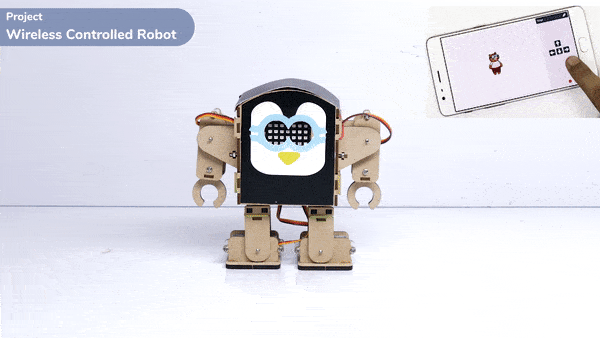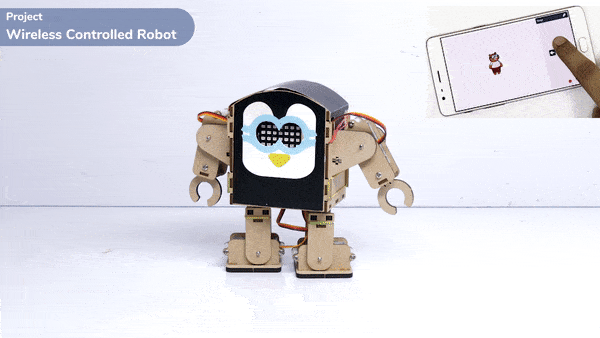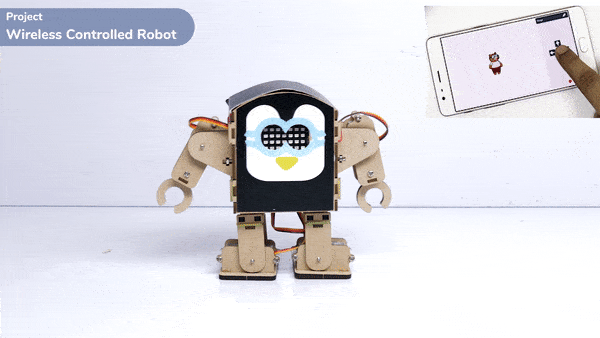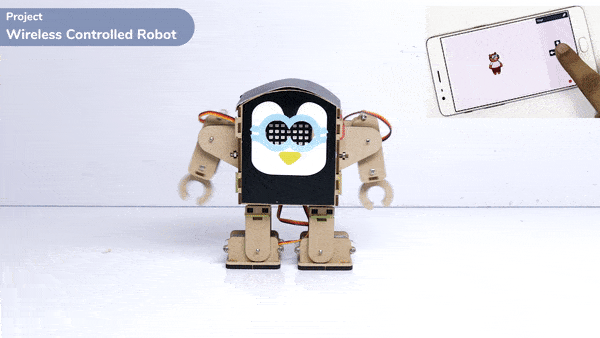
Introduction
A humanoid is a type of robot or artificial system that is designed to resemble a human being in its form and functionality. Humanoid robots are typically equipped with sensors, actuators, and artificial intelligence capabilities that enable them to interact with their environment and perform tasks that are similar to those of a human being. Humanoid robots are used in various fields, including robotics research, entertainment, healthcare, education, and customer service.
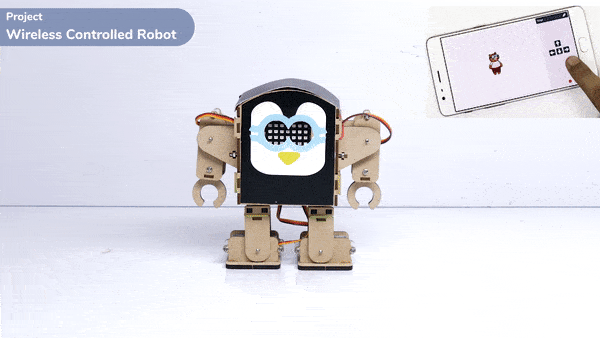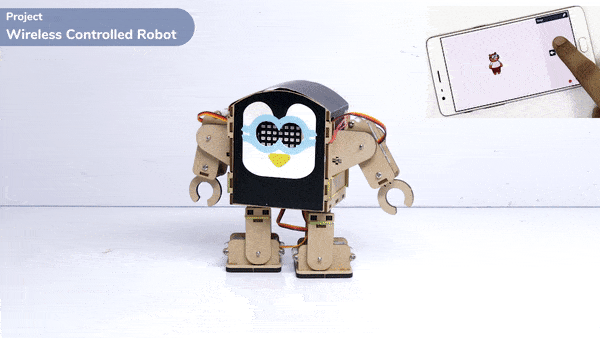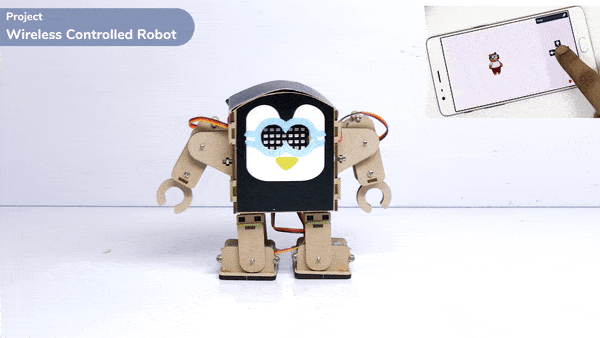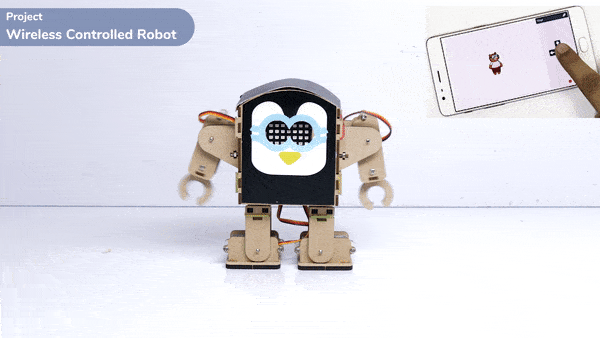
Logic
The Humanoid will move according to the following logic:
- When the “UP” key is pressed – Humanoid will move forward.
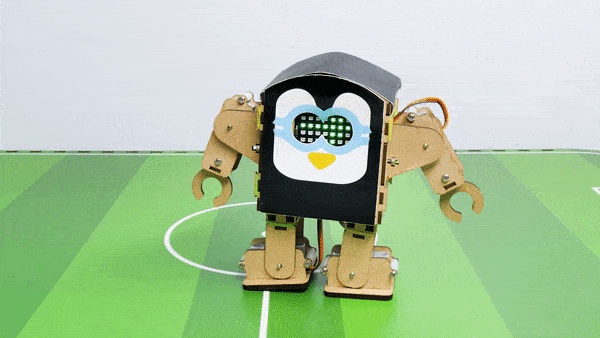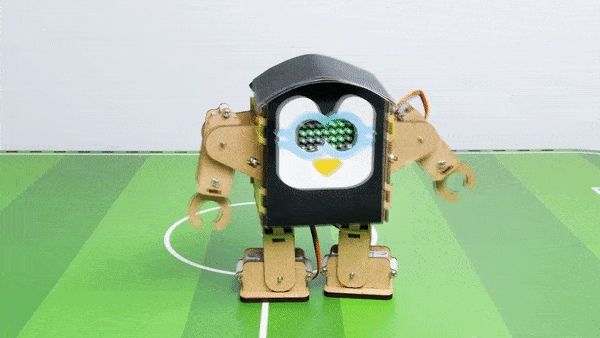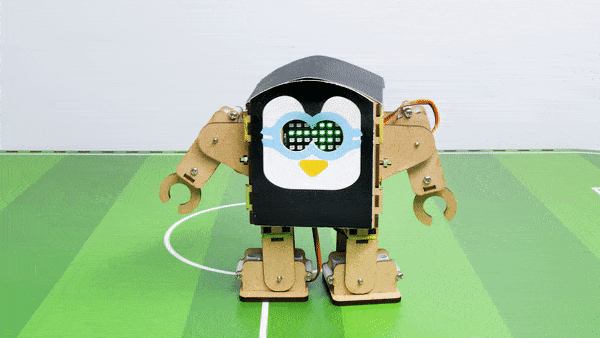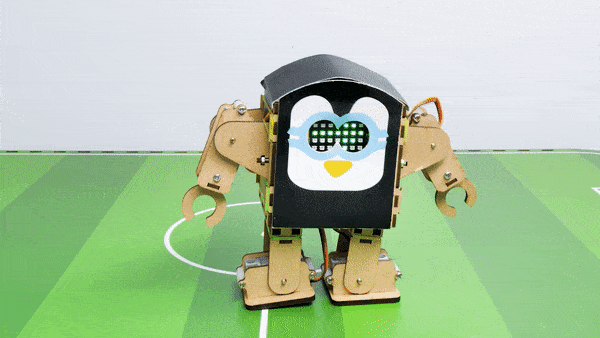
- When the “Down” key is pressed – Humanoid will move Backward.
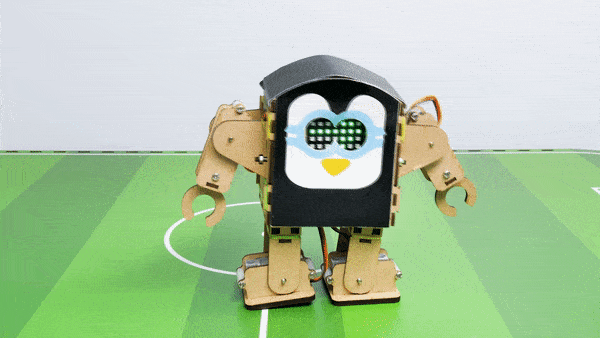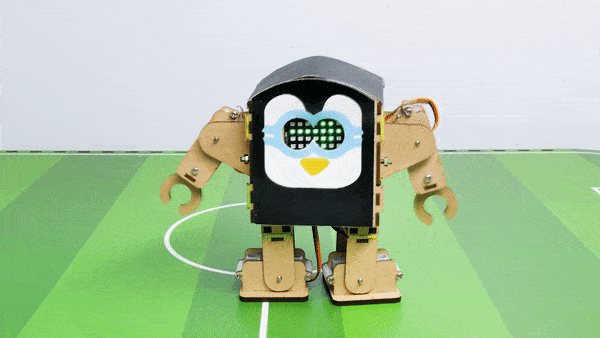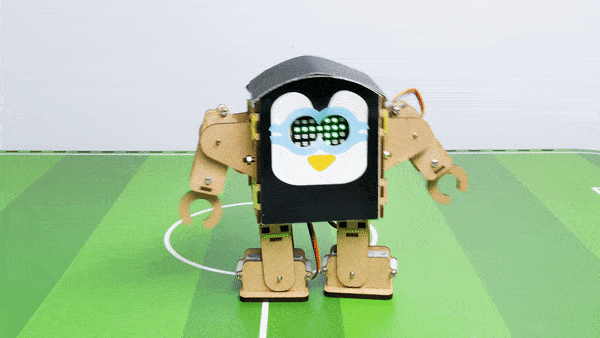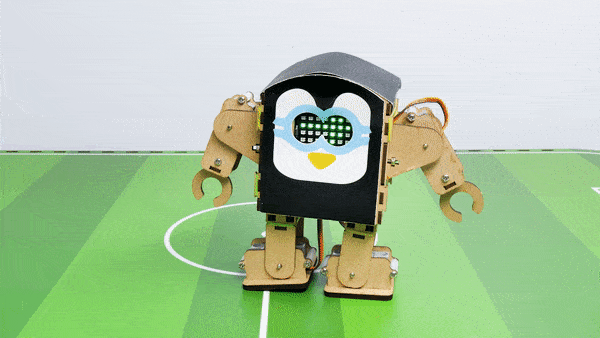
- When the “Left” key is pressed – Humanoid will turn left.
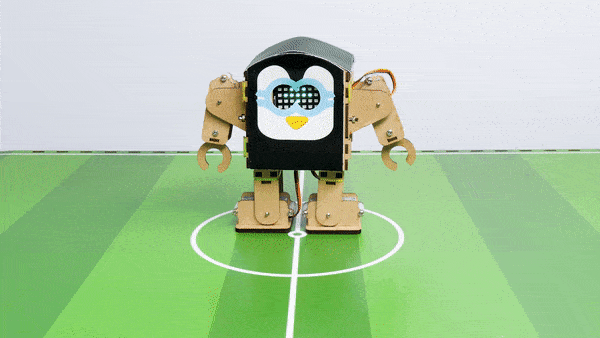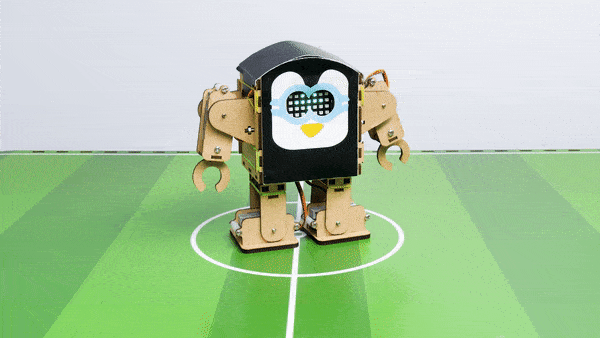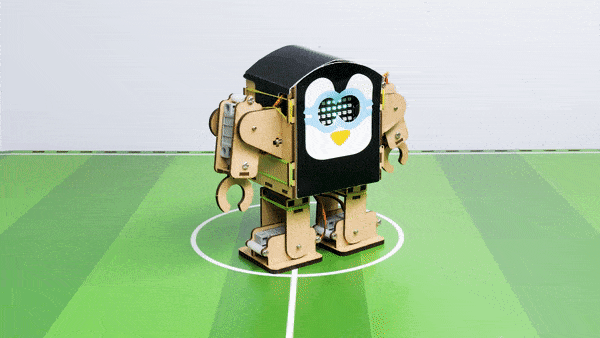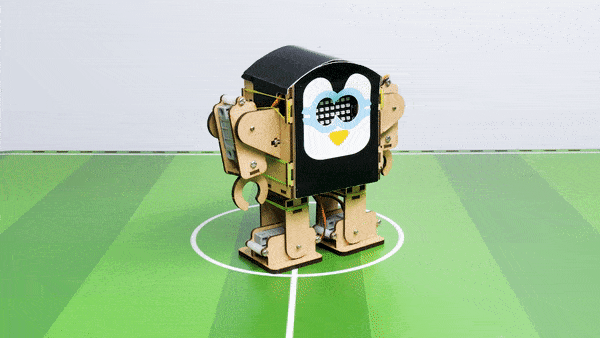
- When the “Right” key is pressed – Humanoid will turn Right.
Code
The program uses the up, down, left, and right arrows to control the robot and make it move forward, backward, left, and right. Every time you press one of the arrows, Humanoid will move in the direction you choose.
sprite = Sprite('Tobi')
quarky = Quarky()
import time
humanoid = Humanoid(7, 2, 6, 3, 8, 1)
while True:
if sprite.iskeypressed("up arrow"):
humanoid.move("forward", 1000, 1)
time.sleep(1)
if sprite.iskeypressed("down arrow"):
humanoid.move("backward", 1000, 1)
if sprite.iskeypressed("left arrow"):
humanoid.move("left", 1000, 1)
if sprite.iskeypressed("right arrow"):
humanoid.move("right", 1000, 1)Explain the code
- The code defines a sprite named “Tobi” and creates an instance of a humanoid character named “quarky” using a Humanoid class.
- It then enters into an infinite loop that continuously checks if certain arrow keys are pressed using the sprite.iskeypressed() method.
- If the “up arrow” key is pressed, it calls the humanoid.move() method with parameters “forward”, 1000, and 1, which indicates that the humanoid should move forward at a speed of 1000 units with a duration of 1 second.
- If the “down arrow” key is pressed, it calls the humanoid.move() method with parameters “backward”, 1000, and 1, which indicates that the humanoid should move backward at a speed of 1000 units with a duration of 1 second.
- If the “left arrow” key is pressed, it calls the humanoid.move() method with parameters “left”, 1000, and 1, which indicates that the humanoid should move to the left at a speed of 1000 units with a duration of 1 second.
- If the “right arrow” key is pressed, it calls the humanoid.move() method with parameters “right”, 1000, and 1, which indicates that the humanoid should move to the right at a speed of 1000 units with a duration of 1 second.
- The code uses the time.sleep() function to pause for 1 second in each iteration of the loop, allowing for smoother movement of the humanoid.
Output