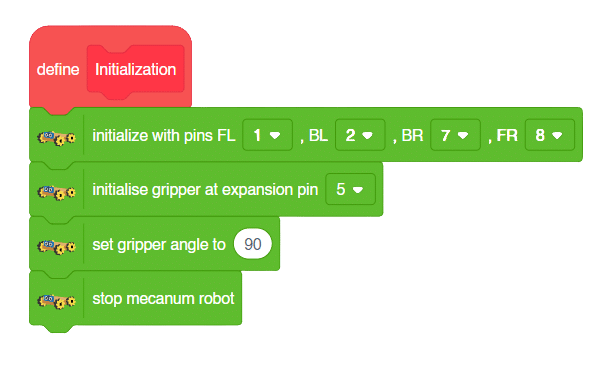
- Drag and drop the Set Pins link1() link2() base () gripper() block to adjust all the pins to their correct angles.
- Set the orientation along the Z-axis by using a value of -10 in the downward direction using set offset along length() & Z() block.
- Set the gripper to open and close at the appropriate angle using () gripper block.
- Set the arm to its home position using home() block.
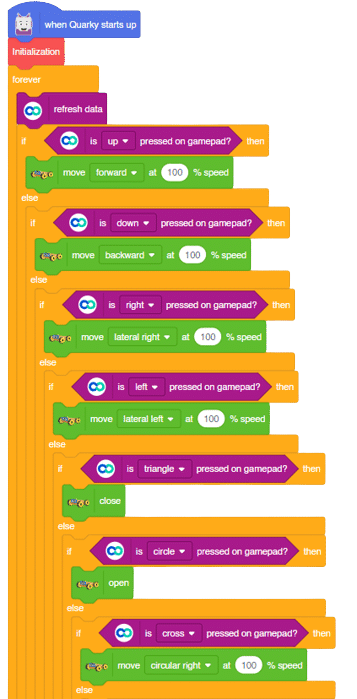
- Open the gripper using (open) gripper block.
- Move the arm to a specific direction and point using move() in() axis in ()ms block.
- Close the gripper.
- The arm will pick up the chess piece and place it in a specific location while following the rules of chess.
- Press the “Run button to execute the code.
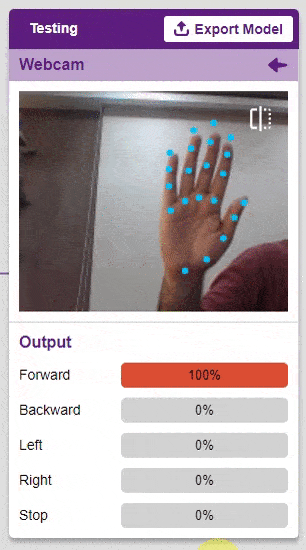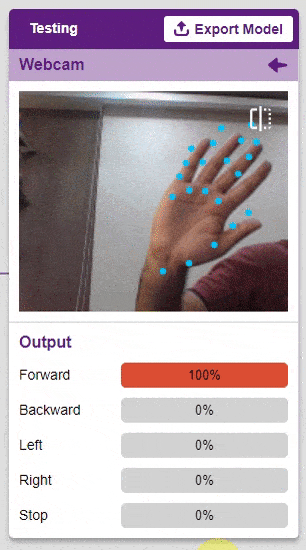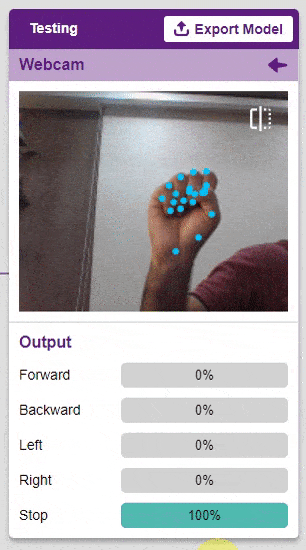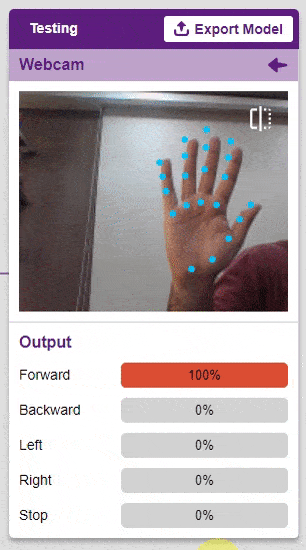
Output

Read More