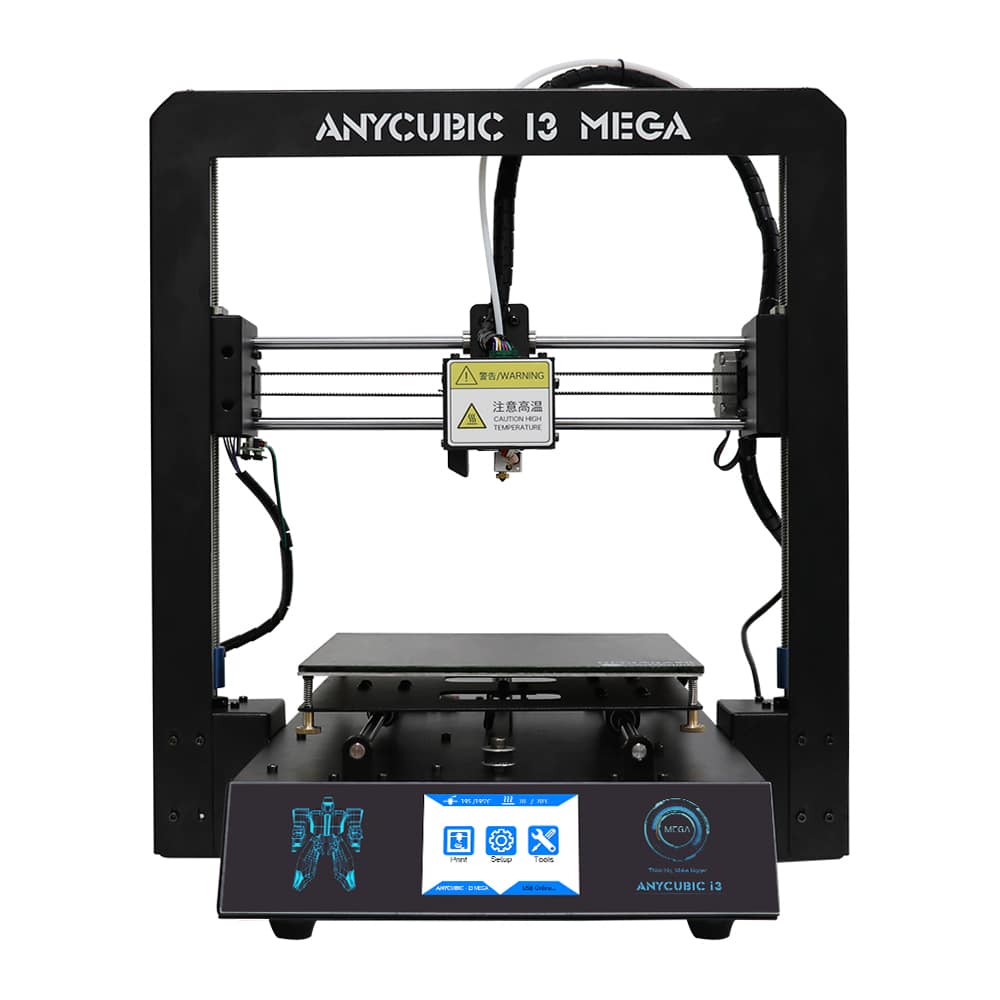
What is 3D Printing
We all have wondered about how can we bring our ideas into reality. But with the advancement in technology, we are now able to do it. You must have heard the phrase 3D Printing. Unlike regular printing which involves 2D printing of images on paper, 3D printing will actually print a physical object.
3D printing is simply a process which takes the digital file or your design and prints it layer-by-layer until you have your physical object ready in your hands.
Types of 3D Printing
3D Printing is also known by the name of Additive Manufacturing. As it adds layers on top of layers in the object, unlike the Subtractive Manufacturing which removes the material.
There are different types of additive manufacturing, out of which the following the following are the most common types:
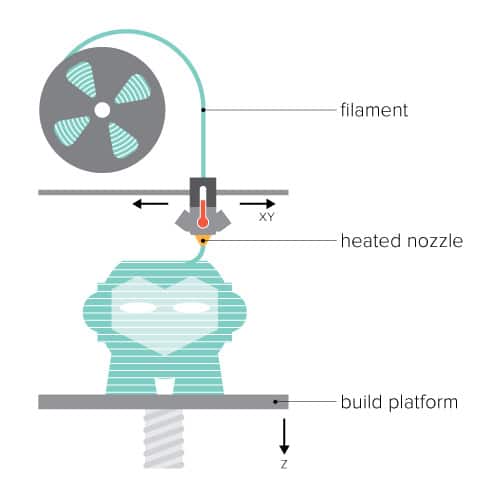
- Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM): It is the most popular of all. It builds layers on layers by pouring melted filament from the extruder. The layer solidifies immediately after it touches the print bed or the layer below it. Also, it is the cheapest and easiest to use from all. Thus, it is most suitable to use at homes, or in schools.
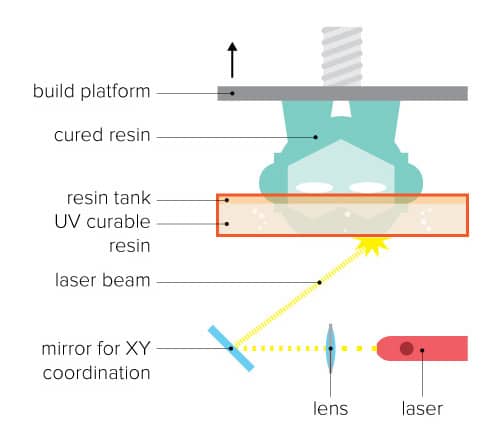
- Digital Light Processing (DLP): Unlike FDM, it uses an extremely thick liquid called resin. The platform is then dipped into the tank of resin also known as a vat. Then the light from the projector is mapped on the bed solidifying one layer at a time. The objects made with it, have a smooth finishing along with great detailing.
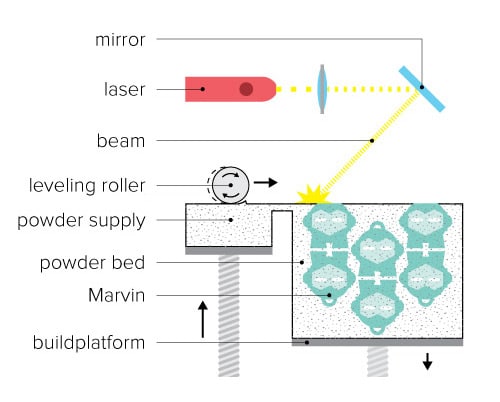
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): It uses nylon like powered material to create the object. We then use laser to solidify the power type material layer-by-layer. It creates objects which are complex designs and for industrial purposes.
Application of 3D Printing
You must have now started to think about the applications of 3D Printing. There are a number of fields which require 3D Printing.
It is most common use is in Manufacturing, Industrial, and Automobile field, where it is used to make prototypes of parts of the machine.
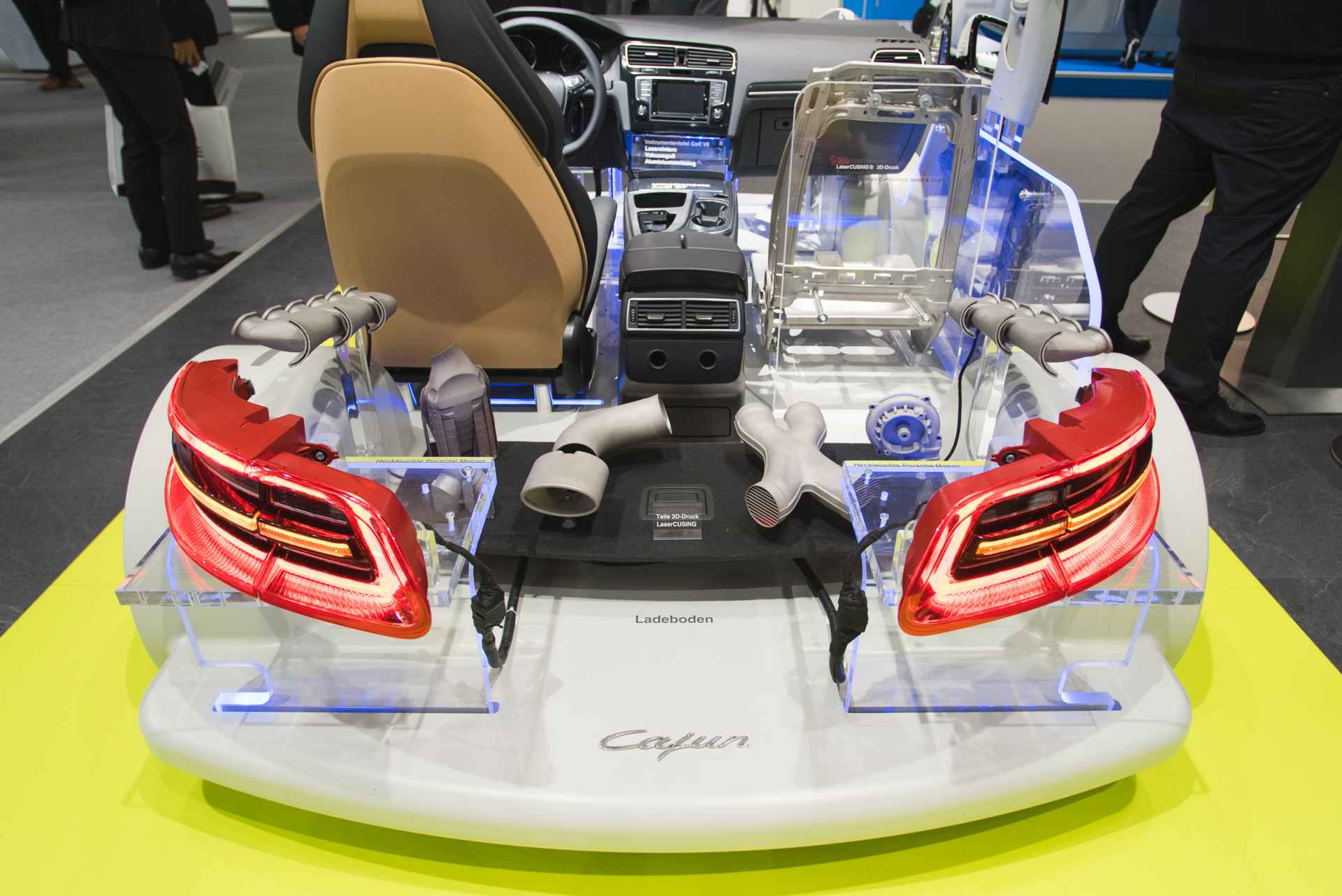

In Architecture and Constructions, where one can make the exact replica of the building but at a smaller scale.

In Medical, where it can make models for guiding or education.
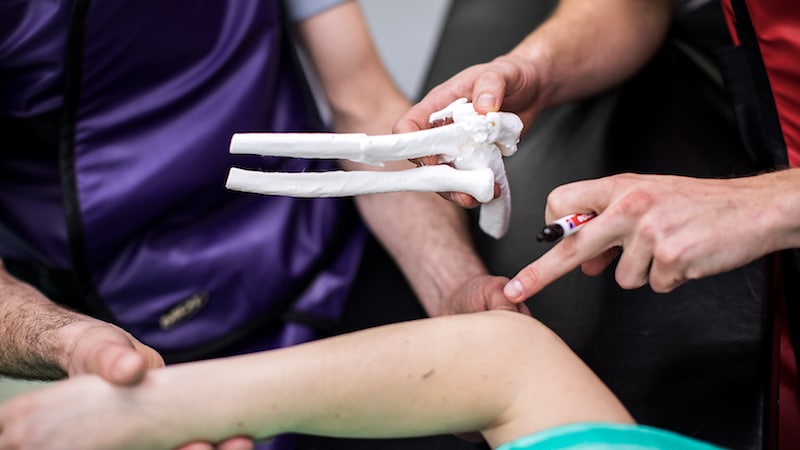
In Education, one can actually make the whole prototype of particular topics so that student can understand the topics better. Also, the working models can be made using 3D Printing Technique.
These are some of the application of 3D Printing, you can find many other on the internet.
3D Printers
Different types of 3D Printing is basically different types of 3D Printer.
The 3D Printer which is most used is FDM.
The basic component of a 3D printer is
- Print Platform
- Print Head
- Extruder
- Filament Sensor
- Filament
- Components for XYZ Motion
- SD Card Slot
Process
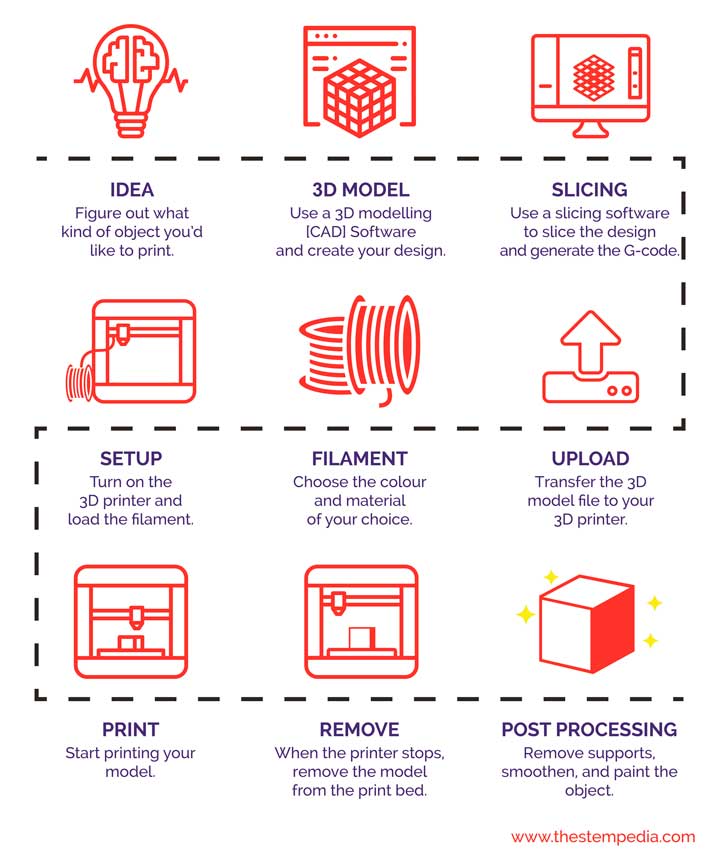
This point portraits the complete process of 3D Printing
- Ideation: The first thing before designing obviously is ideation.
- Designing: Then comes designing. Whatever we thing must first be in the digital file. There is various software available for designing like TinkerCAD, AutoCAD, etc. The one we are going to use is TinkerCAD. It is a free web application to design. The file is then stored is in the form of .STL accepted by the slicing software.
- Slicing: As we know 3D Printer prints object layer-by-layer. It is time to slice the object in layers. For this, we are going to use Slicer. Out of many available, the one we are using is CURA. It is also free software. Once you go through the software you will find that there are a number of options or settings available to change. Each one of them holds special duty.
- Uploading to the SD Card: Once sliced, the file is then downloaded into an SD Card. It converts .STL file into G-Code. As printers only work on gcode. Once we have gcode in the Card. Insert the SD Card into the card slot.
- Choose the filament: Next thing you need to do is decide the filament color and material that you want to use.
- Setup the Printer: Next, you need to insert the filament into the printhead through extruder via the nozzle.
- Start Printing: Once you insert the filament, it’s time to bring our design into a physical model. Press Print to start the printing.
- Remove the Model: Once printing is completed, take out the model from the print bed using a spatula.
- Post Processing: You may need to remove the supports if present for a smooth model. You can even paint the model as you like.
Thus your imagination can now turn into reality with the help of 3D Printing Technology.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 3D Printing is an amazing technology that has revolutionized the way we design, create, and imagine. It has limitless possibilities and applications, from medical to industrial to educational. With the help of 3D Printing, we can turn our ideas into reality with the help of 3D Printers. 3D Printing has made it easy for us to create complex models with great details, smooth finishing, and accuracy. With a little bit of knowledge, anyone can use 3D Printing to create their own unique models.